introduction to hard..
advertisement

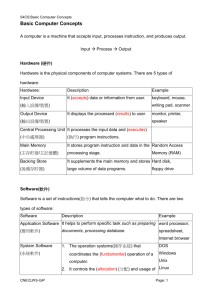
CSCI 1412 Tutorial 1 Introduction to Hardware, Software Parminder Kang Email: Pkang@dmu.ac.uk Home: www.cse.dmu.ac.uk/~pkang Q1: Difference between hardware and software? Hardware: Hardware is best described as a device that is physically connected to your computer or something that can be physically touched. plastic, metal and glass components Example: • display devices; LCD. • storage; hard drive, CD, DVD, FDD. • Input; Keyboard, mouse, scanner, bar code reader. • Output; printer, display devices. • Communication; NIC. Software: software is a general term used to describe a collection of computer programs, procedures and documentation that perform some tasks on a computer system. • set of instructions and data • processed by the hardware • used to control the hardware Example: Application Software (word processors) System Software (Operating Systems), to provide the necessary services for application software. Middleware which controls and co-ordinates distributed Systems. What is Firmware? Q2: Software, Program and Data? Program: In order to do any specific job you have to give a sequence of instructions to the computer. This set of instructions is called a computer program. Software: software is a general term used to describe a collection of computer programs, procedures and documentation that perform some tasks on a computer system. Software refers to the set of computer programs, procedures that describe the programs, how they are to be used. The process of software development is called programming. Example: Application Software (word processors) System Software (Operating Systems), to provide the necessary services for application software. Middleware which controls and co-ordinates distributed Systems. Data: Distinct pieces of information, usually formatted in a special way. Programs are collections of instructions for manipulating data. Data can exist in a variety of forms . 1. numbers or text on pieces of paper 2. bits and bytes in electronic memory 3. facts stored in a person's mind. Types: ASCII, binary. For example: database and metadata. Set of instructions set of Programs software System software Application software Q4: Application, System/Utility and Programming Language software? Application Software: Application software is set on programs to carry out Operations for specific application. Example: MS office COBOL (Common Business Oriented Language ) for business applications FORTRAN (Formula Translation) is useful for scientific application. System Software: system software is defined as a set of one or more programs designed to control the operation of computer system. Also knows as Operating System. Main Function: controlling all operations required to move data into and out of the computer. essential for the development of applications software Example: DOS, UNIX and WINDOWS Utility Software: • Manage and tune computer hardware, Operating system and application software. •maintenance & problem solving tools - housekeeping Example: • Virus Scanner, Disk Defragmenter. • System Mechanic, Register cleaner etc. • Network Managers. Programming Language: A programming language is artificial language that can be used to write programs. Programs are used to control the behaviour of machine. Types: High Level and Low Level. Programming Language Low Level High Level • easier to learn and use. • hardware independent. • efficiency; source code needs to convert into machine code before execution Machine language • Written in machine code • no translation required by CPU. Hence fast execution. • difficult to learn and debug the code. • Hardware dependent. Assembly Language • program consist of set of letters and symbols. • one-to-one translation between Assembly language and machine code. Hence retain efficiency. • easier to learn and debug than machine language. • still Hardware dependent. Q5: Define Supercomputer, Mainframe, minicomputer and dedicated computer? Supercomputer: • very expensive machines. • used for complex applications that requires immense amount of mathematical calculations. Uses: • Climate research, weather forecasting, • molecular modelling, quantum mechanical physics. • Simulation. Mainframe: • A very large and expensive computer. • Simultaneously supports hundreds or thousands of users. • and provides greater availability and security. Uses: • bulk data processing eg. Financial transaction processing. Difference between mainframe and supercomputer? Minicomputer: • It is a multiprocessing system. • lies between workstation and mainframe. • supports ten to hundreds of users. Uses: • the functions are similar to the mainframe but at smaller scale. Eg: • SPARC (by Sun Microsystems) and POWER (by IBM) Dedicated computer: • Special purpose computer, dedicated for one or few tasks. • often used in real time control. • also known as Embedded systems. Eg: • industrial automation and control (nuclear power plant controller) • cars •Washing machine, security alarms, GPS etc. Q6: functionality of components of CPU? Control Unit: • Fetch • Decode • and Execute. ALU: • Performs arithmetic and logical operations Memory: • Registers • Hold data, instructions and intermediate results.