Grade 8 healthy living presentationx
advertisement
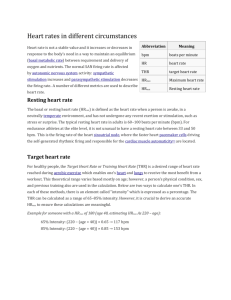
Combined picture and text effects for PowerPoint slides 1 Reproduction instructions For your reference, the steps required to reproduce each of these slides have been included in the Slide Notes. 2 Printing instructions To print the reproduction instructions in this file: 1. Select the slide that you want to reproduce. 2. Place your cursor in the Slide Notes. 3. Press CTRL + A, and then Copy the text. 4. Open a new document in Microsoft Word. 5. Then Paste the text into the Word document. 6. Print the Word document. 3 Removing instructions If you notice delays in slide effects or a decrease in performance, you may want to remove the reproduction instructions in the Slide Notes. To remove the instructions from a particular slide: 1. Place your cursor in the Slide Notes. 2. Press CTRL + A, and then press DELETE. What Makes a Healthy Life? 1. Nutrition 2. Physical Activities (Exercise) 3. Mental Wellness 4. Sleep 5. Time Management 6. Relationships (to be covered in Religion) 1. Nutrition Follow Canada’s Food Guide for servings • 5 – 10 Fruits and Vegetables a day • 5 – 12 Grains and Cereals • 3 - 4 Dairy • 2 - 3 Meat and Alternatives •Eating Well with Canada’s Food Guide Having the Amount and Type of Food Recommended and Following the Tips in Canada’s Food Guide will help: • Meet your needs for vitamins, minerals and other nutrients • Reduce your risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, certain types of cancer and osteoporosis • Contribute to your overall health and vitality Create a daily menu: • Write a menu plan for one day – breakfast, lunch, and dinner. Include the 4 food groups and the minimal number of servings for each group. • Does your day menu include 5-10 vegetables, 5-12 grains, 3-4 dairy, and 2-3 meats and alternatives? The type of food that you eat is as important as the amount that you eat! Canada’s Food Guide also Recommends: – Satisfying your thirst with water – Enjoying a variety of foods from the four food groups Canada’s Food Guide also Recommends: – Limiting foods and beverages high in calories, fat, sugar or salt – Examples include cakes and pastries, doughnuts and muffins, french fries and potato chips, nachos and other salty snacks, alcohol, fruit flavoured drinks, soft drinks, sports and energy drinks Read the Label • Compare the Nutrition Facts table on food labels to choose products that contain less fat, saturated fat, trans fat, sugar and sodium • Keep in mind that the calories and • nutrients listed are for the amount of food found at the top of the • Nutrition Facts table Eating Well and Being Active Work Together for a Healthier You! • The benefits of eating well and being active include: • • • • • • Better overall health Lower risk of disease A healthy body weight Feeling and looking better More energy Stronger muscles and bones The is what a total daily average intake should look like: 60% - Carbohydrates 20 – 30 % Fat (ONLY 10% should be Saturated Fat) 10-20% Protein •Carbohydrates generally provide the energy for daily activities. Carbohydrates can be simple or complex. The more complex the carbohydrate, the longer the energy will last since it takes longer to get the energy from the nutrient. • The protein builds the muscle and bones necessary to make a body grow and repair. •Fats and lipids provide a way for the body to absorb vitamins and minerals. They also provide warmth and insulation. Another benefit is that they keep the skin healthy. Fats are also a way the body stores extra energy. What to eat? The great dilemma! • You have an upcoming activity and your family hasn’t eaten yet. Your parents decide that you will pick up some fast food on the way to your activity. How can you make a healthy choice that includes all 4 food groups? Write at least 3 solutions from the fast food locations in town. Tips for Eating At a Restaurant Most restaurant portions are way larger than the average serving of food at home. Ask for half portions, share an entrée with a friend, or take half of your dish home. Here are some other restaurant survival tips: Ask for sauces and salad dressings on the side and use them sparingly. Use salsa and mustard instead of mayonnaise or oil. Ask for olive or canola oil instead of butter, margarine, or shortening. Use nonfat or lowfat milk instead of whole milk or cream. Order baked, broiled, or grilled (not fried) lean meats including turkey, chicken, seafood, or sirloin steak. Salads and vegetables make healthier side dishes than french fries. Use a small amount of sour cream instead of butter if you order a baked potato. Choose fresh fruit instead of sugary, high-fat desserts Tips for Eating At the Mall or Fast-Food Place It's tempting to pig out while shopping, but with a little planning, it's easy to eat healthy foods at the mall. Here are some choices: • a single slice of veggie pizza • grilled, not fried, sandwiches (for example, a grilled chicken breast sandwich) • deli sandwiches on whole-grain bread • a small hamburger • a bean burrito • a baked potato • a side salad • frozen yogurt • Choose the smaller sizes, especially when it comes to drinks and snacks if you have a craving for something unhealthy, try sharing the food you crave with a friend Be aware of the food you eat: • YouTube - Do you know where your food comes from? - Eat Real. Eat Local. Buying local and buying organic helps the local farm industry, helps promote the local economy, and is a healthier choice than eating foods that have been sprayed with chemicals that are known