Supporting Students After Instruction
advertisement

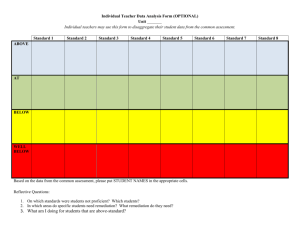
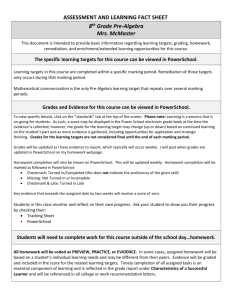
Supporting Students After Instruction Why do students continue to struggle? Work in groups of four to develop and categorize a list of possible reasons for the following: Even after you have supported students prior to the lesson, provided them with targeted intervention during the lesson, you still have a handful of students who do not understand the concepts or still cannot demonstrate mastery of the required skills. Categorize your list Academic use remediation alone Remediation and behavior management What is Remediation? • Acceleration was offered before students started the unit of study. • Intervention was offered during the instruction. • Remediation is an opportunity to provide additional support to those students who still do not understand key concepts in spite of attempts to support them. Two Types of Remediation • Short-term remediation is designed to get students ready for the summative assessment. • Ongoing remediation focuses on longtermed skill development to address large gaps in background knowledge or basic skills. • All remediation usually occurs outside the classroom. What do You Remediate? • Not everything being taught needs to be remediated. Skills taught again in later units or “nice-to-knows” that are not essential to mastery may not be necessary. • Material that makes up a substantial part of the assessment content or skills. • Material that is critical to the next unit or later units or study. • Specific concepts with which the student struggles. Who do You Remediate? • Constantly analyze formative data to determine students with deficits in their learning. • Determine all students close to mastery. • Determine students who need intensive remediation. • Students who struggle with context(test structure) rather than content. Selecting Remediation Strategies • Working in your group of four read the following statement and make a list of possible remediation strategies your teachers could choose from. • Selecting effective remediation strategies requires that at teacher find out as much as they can about why a student is still struggling. Students don’t have to be retaught all the material, they probably have gaps in understanding that have prevented them from grasping key concepts. Error Analysis • Have student review first assessments to analyze errors. • Determine and present probable causes of error. • Determine how to prevent this error in the future. • Students should present an error analysis before they can retest. Reteach • Teach concepts the students don’t understand a different way. • Focus on only the key concepts and skills students need to know. • Re-teaching should occur shortly after a students’ assessment shows they did not understand much of the material. • Teaching should be different than regular instruction. • Should not create additional work for students. Tutoring • Can use teacher or peer tutoring or both. • Should help students develop specific skills. • Should target the learning task with which they are struggling. • Should be temporary. • Electronic or on-line tutorials can be used. Additional Practice • Not drill and kill! • Practice should focus on helping students develop fluency and proficiency. • Practice should be distributed over a period of time. Use several sessions. • Should be meaningful • Should be short • Should have built in feedback. Organization and Study Habits • If poor performance is due to poor learning habits, the remediation may need to focus on this. • Work on learning strategies • Work on organization of notebooks, notetaking strategies. • Teach them how to use graphic organizers. • Allow them to retake the assessment after they have applied these new strategies. Alternative Instructional Strategies Match students best learning style. Hands-on verses lecture. Working with a partner or small group. Breaking information down into small learning targets and teaching small chunks at a time. • Remediation is not simply going over the material more slowly. Its teaching concepts a different way. • • • • Reassessing • After providing the corrective action. • Reassess to improve learning not grades. • Reassess only when it helps students learn information they need to move on. • Reassess in a new or different format, as applicable. • Reassess as close to the original assessment as possible. Next Step: Pyramid of Intervention • Next principal’s meeting bring with you your school’s plan of intervention. • We will discuss the pyramid of intervention. • We will use the tuning protocol to tune your schools intervention plan. • Review the Georgia Student Achievement Pyramid of Interventions before the next meeting.