Banquet & Buffet Food Production: Planning & Preparation
advertisement

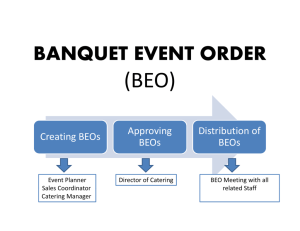
Banquet and Buffet Food Production 5 OH 5-1 Food Production Chapter Learning Objectives Compare and contrast planning and production processes for quantity events (banquets and buffets) relative to full-service meals. Identify procedures important in planning quantity events. Review procedures for preparing foods for quantity events. OH 5-2 Banquets and Buffets Banquets Ceremonial dinners honoring a guest or an occasion Buffets OH 5-3 Meals at which guests serve themselves from various dishes displayed on a table or serving line Banquets and Buffets continued Production techniques including the use of standardized recipes for all items are the same for banquet and buffet operations. OH 5-4 Factors Influencing Quantity Events Kitchen capacity is critical. Kitchen layout is very important. OH 5-5 Kitchen Equipment Considerations Storing area Cooling area Cooking area Holding area Hot preparation area Reheating area Assembly and carving area OH 5-6 À la Carte Menus Must provide balance among cooking stations. Recipes require testing before service. OH 5-7 Special Event Menu Each menu may differ from those used at previous events. Preplanned menus are typically available for customer consideration. OH 5-8 Event Logistics Banquet guests will enjoy their meal. OH 5-9 Location of Special Events In-house events are held at the property. Off-site events are provided at external locations. OH 5-10 How Would You Answer the Following Questions? 1. Meals at which guests serve themselves are called _______. 2. The main difference between à la carte meals, banquets, and buffets is _______. 3. The production capacity of the _______ is a critical factor when considering the operation’s ability to offer a banquet. 4. In-house events are sometimes referred to as on-site _______. OH 5-11 Planning for Quantity Events A banquet/buffet event order (BEO) is a key planning tool. The BEO is sometimes called a function sheet. OH 5-12 Estimating Customer Counts Typically customers must guarantee payment for a specific number of guests. Contracts typically indicate the minimum and maximum number of guests for an event. OH 5-13 Careful Planning with Customers Is Critical Review menu information including product quality. Clarify special requests. Consider beverage and wine needs. OH 5-14 BEO’s Help with Communication All managers involved with the event require a copy. BEOs help to coordinate production and service. OH 5-15 Logistic Problems Problem Result Inaccurate guest count Ordering too much or too little food Insufficient preparation equipment Insufficient preparation time or staff Chef may decide to cancel event due to low number of guests. OH 5-16 Menu Problems Problem Result Menu planning not correct Courses take too long to serve Menu items out of season Not able to keep items at correct temperature, especially if off-site OH 5-17 Production Sheets Help Ensure Food Quality Required information is taken from the BEO. Production sheets are duplicated for all preparation staff requiring them. OH 5-18 Kitchen Responsibilities The sous chef is generally in charge of daily operations. Line cooks have responsibility for cooking specific types of foods. A garde manger is responsible for producing cold foods. OH 5-19 What Is an Expediter? Coordinates placement of orders by service staff Coordinates the production of orders by production personnel OH 5-20 Precooking Foods Definition: To partially cook food in advance of use Common precooking processes: Blanch off Steam off Partially boil OH 5-21 How Would You Answer the Following Questions? 1. Another name for a banquet/event order (BEO) is a _______. 2. Staff who meet with the customer are the only persons who require a BEO. (True/False) 3. The _______ cook is responsible for preparing cold foods. 4. Grill marks are made (before/after) the meat is cooked. OH 5-22 Key Term Review À la carte restaurant Al dente Bain-marie Banquet OH 5-23 Banquet/Buffet event order (BEO) Blanch off Buffet Carving station Key Term Review continued Catering Chafing dish Combination oven Expediter Fire OH 5-24 Full-service restaurant Function sheet Garde manger cook Grill mark Key Term Review continued OH 5-25 In-house event Precooking Line Production sheet Line cook Salamander Partially boil Steam off Chapter Learning Objectives— What Did You Learn? Compare and contrast planning and production processes for quantity events (banquets and buffets) relative to full-service meals. Identify procedures important in planning quantity events. Review procedures for preparing foods for quantity events. OH 5-26