MauryanGuptaEmpiresofAncientIndiaPowerPointPresentation (2).ppsx
advertisement

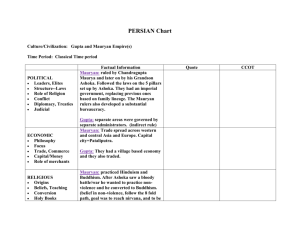
Mauryan and Gupta Empires Power Point Presentation Part 6 of: Ancient India and the Indus River Civilizations teaching unit A.C. Sandler 1 The Mauryan Empire 324 to 183 B.C. • The Persian Empire invaded India during the 500s B.C. • The Greeks, under Alexander the Great, invaded India in 327 B.C. • In 321 B.C. Chandragupta seized control of the Ganges River Valley and established the first Indian empire. 2 Standards 3 The Mauryan Empire 321-298 B.C. • Established a strong government. • Strong military • Local governors & local rulers • Postal system • Extensive spy network 4 The Mauryan Empire 273-232 B.C. • Emperor Asoka • Strong military leader • Chose a reign of peace over military conquest • Focused on building • Roads, hospitals, • Became a Buddhist • Center of a huge trade network from China to the Mediterranean Sea 5 HISTORY STANDARD Indian History 6.5 7. Discuss important aesthetic and intellectual traditions (e.g., Sanskrit literature, including the Bhagavad Gita; medicine; metallurgy; and mathematics, including Hindu-Arabic numerals and the zero). 6 The Gupta Empire 320 A.D.-467 A.D. Golden Age of India • Gupta rule lasted 200 years • Prosperous International Trade • Scientific Advances • Mathematic Advances • Famous literary epics 7 The Gupta Empire International Trade • Ships and caravan carried goods throughout Asia and the Middle East. • Luxury exports: • Gems, pearls, perfumes, salt, pepper, ginger, cinnamon, other spices • Finely woven cloth, red dye, • timber such as teak and ebony 8 COMMON CORE READING STANDARDS FOR LITERACY IN HISTORY / SOCIAL STUDIES 6-8 Craft and Structure 4. Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in a text, including vocabulary specific to domains related to history/social studies. 9 Vocabulary These are the terms and concepts the following slides will be covering: • Stupa • Pilgrims 10 The Gupta Empire Stupa • A funeral mound built to contain the relics or remains of emperors or kings. • The first stupas housed Buddha’s relics, later they were used to house the relics of famous monks. The Great Stupa in Sanchi built in 300 B.C.by Emperor Asoka. • Stupas became a symbol of Buddha’s final nirvana. 11 The Gupta Empire Pilgrims • People traveled along trade routes to visit religious sites and shrines. • Indian cities with famous temples became wealthy from donations given by visiting pilgrims. Karla Caves 200 B.C. 12 Literature Epic Tales • Mahabharata • A tale of a great civil war between two branches of a ruling family. • Ramayana • The heroic story of how Rama rescues his wife from a monstrous demon 13 Technology metallurgy • 12,000 pounds of pure iron • (99.27% iron) • 1600 years old • Has not rusted • Forged all at one time • Stands 23.8 feet tall • Currently located in New Delhi Iron Pillar of the Gupta Dynasty 14 Astronomy • Aryabhata leading mathematician & scientist. • Determined the earth was a sphere • Determined the length of the solar year 354.358 days. • Mapped stellar movements of planets and stars. Aryabhata lived in the 4th century B.C. 15 Sciences Medical advances • Able to set broken bones • Performed operations • Practiced plastic surgery. • Created medicines out of herbs for treating illnesses. Indus River Civilization 3,000 years ago. 16 Sciences Shushruta ( lived between 1000 -600 B.C.) • Practiced: • • • • Plastic surgery Rhinoplasty (reconstructing noses) Eye surgery (removing cataracts) Setting bones • Trained surgeons and midwives • Teachings recorded in the Vedas “Sushruta Samhita” in the Atharvaveda. Shushruta lived in the Indus River Civilization; his medical knowledge is used by modern doctors. 17 Math Concepts • Gupta, India 500 A.D. • Concept of zero • Algebra • Infinity • Symbols for numerals 1-9 • Mathematic algorithms 18 Math Concepts Hindu- Arabic numerical system • The symbols for numbers were adopted by Arab traders in the 700’s A.D. and replaced the Roman numerals in Europe by the 1200’s. 19 Math Concepts -Algorithms are a series of steps followed to solve a mathematical problem. -Today programmers use algorithms to write computer programs. 20 What did Gupta mathematicians invent? • A. early forms of computers • B. long division • C. the zero • D. geometry 21 Language Arts Common Core Standard SPEAKING AND LISTENING STANDARD GRADE 6-8 Comprehension and Collaboration 1. Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions (one-on-one, in groups, and teacherled) with diverse partners on grade level topics, texts, and issues, building on others’ ideas and expressing their own clearly. d. Review the key ideas expressed and demonstrate understanding of multiple perspectives through reflection and paraphrasing. 22 Reflect & Discuss Which accomplishments of the ancient Indians surprised or astonished you? Why? Discuss with your neighbor: Share out as a class 23 Common Core Standards 24 Prewriting Activity • As a class fill out the graphic organizer on the next slide, with the accomplishment and reason. • To aid you in getting started, one example and corresponding reason is written down. 25 That is such a delicate surgery, how did they keep everything sterile, and where did they get the surgeon’s instruments? Accomplishments in ancient India. 26 Writing Opportunity • Using the sentence starters on the next slide write a 4-6 sentence paragraph about the accomplishments from the Indus River Civilization, The Mauryan Empire and or the Gupta Empire. • Be sure to include many specific details in your paragraph. 27 Writing Opportunity Ancient Indians were really smart • I didn’t expect ________________ because ____________________________________. • It is amazing that ___________ did _________ because______________________________ . 28