(iObservation) PPT
advertisement
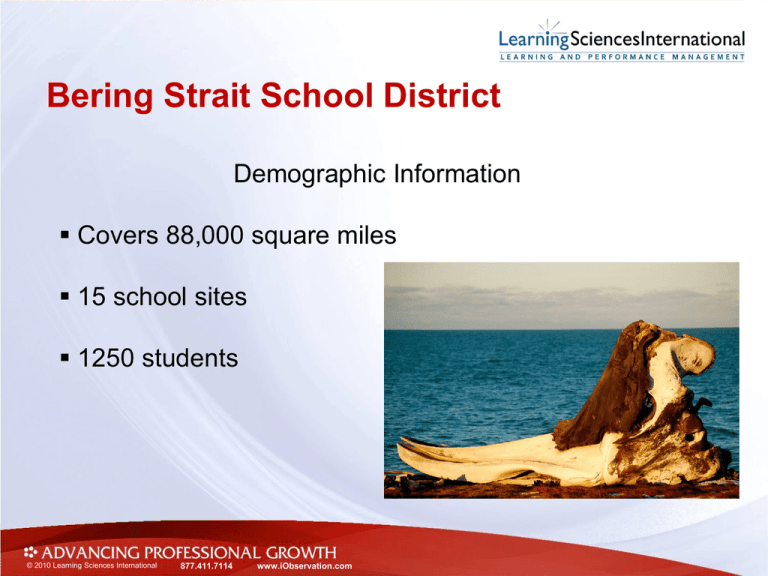
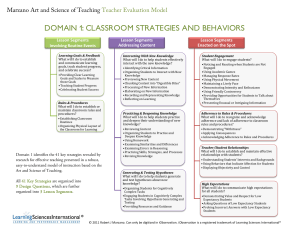
Bering Strait School District Demographic Information Covers 88,000 square miles 15 school sites 1250 students © 2010 Learning Sciences International 877.411.7114 www.iObservation.com How the Decision Was Made BSSD has four School Improvement Grant schools (SIG) Gambell, Savoonga, Stebbins and Shishmaref SIG schools are required to implement a new teacher and administrator evaluation instrument. © 2010 Learning Sciences International 877.411.7114 www.iObservation.com How the Decision Was Made We reviewed Marzano’s iObservation, and the Danielson model We chose Marzano’s iObservation because: a) The instructional professional development from Marzano’s Art and Science of Teaching b) The embedded video clips of best instructional practices. c) It’s technology © 2010 Learning Sciences International 877.411.7114 www.iObservation.com How the Decision Was Made One of the biggest factors in our selection of iObservation was it’s coherence with: a) Anita Archer’s Explicit Instruction a) CHAMPS from Safe & Civil Schools © 2010 Learning Sciences International 877.411.7114 www.iObservation.com Implementation Challenges Compressed time for implementation due to the length of the SIG grant. Technology Training on how to use the instrument for the principals Designing the evaluation instrument and the calculations for the use of student performance data © 2010 Learning Sciences International 877.411.7114 www.iObservation.com Big Picture Art and Science of Teaching Teacher Growth Model The Goal: An expectation that all teachers can increase their expertise from year to year which produces gains in student achievement from year to year with a powerful cumulative effect Research-based strategies have a high probability of raising student achievement if they are used: • In the part (segment) or type of lesson that is appropriate for the strategy • At the appropriate level of implementation High Probability vs. High Yield There are no high-yield instructional strategies; there are only high-probability strategies. The simple presence or absence of an instructional strategy does not define effectiveness, but it is rather the teacher’s expertise in adapting that strategy to the classroom within the context of lesson segments that produces gains in student achievement.” Dr. Robert Marzano © 2010 Learning Sciences International 877.411.7114 www.iObservation.com Five Conditions to Support Teacher Expertise Common Language of Instruction Recognition of progress Teacher Expertise Clear Criteria for Success and Plan for Success Focused Feedback and Deliberate Practice Opportunity to Observe and Discuss Teaching and Learning Causal Links to Student Achievement Domain One Domain Two Domain Three Domain Four Common Language of Instruction FOUR DOMAINS • The Four Domains of the Marzano Teacher Evaluation Model contains 60 total elements. • The elements build on each other to support teacher growth, development and performance. • Domain 1: Classroom Strategies and Behaviors, which contains not only the largest number of elements but also those that have been shown in causal studies to have the most direct effect on student performance. • The 60 elements define the knowledge base for teaching and a framework for the systematic development of expertise. Art and Science of Teaching Teacher Evaluation Model STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT Domain 4: Collegiality and Professionalism (6 Elements) Promoting a Positive Environment (2 Elements) Promoting Exchange of Ideas (2 Elements) Promoting District and School Development (2 Elements) Domain 1: Classroom Strategies and Behaviors (41 Elements) Routine Segments (5 Elements) Content Segments (18 Elements) On the Spot Segments (18 Elements) Domain 2: Planning and Preparing (8 Elements) Lesson and Units (3 Elements) Use of Materials and Technology (2 Elements) Special Needs of Students (3 Elements) Domain 3: Reflecting on Teaching (5 Elements) Domain 4: Collegiality and Professionalism (6 Elements) Promoting a Positive Environment (2 Elements) Promoting Exchange of Ideas (2 Elements) Promoting District and School Development (2 Elements) Evaluating Personal Performance (3 Elements) Professional Growth Plan (2 Elements) 13 • Marzano’s iObservation model contains: • Goal Setting • Planning and Reflection Conferences • Classroom Observations • Imbedded professional practice videos of good instructional practices Levels of Performance • Scales: continuum of teaching behavior that documents growth over time and can be used as a formative feedback tool or a summative assessment. Example from Domain 1: Processing New Information Innovating (4) Applying (3) Developing (2) The teacher adapts and creates new strategies for unique student needs and situations The teacher engages students in summarizing, predicting, and questioning activities and monitors the extent to which the activities enhance student understanding The teacher engages students in summarizing, predicting, and questioning activities Beginning (1) The teacher uses the strategy incorrectly or with parts missing Not Using (0) The strategy was called for but not exhibited 15 A System of Feedback Self Observation • Teachers analyze their own teaching through videotapes Self Reflection • Teachers reflect upon their practice Observations Instructional Rounds Walkthroughs Common and Comprehensive Model of Instruction • Observation of an entire lesson • Teacher and administrator teams engage collectively in examining a model or language of instruction • Identify trends and patterns across classrooms, grade levels, schools and district Next Steps For BSSD: Convene a Work Team to revise the student performance data portion of the evaluation instrument. Expand the use of iObservation from the four SIG schools to the entire district using the CREATE grant. a) 3 year grant b) Provide The Art and Science of Teaching professional development to the remaining 11 schools c) Train principals and teachers on the iObservation instrument. d) Provide ongoing support to the four SIG schools. Questions: