Statewide Collaborative Initiative PowerPoint
advertisement

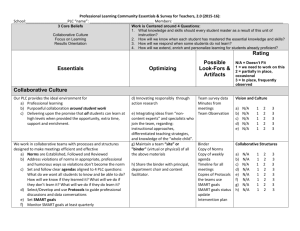
Statewide Collaborative Initiative WELCOME AND INTRODUCTIONS Outcomes Develop an understanding of the “Why,” “What,” and “How” of the Statewide Collaborative Initiative Provide a general description of what the work will look like Why A Statewide Collaborative Initiative To improve learning outcomes for all students To close the gap between under-performing students and their peers This is a Collaborative Process Initial steps include: Identifying the structure of collaborative data teams, i.e. grade level, content, integration of special teachers. Establishing roles and rules for collaboration. Allotted time for Collaborative Teams Topics for Understanding Core Academic Standards Formative Assessments Data team process/protocols Hattie’s research on effective practices What Does the Work Look Like Teams agree to teach to specific reading or mathematics Core Academic Standards. Teams develop and administer (common) formative assessments to determine student progress. Teams analyze assessment data to group students for teaching. Collaborative teams agree to learn and implement four effective teaching/learning practices throughout the year. The Work continued Formative assessments are given to track student progress. Teams re-teach with another effective practice to students who have not met the learning goal/target. Students are re-tested and the results are analyzed by the team. The Work continued Strong evidence from the research synthesis work of John Hattie suggests that key teaching/learning practices, coupled with formative assessments, analysis of assessment results, and re-teaching accelerates learning for all students All activities aligned with Missouri Teacher Leader Standards The How All teachers will participate on a collaborative data team. The team will identify a content area of English Language Arts or Mathematics to focus their attention and report progress (recommended, but not required, for the entire building to have the same focus). Each building will select four “effective” teaching learning practices (Hattie’s) for the year and agree to use these practices. How continued Each team will develop, administer, score, and analyze results of (common) grade appropriate formative assessments aligned to Core Academic Standards chosen by the team. Once the process is initiated, the assessments will be shared with other buildings in the region on a monthly basis. Product A summary analysis based on the formative assessment will be developed. Basic information will include: Core Academic Standards addressed. teaching/learning practices implemented. number and percent of students assessed in gradelevel. number and percent of students in proficient/close to proficient/far but likely/and far but not likely. . Product continued number and percent of students with disabilities in proficient/close to proficient/far but likely/and far but not likely. teaching/learning practice used to re-teach. number and percent in each level based on re-test (may use the same or similar assessment which does not need to be shared). *Proficient/close to proficient/far but likely and far but not likely reflect the language of data teams and relates to high/medium and low in your letter. Outc0mes All activities aligned with the teacher/leader standards and with the Core Academic Standards All content areas will benefit Builds a common vocabulary Builds a toolbox of effective teaching/learning practices with the expectation that teachers will be able to use them with a high level of effectiveness All schools will get access to a pool of formative assessments Increased student achievement Considerations Who will be on your leadership team? What school improvement/professional learning activities are you already implementing? How does this connect with those activities? Do you already have time embedded into your schedule for collaboration? Where are you regarding: The collaborative use of assessment data to make instructional decisions? The use of research based instructional practices? The transition to the Core Academic Standards? FYI Professional learning opportunities will be provided. These may occur monthly and involve cohorts. The initiative is an amendable three year project. Some funding is associated with the project, primarily to provide time for collaboration. Month Activity Nov-Dec Collaborative team building •Roles and rules •Core academic standards •Decision Making for Results—classroom only •Introduction to Hattie’s work—effect size •How to access web-based supports Jan-Feb •2 effective teaching/learning practices •How to develop common formative assessments •How to administer/score formative assessments Feb-May (monthly process) •Teach •Assess •Analyze •Re-teach •Re-assess •Re-analyze •Submit CFA •Submit data March •Add two more effective teaching/learning practices to the toolbox of all teachers Questions? Piagetian Programs Piagetian Programs usually share some common features. First, students are engaged through activation of a schema. Basically, setting the stage for learning something new by invoking things they already know. Second, students do an experiment where they are allowed to “mess around” with a concrete phenomenon. Third, an extensive class or tutorial discussion or activity takes place where students attempt to make sense of what they’ve seen. This is the most critical stage, and must include scaffolding, guided questioning, modeling, shaping, concept mapping and so on. Finally, having developed a set of principles or a theory, students are made to apply the theory to a novel problem or situation. Some have formalized this learning cycle into four stages and an acronym: Activation (A; the set up), Concrete (C; the experiment), Invent (I; the discussion etc.), and Apply (A; the application to a novel problem); ACIA. Suggested Learning Strategies (1) Self Reporting Grades (3) Response to Intervention (4) Providing formative evaluations - Formative Assessment (7) Class Discussion (9)Teacher clarity (10)Feedback (11)Reciprocal Teaching (12) Teacher-Student Relationships (14)Meta-cognitive strategies (16) Classroom Behavioral (17) Vocabulary Programs (21)Self-verbalization and self-questioning (24)Problem-Solving Teaching (28) Cooperative v. Individualistic learning (29) Direct Instruction (53) Questioning (0.48) Rank these 12 effects Student-teacher relationships Teaching study skills Reading Recovery Feedback Homework Acceleration (speed up a year) Ability grouping Classroom size Open vs. traditional classes Cooperative learning Retention (hold back a year) Shifting schools Rank of these 12 effects 1 Acceleration (speed up a year) 2 Feedback 3 Student-teacher relationships 4 Teaching study skills 5 Reading Recovery 6 Cooperative learning 7 Homework 8 Classroom size 9 Ability grouping 10 Open vs. traditional classes 11 Retention (hold back a year) 12 Shifting schools Rank these 12 effects: Answers 1 Acceleration (speed up a year) .88 2 Feedback .73 3 Student-teacher relationships .72 4 Teaching study skills .59 5 Reading Recovery .50 6 Cooperative learning .41 7 Homework .29 8 Classroom size .21 9 Ability grouping .12 10 Open vs. traditional classes .01 11 Retention (hold back a year) -.16 12 Shifting schools -.34 Influences on Achievement