Setting Prices
advertisement
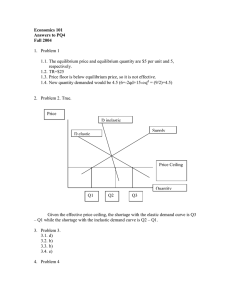
Setting Prices • Advantages of prices – Prices are neutral because they do not favor the buyer or the seller. • They are the result of competition • Prices are flexible, allowing for expected changes in the market • Prices have no administration costs. • Prices are familiar and easily understood The price adjustment process • Together supply and demand form a complete picture of the market. • The equilibrium price is the price at which supply and demand meet • Surpluses occur when supply exceeds demand • Shortages occur when demand exceeds supply • Price adjustments help a competitive market reach equilibrium Explaining and Predicting Prices • A change in price is normally the result of a change in supply, a change in demand, or both • Even small changes in an inelastic supply can cause big changes in price. • Elastic supply and demand help keep prices from changing dramatically Competitive price theory • In theory, a competitive market allocates resources efficiently. • To be competitive, sellers are forced to lower prices • Competition among buyers keeps prices from falling too low. Price ceilings and price floors Price ceiling • Law sets price ceiling, or maximum price that sellers can charge for a good or a service. • Price ceilings often set by local and federal governments. • Excess demand and excess supply occur when quantity demanded is greater or less than quantity supplied Price floor • Government sets price floor, or minimum price that must be paid for a good or service • Minimum wage is the price floor that an employer must pay their workers per hour