Introduction to Understanding by Design
advertisement

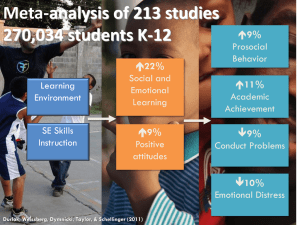
I’m In Activity • Reflect on the morning in 1-2 sentences • “I’m in” Social Emotional Learning Standards applied to Understanding by Design and Leah Evans, Congregation Universal Design for Learning Purpose • In this presentation you will see that: – SEL Standards help frame the essential understanding – Curriculum planning can occur in the context of social-emotional learning – The UbD template provides a process with which to define learning, as well as a common language – The UDL framework creates access for students and builds capacity for teachers Outcomes • You will have an opportunity to: – Design lessons around SEL Standards – Identify essential understanding and essential questions related to a context – Learn about and engage with the Understanding by Design template – Learn about and apply the principles of Universal Design for Learning Reflection #1 In what ways do you currently support your students’ social and emotional needs? Universal Design for Learning Universal Design for Learning a framework for improving and a mindset the increasing Understanding by Design college/career readiness standards literacy SELS instructional core access cultural relevance common core standards the roadmap PBS What is Universal Design for Learning? “UDL” Why UDL? • Early 1990’s: • • • • CAST applied universal design to the learning sciences Recognizes the reality of diversity Identifies and breaks down barriers More efficient than individual solutions Benefits more people + Why Neuroscience? Neuroscience is an alternate representation of what underlies what we do and how we learn If we consider neuroscience in our instructional planning, we will meet the needs of more student brains. The Brain Networks **Affective** Strategic SEL Recognition 3 Principles of Universal Design for Learning Affective **Engagement** • Multiple Means of Representation (Action & Expression) SEL • Multiple Means of Action & Expression • Multiple Means of Engagement Strategic Recognition (Representation) Principles of Universal Design for Learning Multiple Means of Representation – Recognition Network of the brain • The “WHAT” of learning – Provide multiple examples – Highlight critical features – Provide multiple media and formats – Support background context …Recognition network… Multiple Means of Representation Principles of Universal Design for Learning Multiple Means of Action & Expression - Strategic Network of the brain • The “HOW” of learning – – – – Executive functioning Provide opportunities to practice with supports Provide ongoing, relevant feedback Offer flexible opportunities for demonstrating skill …Strategic Network… Multiple Means of Action & Expression Principles of Universal Design for Learning Multiple Means of Engagement **This is where SEL lives - Affective Network of the brain • The “WHY” of learning – Offer choices of content and tools – Offer adjustable levels of challenge – Offer choices of rewards – Offer choices of learning context …Affective Network… Multiple Means of Engagement Reflection #2 Recall a time when you activated a student’s affective network. What were the outcomes for this student? Checkpoint • What questions do you have about Universal Design for Learning? What is Understanding by Design? “UbD” The UbD Template …backwards design… To begin with the end in mind means to start with a clear understanding of your destination. It means to know where you’re going so that you better understand where you are now so that the steps you take are always in the right direction. Stephen Covey, 7 Habits of Highly Effective People The three stages of backwards design 1. Identify Desired Results 2. Determine Acceptable Evidence 3. Learning Plan - Experiences - Instruction Stages in Understanding by Design Stage 1: IDENTIFY DESIRED RESULTS What do we want our students to learn ~ What are the BIG IDEAS? What are your instructional goals? What are your essential understandings? What are your essential questions? Stage 2: ASSESSMENT How will we know that our students have learned the content? What performance tasks measure learning? What other evidence can you collect? Stage 3: LEARNING PLAN What are learning activities/instruction will enable students to achieve desired results? What background knowledge, skills, or abilities will our students need? What are the most effective instructional methods? Stage 1: Essential Understandings • Summarize big ideas students should know 20 years from now • Have lasting value beyond the classroom • Synthesize what students should understand Stage 1: Essential Questions • Probe deep issues • Foster inquiry • Foster transfer of learning • Often interdisciplinary in nature Clarify Content Priorities Worth Being Familiar With Important to Know and Do Essential Understandings Pair Share • Consider your area of expertise • Identify a concept or a skill you teach students that has lasting value beyond the classroom Tsunami in Japan Essential Understandings • Empathy is the core of effective relationships Essential Questions • What is empathy? • How can people show empathy toward others? Knowledge & Skills: Students will know and be able to… •Use key terms: relationship •Identify ways in which they are empathetic •Recognize ‘self ’ compared to ‘others’ SEL Standard Power Standard 1: EMOTIONAL DEVELOPMENT Empathy: Recognize and understand others' feelings while building awareness of how one's behavior influences others Being on Time to Class Essential Understandings • Being on time is important in the working world because the people who are on time to work are the people the boss wants to keep. Essential Questions • Why is being on time important for academic success? • Why is being on time is important for keeping a job? Knowledge and Skills: Students will know and be able to… •Use key terms: professionalism, responsibility •Identify the meaning of “on time” •Identify strategies that will contribute to being “on time” •Plan in advance-setting clocks, getting clothes ready etc SEL Standard Power Standard 2: • Go to bed on time • Have a back up plan for transportation. • Articulate the importance of being on time • Communicate transportation issues with a staff member SELF CONCEPT Lifelong Learner: Set and achieve goals to enhance personal success Checkpoint • What questions do you have about identifying essential understandings or essential questions? Practice Essential Understandings Essential Questions • Big ideas - 20 years from now • Probe deep issues • Value beyond the classroom • Foster inquiry • Synthesize what students should understand • Foster transfer of learning • Often interdisciplinary in nature SEL Standard: You choose 1 Stages in Understanding by Design Stage 1: IDENTIFY DESIRED RESULTS What do we want our students to learn ~ What are the BIG IDEAS? What are your instructional goals? What are your essential understandings? What are your essential questions? Stage 2: ASSESSMENT How will we know that our students have learned the content? What performance tasks measure learning? What other evidence can you collect? Stage 3: LEARNING PLAN What are learning activities/instruction will enable students to achieve desired results? What background knowledge, skills, or abilities will our students need? What are the most effective instructional methods? “You don't change performance without changing the instructional core” Richard Elmore, Harvard University Professor The Instructional Core Richard Elmore, Harvard University Content (curriculum) 3 Points of entry for improvement of instruction All 3 points have equal importance Learning Task Teacher (instructional strategies) Student (engagement) Reflection #3 In what ways could you collaborate around SEL Standards with your colleagues? Resources • Center for Applied Special Technology. http://www.cast.org/ • Collaborative to Advance Social and Emotional Learning. http://www.casel.org • Evans, Leah. Congregation. Used with permission. • McTighe, Jay and Grant Wiggins. Understanding by Design: Expanded 2nd Edition • McTighe, Jay and Grant Wiggins. Understanding by Design: Professional Development Workbook • http://udl2009.wikispaces.com/file/view/UDL+word+cloud.bmp • http://www.arps.org/users/ms/coaches/backward%20design%20101.htm • Zins, Joseph, et al (1998). Enhancing Learning Through Social and Emotional Education. Think: The Journal of Critical and Creative Thinking, 9, 18-20. Presenter Contact: Amy Clements, Program Support Teacher – Ed. Services 608.442.2166 aclements@madison.k12.wi.us Stoplight Activity • Think about your students and your work… 3. STOP 2. CONTINUE 1. START