Designing CBC
advertisement
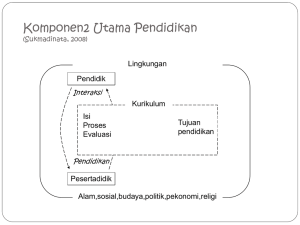
Designing CBC Komitmen Kita Semua Komitmen Nasional 4 Misi Menuju Indonesia Sehat 2010 Menggerakkan Pembangunan Nasional Berwawasan Kesehatan Mendorong Kemandirian Masyarakat Untuk Hidup Sehat Memelihara dan Meningkatkan Pelayanan Kesehatan yang Bermutu, Berkeadilan, Merata, dan Terjangkau Memelihara dan Meningkatkan Kesehatan Individu, Keluarga dan Masyarakat beserta Lingkungannya INDONESIA SEHAT 2010 Model-Model (dalam kesisteman) (Desentralisasi) Keluarga Sehat Desa Sehat Kecamatan Sehat Kota/Kabupaten Sehat Propinsi Sehat Sehat adalah Hak Manusia (Dasar Moral) Sehat adalah Investasi Paradigma Sehat (Dasar Fikir) Pembangunan Berwawasan Kesehatan (Wawasan) Moral Sistem & Manajemen Private Goods (Kesehatan Individu & Keluarga) Desentralisasi Model, Sistem: Pelayanan Kesehatan Primer Pelayanan Kesehatan Sekunder Asuransi (Sosial, JPKM, Private) Public Goods (Kesehatan Kewilayahan) Model, Sistem: Pengembangan Kesehatan Wilayah • Pemerintah • Lintas Sektor • UU Kesnas (Normatif) • UU SKN Baru (Implementatif) • RUU JSN • RUU Praktek Kedokteran • UU Lingk, UU Pendidikan • UU Konsumen, dll Sistem Kesehatan Nasional (2004) Untuk masa mendatang apabila Sistem Jaminan Kesehatan Nasional (SJKN) telah berkembang, pemerintah tidak lagi menyelenggarakan UKP strata pertama melalui Puskesmas. Penyelenggaraan UKP strata pertama akan diserahkan kepada masyarakat dan swasta dengan menerapkan konsep dokter keluarga, kecuali di daerah yang sangat terpencil yang masih dipadukan dengan pelayanan Puskesmas Basis Kompetensi (Pendidikan) Kewenagan Dlm Pelayanan Sistem Pendidikan Berjenjang (Terstruktur) A B C (Spesialis) Sehat PROMOTIF, PREVENTIF, PROTEKTIF (Komunikasi, Edukasi, Informasi) Sakit UPAYA KURATIF A = Pendidikan Dokter Umum A + B =Pendidikan Dokter Keluarga (5 Star Doctors) C = Pendidikan Dokter Spesialis Kurikulum A = KIPDI II A + B = KIPDI III (5 Stars Doctors) Ciri Khusus Dokter Keluarga (Kompetensi): ‘Care and Cure Provider’ WHO ‘Decision Maker’ ‘Communicator’ ‘Community Leader’ ‘Manager’ Dokter Keluarga Harus Dapat Bicara Tentang Kesehatan Bukan Hanya Tentang Penyakit Gizi ‘ Life Style’ Kesehatan Ibu dan Anak Lingkungan Sehat Olah Raga dan Rekreasi ‘Medical Back-up’ Saat mendatang Dokter Keluarga …………… (langsung) Saat ini 4 tahun 2 tahun Ko-asisten Mahasiswa Tk I Dokter Umum Kurikulum Dokter Keluarga 5 Star Doctor, WHO 7 Tahun ? Dokter Keluarga adalah Dokter Umum (Baru) Definition of Competencies (1) Competence includes a broad range of knowledge, attitudes, and observable patterns of behaviour which together account for the ability to deliver a specified professional service. McGaghie, et.al, 1978, WHO Definition of Competencies (2) Competencies combine appropriate supporting knowledge and professional attitude, and they are performed reliably in natural settings without assistance. Chambers, 1993, J. Dent Educ Definition of Competencies (3) Professional competence is the habitual and judicious use of communication, knowledge, technical skills, clinical reasoning, emotions, values, and reflection in daily practice to improve the health of the individual patient and community: What you know How you use what you know How you add to what you know Epstein and Hundert, 2002, JAMA What is Competency? seperangkat tindakan cerdas dan penuh tanggungjawab dimiliki seseorang sebagai syarat untuk dianggap mampu oleh masyarakat dalam melaksanakan tugas-tugas di bidang pekerjaan tertentu (SK Mendiknas No. 045/U/2002) Features of a Competency Statement Focuses on outcome performance Integrates a broad range of related knowledge and skills objectives Contextualized – related to a practical task in the field Drawn from multiple domains, including affective and moral dimensions Include professional behaviours relevant to the task Indicates a level of expected ability Educational Objectives States an aspect of knowledge, skills or attitude to be acquired Generally discipline specific Context-free Professional values unaddressed Defines knowledge, skills and attitude Educational Outcome: Competencies Integrates related knowledge, skill and attitude objectives Drawns from multiple disciplines relevant to the practice Related to an actual task in the field – contextualised Driven by professional practice and values Defines a level of ability for an observable outcome Discipline-based Curriculum Curriculum defines content, structure and process Discipline-based Exposure to specific content for a preassigned time Assessment by counting Norm-referenced Competency-based Curriculum Curriculum defines outcomes for proficient practice Integrative Time and sequence derived from assessment Assessment of actual performance Criterion-based Building a Competency-based Program Clinical problem, patient, task, setting Identify essential competencies for practice Determine competency components: objectives and performance levels Identify learning activities and strategies Develop assessment tools and standards for competency