Reproduction
1. Male Reproductive System
2. Female Reproductive System
1. Outline: Male Reproductive
System
A) Path of sperm
B) Function of seminal fluid
C) Hormone regulation
A) Path of sperm
Sperm is separated into 3 parts
1) Head- nucleus (23 chromosomes)
-acrosome (contains enzymes to break through egg)
2) Midpiece- contain mitochondria (produce ATP for tail)
3) Tail- movement
A) Path of sperm
Sperm is made in the seminiferous tubules in the
testes (scrotum is the pouch of skin that
encloses the testes)
A) Path of sperm
Sperm moves into the epididymis
-sperm matures
A) Path of sperm
Sperm flows into the vas deferens
-Leads away from testes
A) Path of sperm
Sperm flows past 3 accessory glands that produce
seminal fluid
-Seminal vesicles
-Prostate gland
-Cowper’s glands (AKA Bulbourethral glands)
A) Path of sperm
Flows into Urethra where it exits the penis
A) Path of sperm
B) Function of seminal fluid
2 Seminal vesicles
-Alkaline fluid- neutralizes acidic vagina
-Fructose,
-Prostaglandins
1 Prostate gland
-Alkaline fluid- neutralizes acidic vagina
-Zinc- maintains healthy sperm (stable DNA)
-Citrate- energy
2 Cowper’s glands
-Pre-ejaculate of Alkaline fluid to neutralize acid
urine in urethra
C) Hormone regulation
1) Hypothalamus in brain secretes Gonadotropin
releasing hormone (GnRH)
2) GnRH stimulate the anterior pituitary in brain
to secrete Gonadotropic hormones
a) Follicle-stimulating Hormone (FSH)
-Promotes production of sperm in
seminiferous tubules
b) Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
-stimulates testosterone production by
interstitial cells of testes
C) Hormone regulation
Cross section of a rabbit testicle
-Large round = seminiferous tubules
-Small triangular = interstitial cells
C) Hormone regulation
Testosterone
Steroid hormone (lipid)
Made in the SER
brings about and maintains 2° sex characteristics
-deeper voice
-body and facial hair
-muscle development
-oils (acne) and sweat (stinky)
C) Hormone regulation
Hormone feedback loop
What should I know?
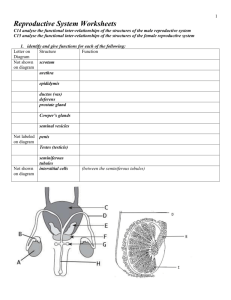
1. Identify and give functions for each of the following:
– testes (seminiferous tubules and interstitial cells)
– scrotum, epididymis, ductus (vas) deferens
– prostate gland, Cowper’s glands, seminal vesicles
– penis, urethra
2. Describe the path of sperm from the seminiferous tubules to the
urethral opening
3. List the components of the seminal fluid (as contributed by the
Cowper’s glands, prostate gland, and seminal vesicles), and
describe the functions of each component
4. Identify the tail (flagellum), midpiece, head, and acrosome of a
mature sperm and state their functions
5. Describe the functions of testosterone
6. Describe the homeostatic regulation of testosterone levels by the
hypothalamus, anterior pituitary, and testes