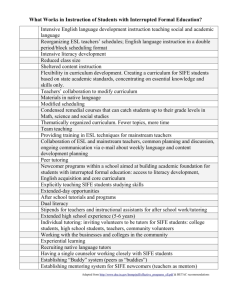
Bridging the Gap for SIFE - Bridges to Academic Success
advertisement

Investigating the Second Language Reader with Low Native Language Literacy Dr. Elaine C. Klein and Dr. Gita Martohardjono Research Institute for the Study of Language in Urban Society (RISLUS) The CUNY Graduate Center Email: slal@gc.cuny.edu AAAL, Washington, D.C, March 29, 2008 The Questions In young readers, native language (L1) preliteracy and word level reading skills transfer to the second language (L2). How does reading develop among older atrisk L2 learners (SIFE)? Higher level reading skills? Transfer of skills? 2 Who are SIFE? ‘SIFE’ (‘Newcomers’), a subgroup of ELLs: Recently arrived adolescent students Little or no English Assumed to have: - Low literacy and academic preparation - Gaps in prior schooling (+2 yrs) 3 Research on adolescent L2 readers Overlooked and underserved Very high drop-out rates Few appropriate assessment tools for identification and tracking Need for more systematic research (e.g. Velasco & Fix 2000; Short, Boyston & Coltrane 2003; Freeman, Freeman & Mercuri 2003; Morse 2005; August & Shanahan 2006; Short & Fitzsimmons 2007) 4 Some Facts about SIFE in NYC Schools* About 15,000 SIFE comprise 11% of ELLs Most enter 8th-10th grades 59% have Spanish native language Graduation rates far lower than other ELLs *Bilingual Education Student Information Survey (BESIS) 2006-2007: NYC DOE Office of English Language Learners, 2007. 5 SIFE Profile and Progress What academic skills do SIFE bring to school in the US? How do SIFE compare to their peer groups? What academic skills do SIFE gain over one year (T1 T2)? 6 The SIFE Project In Progress 18 month Longitudinal Study Participants: 98 students identified as SIFE 9th and 10th grade Native language: Spanish Schools: 5 inner-city high schools in NYC Various program types Native language support 7 Data Collection Measures of typical language development: Versant (Oral Spanish and English) Syntactic development (Spanish and English) Academic literacy diagnostics: Reading and content areas (Spanish and English) Benchmark assessments (State and citymandated tests) 8 Results: Typical L1 Development Versant: oral vocabulary, sentence mastery, fluency Overall Mean % Correct = 79, SD = 16 Syntactic comprehension: Overall Mean % Correct = 89, SD = 12 9 Academic Literacy Diagnostics Pre- and Basic Literacy Higher-Level Literacy - Vocabulary and Reading Comprehension Content Areas - Math - Science - Social Science 10 Results: Pre- and Basic Literacy Phonological & Orthographic Awareness Word Reading Simple Sentence Comprehension Mean % Correct = 96, SD = 4.5 11 Results: L1 Reading Vocabulary Vocabulary: Percentage of Students Scoring at Each Grade Level 21% 17% < Grade 3 Grade 3 9% 27% 8% 18% Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 12 Results: L1 Reading Comprehension Reading Comprehension: Percentage of Students Scoring at Each Grade Level 6% 5% < Grade 2 36% Grade 2 Grade 3 42% 11% Grade 4 Grade 5 13 Difference Between L1 Vocabulary and Reading Comprehension (at T1) Reading Vocabulary Comprehension Mean % Correct 66% 56% Mean Grade Level 5 3.7 (sig; t(97) = 5.5, p < .001) 14 Results: Academic Content Areas Math: Majority at/below grade 3 Science: Majority at/below grade 4 Social Science: Majority at/below grade 4 15 What skills do SIFE bring? Show typical language development: - Oral language, syntactic comprehension Have basic reading skills Show delay in: - Higher level reading skills: (4+ grade levels below expected grade) - Content Area Knowledge: (5+ grade levels below expected grade) 16 Comparison Groups Native English Speaker Groups: 9th and 10th Graders Community College West Indian English speakers Regular ELL Group: 9th-12th Graders Spanish-English Community College Group: Did not meet minimum English language requirements Currently taking ESL classes 17 Comparison Between Native English Speakers and SIFE Mean Grade Level Scores on Vocabulary and Reading Comprehension 10 9 8 Grade Level 7 6 5 Vocabulary 4 3 Reading Comprehension 2 1 0 High School Native English Speakers SIFE 18 Progress in One Year (N=23) Academic gains in L1 skills L2 English development 19 Academic Gains: L1 Vocabulary Percent Correct at each Grade Level Time 1 and Time 2 100% 90% 80% Percent Correct 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% N=23 Time 1 Time 2 10% 0% 3 4 5 6 Grade Level 7 9 20 Academic Gains: L1 Reading Comprehension Percent Correct at each Grade Level Time 1 and Time 2 100% 90% 80% Percent Correct 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% N=23 20% Time 1 10% Time 2 0% 2 3 4 5 Grade Level 6 7 9 21 Difference Between L1 Vocabulary and Reading Comprehension (at T2) Vocabulary Mean Grade Level 6.8 5 Reading Comprehension 5.4 3.7 t(22) = 2.9; p < .01 22 A Closer Look at Reading Comprehension Basic Understanding (24%): Recall factual information Identify relevance Text Level Skills (76%): Inferencing Interpretation Critical Analysis 23 L1 Grade 5 Text Level Skills Text Level Skills Mean % Correct Time 1 49% Mean % Correct Time 2 57% 24 L2 English Development After 1 year: Oral Language: Overall: Very limited speaking and listening skills Vocabulary: Basic; slow, simple speech Syntactic Comprehension: Mean percent correct = 58% Benchmark ESL Reading Test: Approximate Grade Level Score = 3rd to 4th Grade 25 Summary of SIFE Progress In one year: Significant gains in L1 reading skills Modest gains in L2 English skills Gap between L1 vocabulary and reading comprehension persists Lowest performance still on L1 text level reading skills 26 Transfer of Skills Native Language (T1) Vocabulary Reading Comprehension English L2 (T2) Vocabulary and Reading Comprehension approximate grade level = 4.7 = 3.6 = 3-4 Higher level reading skills transfer from L1 to L2. 27 Summary and Conclusions SIFE Do not have L1 developmental delays in oral language or word-level reading Lag in knowledge base in L1 Lag in higher-level reading Most severely in text level reading Transfer reading skills from L1 to L2 Accelerate development of these skills in L1. 28 THANK YOU! Acknowledgements NYC Department of Education Participating schools and SIFE liaisons Participating community colleges All participants and teachers RISLUS Research Team 30