Publication Bias, Sensitivity analysis
advertisement
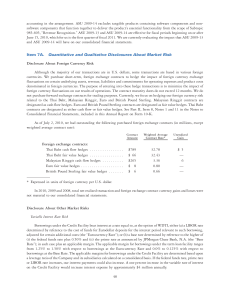
Publication/Availability Bias Problems with bad data Problem of missing studies • Missing at random is okay • Nonrandom is a problem • Sources of nonrandom samples of studies – Publication bias – significant, small N – Grad student work; other filedrawer – Deliberate misrepresentation for financial reasons Forest Plot Drift to the right by precision? Source: Borenstein, Hedges, Higgins & Rothstein, 2009, p. 282 Funnel plot Assymetry? Esp lower right. These appear biased and heterogeneous to me. Source: Sutton (2009). In Cooper, Hedges, & Valentine (Eds) Handbook fo Research Synthesis Methods p. 501 Fail-safe N • How many studies do we need to make the result n.s.? (Rosenthal) • How many studies do we need to make the summary effect small enough to ignore? (Orwin) kobt (d obt d c ) k fs d c d fs Corwin, R. G. (1983). A fail-safe N for effect size in meta-analysis. Journal of Educational Statistics, 8, 157-159. kfs = failsafe studies kobt = studies in meta dobt = summary ES dc = desired lower boutnd dfs= studies with this (eg 0) size needed to lower ES Trim & Fill Creates symmetry; Adjusts summary ES Source: Borenstein, Hedges, Higgins & Rothstein, 2009, p. 287 Cumulative Forest Source: Borenstein, Hedges, Higgins & Rothstein, 2009, p. 288 Egger’s Regression Ti = effect size; vi=sampling variance of ES zi Ti / vi zi 0 1 (1/ vi ) i Should be flat (centered) if no bias. This shows small studies have higher values. Source: Sutton (2009). In Cooper, Hedges, & Valentine (Eds) Handbook fo Research Synthesis Methods p. 441 Sensitivity Analysis Outliers. Run twice. Pray. Source: Greenhouse & Iyengar (2009). In Cooper, Hedges, & Valentine (Eds) Handbook fo Research Synthesis Methods p. 422 Sensitivity Analysis Varying levels of tau-squared Source: Louis & Zelterman (1994). In Cooper, Hedges (Eds) Handbook of Research Synthesis p. 418