Emotions & Communication: Understanding Feelings & Expression
advertisement

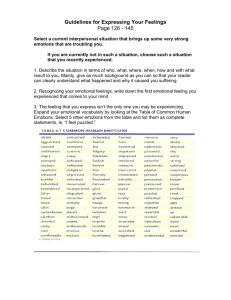
Chapter 7 Emotions & Communication What am I feeling? Is that right? How do I constructively express feelings? Saarni & Goleman Saarni-first originated emotional competence Goleman-capitalized on it with Emotional Intelligence, the IQ of emotional competency What are Emotions? 4 Components 1. Physiological-bodily changes occur 2. Nonverbal reactions-observable changesPowerful way in expressing/conveying emotions 3. Cognitive interpretations-the mind’s role in determining emotional state 4. Verbal expression-sometimes words are necessary & cannot rely on perceptiveness to sure you are understood accurately Different Degrees of Intensity Annoyed Angry Furious Content Happy Ecstatic Anxious Afraid Terrified Liking Loving Adoring Influences on Emotions Physiological ORGANISMIC-James & Lange Physical first, then emotions-most instinctual Example: Almost hit garbage on freeway—swerve—heart racing, sweaty palms, etc.--FEAR Stimulus Physiological Response Emotion Influences on Emotions Perceptual APPRAISAL THEORY Subjective perceptions shape external phenomena, gaining meaning only as we attribute significance to them Example: Taking a test—low test score—not very smart— (event) (perception of event) disappointment/shame, etc. (response) (interpretation) Influences on Emotions COGNITIVE LABELING-how you label the physiological response –use of language Example: Taking a test—low test score—anxious— (event) (physiological-knot-in-stomach) disappointment/shame, etc. (response-comes from label not perception) (label response w/ language) Social Influences Hochschild-Interactive View of Emotions Framing Rules-define emotional meaning Feeling Rules-right to feel or expected to feel Deep Acting-control inner feelings Surface Acting-control outward expression Emotion Work-effort made to think about what is appropriate in situations-allows engaging in deep acting Obstacles Social Expectations Gender Vulnerability-Risky/disky Protecting Others Social & Professional Roles Why We are Ineffective in Expressing our Emotions 1. Speaking in Generalities-What does the speaker really feel? General & abstract statements “I feel bad”, “I’m happy”, “I’m fine”, “I’m frustrated” Angry, confused, hurt, anxious, disappointed, etc. Tend to recognize only a few emotions leaving us with limited emotional vocab to clearly communicate More Ineffectiveness Not owning feelings Use too much “you” language You made me ! Need to reword statement to make it your own I feel angry when you do not follow through on what you say you will do. I feel (emotion) when you (describe the behavior). Ineffectiveness cont. Counterfeit Emotional Language-language that seems to express emotions but does not actually describe what a person is feeling. Why can’t you leave me alone!-no feeling That’s just how I feel!-figure it out first I feel this discussion is getting off onto another subject.states a thought not a feeling Exercise-Find the Feeling 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. This was a great evening! You’re being awfully sensitive about that. I can’t figure out how to approach him. I’m confused about what you want from me. I don’t know how to tell you this… I feel as if you’re trying to hurt me. It’s hopeless. I feel like the rug has been pulled out from under me. Re-Write to Exercise Facilitative vs Debilitative Contribute to effective functioning Vs Detract from effective functioning Characteristics: intensity duration Irrational Thinking & Debilitative Emotions Fallacy of Perfection Fallacy of Approval Fallacy of Shoulds Fallacy of Overgeneralization Fallacy of Causation Fallacy of Helplessness Fallacy of Catastrophic Expectations Minimizing Debilitative Emotions Monitor emotional reactions Note the activating event Record your self-talk Reappraise your irrational beliefs