Presentation - University of Wisconsin–Madison
advertisement
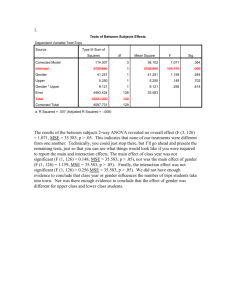
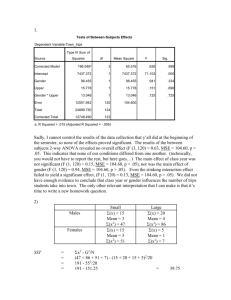
ECE 539 Course Project NEURAL NETWORK APPROACHES FOR AUTOMOBILE MPG PREDICTION 12/14/2010 Xiaofei Sun University of Wisconsin-Madison Motivations Nowadays, fuel economy becomes a great concern of the governments and drivers MPG varies with vehicle specs and conditions Database available online only accounts for different models Large amount of data required Build NN models to predict the MPG based on given specs and conditions MLP RBF 1/8 Data Description Source: UCI Machine Learning Repository http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Auto+MPG 8 Inputs: 1. cylinder # 2. displacement 3. horsepower 4. weight 5. acceleration 6. year 7. origin 8. manufacturer 1 Output: MPG 2/8 Data Preparation 392 sets of data Correlation coefficients between I/O were calculated 0.9 Correlation Coefficient 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 3/8 Linear Regression 7-way cross validation Training MSE = 11.12 Tuning MSE = 12.70 50 45 45 40 35 y = 1.1164x - 1.8062 R² = 0.8476 35 30 30 Target Target 40 y = 1.0058x - 0.142 R² = 0.8335 25 20 25 20 15 15 10 10 5 5 0 0 0 10 20 Output 30 40 0 10 20 Output 30 40 4/8 Multi Layer Perceptron MATLAB Neural Network Toolbox Used Learning algorithms: Gradient descent with momentum Scaled conjugate gradient Levenberg-Marquardt Datasets were randomly divided into three subsets: 60% for training 20% for validation (early stopping) 20% for testing 5/8 Multi Layer Perceptron Structure: 7-12-1 feedforward network Log-sigmoid function for hidden layer Linear function for output layer Test MSE = 5.11 Training MSE = 4.03 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 y = 1.0055x - 0.1154 R² = 0.9346 Target Target 0 10 20 30 Output 40 50 45 40 y = 0.9775x + 0.5947 35 R² = 0.9157 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 0 10 20 30 Output 40 50 6/8 Conclusions and Future Work MLP yields better performance than linear regression after fine tuning 14 12 10 8 6 MLP 4 Linear Regression 2 0 Training MSE Test MSE Will construct radial basis function network, and compare with MLP 7/8 Any Questions? 8/8