to be toxic. Furthermore, local and organic is debatably tastier since it’s likely fresher than store bought food. One such way of eating is often referred to as the 100 mile diet – eating what is in season, from farms and producers no further than 100 miles away. This can be difficult to do especially in areas where it’s too cold to grow produce year round. Making good food choices is not always easy to do but in the end, you are worth putting good food into your body! Food Companies use advertising to get you buy their products but do you know the food process of how the food gets to your table? • YouTube - Food, Inc Do you know how the food processing assembly line happens? • YouTube - The Official Meatrix I What food do you find acceptable? • As our populations continue to rise, there is a need to feed everyone. How are we going to do that if germs, molds, bacteria, and other things destroy large amounts of food. One solution is to genetically modify the food that we eat. However, some scientists have some concerns with the long term implications of this option. It could put our entire population at risk. Others would argue that eating organic is the best or even the only way to stay healthy. However, it is a more expensive way to eat that not everyone can afford and is not available everywhere. What solutions do you see? Stay Active Daily Being active on a daily basis is one way to promote a healthy and balanced lifestyle. It means more than just participating in P.E. class. It means being active outside of school. Choosing to walk instead of drive. Joining a community sports team or program. Getting your heart rate up. Being active is a lifestyle choice that will help you stay healthy for a lifetime. Be Active • Canada’s Physical Activity Guide recommends building: • 30 to 60 minutes of moderate physical • activity into daily life for adults • At least 90 minutes a day for children • and youth • Start slowly and build up! A Healthy Heart Heart Rate and Health • Resting heart rate (HRrest) is a person's heart rate when they are at rest: awake but lying down, and not having immediately exerted themselves. Typical healthy resting heart rate in adults is 60–80 bpm [2], with rates below 60 bpm referred to as bradycardia and rates above 100 bpm referred to as tachycardia. Note however that conditioned athletes often have resting heart rates below 60 bpm. Maximum Heart Rate • HRmax is the maximal safe heart rate for an individual. Conducting a maximal exercise test can require expensive equipment. For general purposes, people instead typically use a formula to estimate their individual Maximum Heart Rate. • HRmax = 220 − age is the most common formula for finding out a person’s maximum heart rate Target Heart Rate • The Target Heart Rate (THR), or Training Heart Rate, is a desired range of heart rate reached during aerobic exercise which enables one's heart and lungs to receive the most benefit from a workout. This theoretical range varies based on one's physical condition, gender, and previous training. Below are two ways to calculate one's Target Heart Rate. In each of these methods, there is an element called "intensity" which is expressed as a percentage. The THR can be calculated as a range of 65%–85% intensity. However, it is crucial to derive an accurate HRmax to ensure these calculations are meaningful (see above). • Example for someone with a HRmax of 180 (age 40, estimating HRmax as 220 − age): 65% intensity: (220 − (age = 40)) × 0.65 → 117 bpm 85% intensity: (220 − (age = 40)) × 0.85 → 153 bpm Recovery Heart Rate • This is the heart rate measured at a fixed (or reference) period after ceasing activity; typically measured over a 1 minute period. • The general rule is: The quicker your heart recovers, the healthier your heart • Training regimes sometimes use recovery heart rate as a guide of progress and to spot problems such as overheating or dehydration. After even short periods of hard exercise it can take a long time (about 30 minutes) for the heart rate to drop to rested levels. • To determine your rate of recovery, use the following formula: • Recovery heart rate = (exercise heart rate - recovery heart rate after 1 minute) / 10 • Recovery Rate Number = Condition Less than 2 = Poor 2 to 2.9 = Fair 3 to 3.9 = Good 4 to 5.9 = Excellent Above 6 = Outstanding • The recovery heart rate also measures the intensity of your exercise. Very little drop in the one minute pulse could indicate that you were probably working too hard and your body was having a difficult time recuperating. Endurance Activities Strength Activities Stretching 1 text heading subtext 2 text heading subtext 3 text heading subtext JAN FEB MAR Project title Scheduled dates Team members Project title Scheduled dates Team members APR MAY JUN text text Caption or statement | text label | text label Topic one text label Topic two text label Topic three text label First line of text goes here Second line of text from left Third statement here First text statement positioned here at guide intersection Second text statement positioned here at guide intersection Sample statement or caption goes here Sample heading First line of text Second line of text Third line of text label one label two label three label four First text Second Final text text statement statement statement Picture caption Picture caption Picture caption first line of text goes here second line of text goes here third line of text goes here fourth line of text goes here : 10 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 Time for a short break Statement or caption