Sociology CH12 Education
advertisement

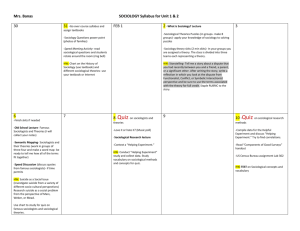
Bureaucracy in Education Federal government Department of education (No Child Left Behind) State Department of Education (DESE) Board of Education Superintendent Central Office Administrators Curriculum specialists, CFO Building head principals Assistant principals Counselors Building instructional specialists Teachers Students Formal schooling Education that is provided and regulated by society Ch12 Section 1 Advantages of formal education (aka bureaucratic or factory model) Tendency to specialize in subject areas Age based classrooms Efficiency Educate more students for less money Criticisms of Formal schooling • • • • Children are not inorganic raw materials made to be molded into factory products Too rigid Too standardized ….b/c one-size does not fit all Not individualized Your Opinions List five things that are wrong with Ursuline List five things that are right or positive about Ursuline positive Serviam Uniforms Interesting teachers Pretty campus Math lab Advisement Students are given Autonomy Friendly environment Teach values Strict No one left behind if they ask for help Nice administrators Classes are fun Options with electives complaints No discipline No options for classes teachers don’t care Bad food Lame teachers Aren’t flexible Laptops Little academic emphasis Inflexibility Too much busy work Little discussion ALL ppt We get little respect Unhappy teachers Costs a lot Too many movies Educational success and its obstacles parents students teachers School reforms Democratic reforms in the classroom Open classroom A non-bureaucratic approach to education based on democracy, flexibility and noncompetitive learning. Enhances and reinforces creativity Montessori philosophy – every child helps decides his-or her approach to Cooperative learning Pg 391 Instructional method that relies on cooperation among students Students learn together and teach together Integrative curriculum Pg 391 an approach to education based on student-teacher cooperation Open Classroom experiment 1. Pick a topic in sociology (in this chapter) 2. Decide how you want to … gain more knowledge about the topic and demonstrate your knowledge (a) (b) 1. Get it approved by ME then Begin the process Must have proof of work done Topics must be connected to Sociology Demonstration ideas • Make a skit that exemplifies an idea or sociological concept • Create poem that demonstrates idea • Draw or illustrate ideas that typify a concept • Write a story that uses sociological concepts Create a collage that exemplifies an idea or sociological concept Break down a story (from Am. Lit, for example) explain how it relates to concepts in sociology Assessment based on Scope Depth The area covered by a given activity or subject How deep you go into the content you cover – the complexity of the topic Back To Basics Movement pg 393 Gov. report A Nation at Risk Stated that Gov. report A Nation at Risk Stated that Americans were deficient in “education” and therefore were at risk of being taken over (economically) by worldwide competitors Back to Basics Movement prompted Schools to return back to teaching the “basics” Example: 4-years math 4-years science 4 years reading/writing 4 years of social studies School Choice Movement Voucher system pg 393 A system by which public funds may be used to support tuition (payment) to a school of your choice Charter schools pg 394 Publicly funded schools that operate like private schools by public school teachers and administrators Magnet schools pg 394 Public schools that focus on particular disciplines or areas – fine arts, science, technology, etc… For profit schools Pg 394 Schools that are operated by private companies on government funds. Educational Tracking (398) The European model of education Schools place students in “tracked” programs according to their academic ability. School Examples: College-bound track Service industry track Carpentry track Technical service track Nursing track Business track School desegregation The achievement of racial balance in the classroom Multicultural education An education curriculum that emphasizes differences among gender, ethnic, and racial categories Compensatory education Specific curricular programs designed to overcome a deficiency ex. head start Pros and cons of educational reform Using as graph, indicate (at least) one advantage and (at least) disadvantage of each educational reform movement Voucher system Charter schools Magnet schools For profit schools Tracking School desegregation Multicultural education Compensatory education Sociological perspectives (1) Functionalists perspective emphasizes the positive functions of the educational system (2) Conflict perspective emphasizes the inequities and negative aspects of the educational system (3) Symbolic interactionism emphasizes how culture transmits attitudes and values Section 2 Functionalist … on education Schools serve a purpose; they create a common identity for all students Manifest functions – intended results Latent functions – unintended consequences Page 400 Conflict perspective Popular conceptions about education are not necessarily true Theories Meritocracy A society in which social status is based on ability and achievement Competition A system in which rewards are based on relative performance If one is rewarded for ACT scores, does this mean American education is a meritocracy? Or are some at a disadvantage? Educational equality An attempt to produce the same results for lower-class and minority children as it does for other children Intelligence Cognitive ability Capacity for thinking abstractly Cultural bias unfair measurement of the cognitive abilities of people in some social categories http://wilderdom.com/personality/intelligence ChitlingTestShort.html School desegregation The attempt to achieve a racial balance in the classroom Compensatory education Specific curricular programs designed to overcome educational deficiency Symbolic interactionism “We don’t know how to learn, we learn how we know” Hidden curriculum The non-academic agenda that teaches discipline, order, cooperativeness, and conformity a hidden agenda is also present in textbooks Espousing patriotism, civic duty and responsibility Self-fulfilling prophecy A prediction about oneself that results in behavior that makes the prediction come true