Computer-Architecture-and
advertisement

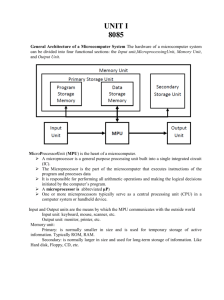
Computer Architecture and Microprocessors By Navdeep Goyal Purpose of Talk • What are the advantages of teaching these topics to physics students • To discuss the curriculum for teaching microprocessors to physics students • Introduction to SAP-1 • 8085 microprocessor Importance . Learning about the design considerations of microprocessors is important . Students opting for further studies in microelectronics are benefitted . Knowledge of working of a processors is important . Starting with working of simplest computer system is always helpful . Better to start with few basic principles of working of computer systems Proposed Sequence • Which device was designed first • Computer or microprocessor? • Bus organised computer systems – – – – – – – – Data Bus Address Bus Control Bus Tri-state Devices Buffer Registers SAP-1, SAP-2 etc 8085 microprocessor 8086 and other advanced microprocessors BUS SYSTEM • In all computer system, the data is transferred from one place to other through common DATA BUS • The selection of device is from the address, which is sent through common address bus • Depending upon control signals data is written onto or read from a particular register TRI STATE DEVICES • TRI-STATE Devices play important role when we are dealing with bus organized computer systems • Three terminal device: – Input, output, control – Available in high active or low active mode – Used at the output of registers, which are connected with common data bus Buffer Registers • The loading of data and reading data from buffer register is with the help of control signals • For loading data onto register a Load (L) signal is used • For receiving data from buffer register an Enable (E) signal is used • For different registers loading or enabling may be high or low active Introduction to Sap-1 • • • • • • SAP-1 stands for simple as possible computer SAP-1 is a computer made from discrete IC’s Its an 8 bit computer with 4 address lines Can handle max. of 16 address locations Instruction set includes instructions LDA, ADD, SUB, OUT, HLT OPCODES • • • • • LDA ADD SUB OUT HLT 0000 0001 0010 1100 1111 OPCODES AND OPERAND Complete code includes opcode and operand Like LDA 04H 0000 0100 One instruction is executed in one instruction cycle Machine Cycle/Instruction Cycle • Instruction cycle may consist of many machine cycles • For SAP-1, Instruction cycle= machine cycle • Instruction cycle=Fetch cycle+Execution Cycle • Fetch cycle is generally same for all instructions Ring Counter SAP-1 How to fabricate various units • Program Counter: 4 bit counter-made from J-K flip-flops-74 LS107 with 74LS126 • Input/MAR: includes address/data switch registers includes buffer register and 2-1 multiplexer • 16X8 RAM • Instruction Register: 8 bit buffer register , 2 nos 74 LS173 • Controller Sequencer: to generate control signals • Accumulator: Buffer register to store intermediate results • Adder Subtracter: Arithmatic unit • B: buffer register Control Signals Fetch T1 T2 T3 010 1 1 011 0011 1110 1110 0110 001 1 0011 0011 Control Words for various instructions Control Unit of SAP-1 Microprogrammed Control Unit • Easier to fabricate • Slower-not useful for commercial microprocessors • Can be used for testing various instructions Variable Machine Cycle • Fixed machine cycle may give many unwanted time states • Execution is going to take longer time • Better to opt for variable machine cycle 8085 Pin Diagram Architecture of 8085 Thanks