TTL - UStudy.in
advertisement

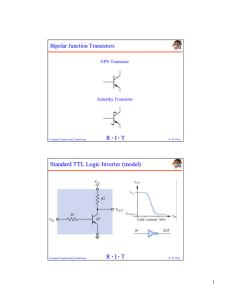
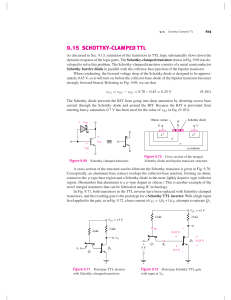
TTL (Transistor Transistor Logic) Introduction Transistor Transistor logic or just TTL, logic gates are built around only transistors. TTL was developed in 1965. Through the years basic TTL has been improved to meet the performance requirements. There are many versions or families of TTL Standard TTL. High Speed TTL Low Power TTL. Schhottky TTL. As such all the families of TTL have three configuration for outputs. Totem - Pole output. Open Collector Output. Tristate Output. TTL circuit Cont., Thus it has two emitter-base junctions that can be used to turn Q1 ON. The transistors Q3 and Q4 are connected in a totempole arrangement. Basic TTL NAND gate Cont., In normal operation, either Q3 or Q4 will be conducting, depending on the logic state of the output. The transistor Q2 acts as a phase splitter. TTL NAND gate 3 input circuit Cont., When both the inputs A and B are at high level, the diodes D1 and D2 will conduct in reverse bias (OFF) and the diode D3 will conduct in forward bias (ON), hence Q1 goes in to cut off. Cont., Now the current flow through the emitter of Q2 will turn On the transistor Q4. At the same time the collector current of Q2 produces a voltage drop across R2 that reduces Q2 collector voltage to a low value. Now the output is low because Q4 is conducting Diode equivalent for Q1 Cont., When either or both inputs are low, the transistor Q1 conducts because the either, or both diodes D1 and D2 are conducting in forward biasing. Now the diode D3 is not conducting properly, so not a sufficient current is flowing through the base of Q2. Hence Q2 goes to cut-off. TTL NAND Gate with a Totem Pole Output Stage Cont., There is no emitter current of Q2, no base current of Q4, and it turns OFF. The high collector voltage of Q2, turns On the transistor. Actually Q3 acts as an emitter follower. Now output is high, because Q4 is in cut-off. The function of diode D is to prevent both Q3 and Q4 from being On simultaneously. Improved TTL Series 74 Series Schottky TTL, 74S Series: higher speed Low-Power Schottky TTL, 74LS series Advanced Schottky TTL, 74AS Series Advanced Low-Power Schottky TTL, 74ALS Series 74F-Fast TTL Comparison of TTL Series Characteristics of TTL gates 1. Operates reliably over the range from 4.75V to 5.25V 2. Operates in ambient temperature range from 0 to 700C 3. One NAND gate requires an average power of 10mW. 4. Propagation delay range from 7ns to 11ns 5. Fan-out: It can drive standard TTL inputs. Advantages Compatible with other logic circuits Low output impedance High speed operation Good noise immunity Low power dissipation High fanout Low cost Disadvantages 1. TTL ICs generate switching transistors 2. Used special techniques for circuit preparation 3. Wired output capability is not possible The End …..Thank you…..