Indian Civilization - BC Learning Network
advertisement

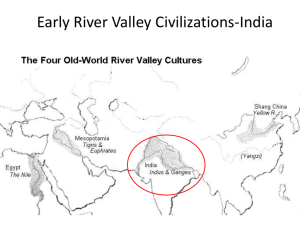
Indian Civilization Indicators Addressed WH.4.1 Purpose Students will trace the development and major achievements of civilization in India with particular emphasis on the rise and fall of the Maurya Empire, the “golden period” of the Gupta Empire, and the reign of the Emperor Ashoka. Time Single Day Materials For the teacher: world map For each student: paper, pencil, information resources Activity A. Introducing the Concept Review with students the ancient history of India, including the Aryan invasions, the rise of Buddhism from Hinduism during the 500s B.C.E., and the trade relations between the various Indian kingdoms and the Roman Empire. Point out the major geographical features that make India unique, including the obstacle of the Himalayas in the north and the surrounding seas that make it an important trading center. Describe the invasion of the Persian ruler Darius I and explain that during that time, one of the kingdoms in the north (Magadha) was expanding rapidly and would become the center of India’s first empire, the Maurya. Point out the area of Magadha on a world map (within the area of the present-day state of Bihar) and explain that Pataliputra (now known as Patna) was its capital. Tell students that another empire, the Gupta, followed about 500 years after the end of the Maurya, and that the achievements of a Mauryan emperor, Ashoka, laid the foundation for much of Gupta culture, which was enlightened and progressive. B. Individual Activity Tell students that they are going to make a comparative timeline. Explain that they will research the achievements, major events, and important people of India during these two empires. Explain that they should place a special focus on the achievements of the emperor Ashoka. Instruct them to create a timeline from 321 B.C.E. to 600 C.E. and to place important events from the Mauryan and Gupta Empires on it. Explain that they should also place at least two important events from each of the following contemporaneous civilizations: Roman (e.g., Punic Wars, reign of Constantine), Chinese (e.g., the Han Dynasty), African (e.g., kingdom of Kush), and pre-Columbian American (e.g., rise of Teotihuacan). Instruct students to write an accompanying one-page essay describing the specific achievements of the emperor Ashoka. Questions for Review As the students work on their timelines, ask them questions such as: 1. What civil projects were undertaken during the Mauryan Empire? 2. Why did the Mauryan Empire collapse? 3. Why was the Gupta Empire so much smaller than the Mauryan Empire? 4. What specific achievements marked Ashoka’s reign?