Chapter 6 - 1of2 supply-chain-management
advertisement
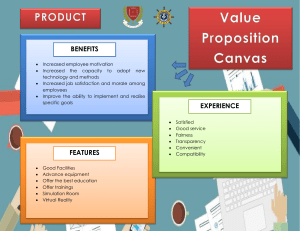
SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 6 HISTORY "Supply chain management is essentially the optimization of material flows and associated information flows involved with an organization’s operations” (p. 331) 70s: Manual data entry and primarily custom programming – no common platform 80s: Common platforms occurred with mini -PCs. Still with custom codes 90s: Common platforms and common codes based on Windows End of 90s: Companies replaced o ld systems when the corruption was too high Start of 00s: Internet took over as the transaction medium SOLUTIONS The history shows that applying information systems, companies can enhance or radically improve many aspects of the supply chain. Such as: Reduction in paperwork, inventory holdings and time Lower SCM system purchase Management costs through use of online services Sharing of demand as a part of ECR Supplier becomes responsible for item availability Human error reduced UPSTREAM/DOWNSTREAM Upstream Buy-side e-commerce Downstream Sell-side e-commerce Supply chain network More accurate reflection LOGISTICS The time-related positioning of ressource, or the strategic management of the total supply chain Inbound: Management of ressources entering on the buyerside Outbound: Management of ressources entering on the seller-side PUSH AND PULL Push supply chain model: A company creates a product and pushes it to the costumers . ”This is a great product, now who shall we sell it to ?” Modern company using push SC model Apple Pull supply chain model: A company researches the costumers needs and creates a product upon that. Modern company using pull SC model custom computers (AlienWare ) VALUE CHAIN A model that considers how supply chain activities can add value to products and services delivered to the customer. Benefits for the customer are created by reducing cost and adding value to customers: within each element of the value chain such as procurement, manufacture, sales and distribution; at the interface between elements of the value chain such as between sales and distribution. In equation form this is : Value = (Benefit of each VC activity – Its cost) + (Benefit of each interface between VC activities – Its cost) VALUE CHAIN MODEL VALUE STREAM The set of all the specific actions required to bring a specific product through the three critical management tasks of any business: 1 the problem-solving task [the processes of new product development and production launch] 2 the information management task [the processes of order taking, scheduling to delivery] 3 the physical transformation task [the processes of transforming raw materials to finished product delivered to customers] VALUE NETWORK Deise et al. (2000) describe value network management as: “the process of effectively deciding what to outsource in a constraint based, real-time environment based on fluctuation” I.E. when a computer company outsources their information systems to the delivery company (Post Danmark) VIRTUAL ORGANIZATION An organization which uses information and communications technology to allow it to operate without clearly defined physical boundaries between different functions It provides customized services by outsourcing production and other functions to third parties.