Estimation of alternative splicing isoform frequencies from RNA
advertisement

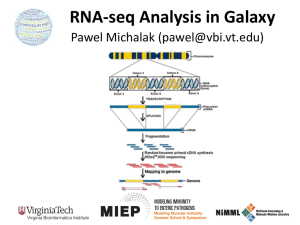
Estimation of alternative splicing isoform frequencies from RNA-Seq data Marius Nicolae Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Connecticut Joint work with Serghei Mangul, Ion Mandoiu and Alex Zelikovsky Outline • • • • Introduction EM Algorithm Experimental results Conclusions and future work Alternative Splicing [Griffith and Marra 07] RNA-Seq Make cDNA & shatter into fragments Sequence fragment ends Map reads A Gene Expression (GE) B C Isoform Expression (IE) D E Isoform Discovery (ID) A B A C D E C Gene Expression Challenges • Read ambiguity (multireads) A B C • What is the gene length? D E Previous approaches to GE • Ignore multireads • [Mortazavi et al. 08] – Fractionally allocate multireads based on unique read estimates • [Pasaniuc et al. 10] – EM algorithm for solving ambiguities • Gene length: sum of lengths of exons that appear in at least one isoform Underestimates expression levels for genes with 2 or more isoforms [Trapnell et al. 10] Read Ambiguity in IE A A B C C D E Previous approaches to IE • [Jiang&Wong 09] – Poisson model + importance sampling, single reads • [Richard et al. 10] — EM Algorithm based on Poisson model, single reads in exons • [Li et al. 10] – EM Algorithm, single reads • [Feng et al. 10] – Convex quadratic program, pairs used only for ID • [Trapnell et al. 10] – Extends Jiang’s model to paired reads – Fragment length distribution Our contribution • EM Algorithm for IE – Single and/or paired reads – Fragment length distribution – Strand information – Base quality scores – Hexamer bias correction – Annotated repeats correction Read-Isoform Compatibility wr ,i wr ,i OaQa Fa a Fragment length distribution • Paired reads Fa(i) i A B j A C C Fa (j) Fragment length distribution • Single reads i A B j A C C Fa(i) Fa (j) IsoEM algorithm E-step M-step Speed improvements • Collapse identical reads into read classes (i3,i5) (i3,i4) (i1,i2) Reads LCA(i3,i4) i1 i2 i3 i4 i5 i6 Isoforms Speed improvements • Collapse identical reads into read classes i2 i1 i4 i3 i5 i6 Isoforms • Run EM on connected components, in parallel Simulation setup 25000 100000 20000 10000 Number of genes Number of isoforms • Human genome UCSC known isoforms 15000 10000 5000 1000 100 0 10 1 10 100 1000 10000 100000 0 5 Isoform length 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 Number of isoforms • GNFAtlas2 gene expression levels – Uniform/geometric expression of gene isoforms • Normally distributed fragment lengths – Mean 250, std. dev. 25 Accuracy measures • Error Fraction (EFt) – Percentage of isoforms (or genes) with relative error larger than given threshold t • Median Percent Error (MPE) – Threshold t for which EF is 50% • r2 Error Fraction Curves - Isoforms • 30M single reads of length 25 100 % of isoforms over threshold 90 80 Uniq 70 Rescue 60 UniqLN 50 Cufflinks 40 30 RSEM 20 IsoEM 10 0 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 Relative error threshold 0.8 1 Error Fraction Curves - Genes • 30M single reads of length 25 100 % of genes over threshold 90 80 Uniq 70 Rescue 60 GeneEM 50 Cufflinks 40 RSEM 30 IsoEM 20 10 0 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 Relative error threshold 0.8 1 MPE and EF15 by Gene Frequency • 30M single reads of length 25 Read Length Effect • Fixed sequencing throughput (750Mb) 0.978 25 0.976 20 Median Percent Error 0.974 r2 0.972 0.97 0.968 0.966 Paired reads 0.964 Single reads 15 10 5 Paired reads Single reads 0.962 0 25 35 45 55 65 Read length 75 85 95 25 35 45 55 65 Read length 75 85 95 Effect of Pairs & Strand Information • 1-60M 75bp reads 0.985 0.98 0.975 r2 0.97 0.965 RandomStrand-Pairs 0.96 CodingStrand-pairs 0.955 RandomStrand-Single CodingStrand-single 0.95 0.945 0 10,000,000 20,000,000 30,000,000 # reads 40,000,000 50,000,000 60,000,000 Validation on Human RNA-Seq Data • ≈8 million 27bp reads from two cell lines [Sultan et al. 10] • 47 genes measured by qPCR [Richard et al. 10] IsoEM 3 3 2.5 2.5 Log(IsoEM) Log(Cufflinks) Cufflinks 2 2 1.5 1.5 R² = 0.5505 R² = 0.4604 1 1 1 1.5 2 2.5 Log(qPCR) 3 3.5 4 1 1.5 2 2.5 Log(qPCR) 3 3.5 4 Runtime scalability • Scalability experiments conducted on a Dell PowerEdge R900 – Four 6-core E7450Xeon processors at 2.4Ghz, 128Gb of internal memory 160 140 RandomStrand-Pairs 120 CodingStrand-Pairs CPU Seconds RandomStrand-Single 100 CodingStrand-Single 80 60 40 20 0 0 Million Fragments 10 20 30 Conclusions & Future Work • Presented EM algorithm for estimating isoform/gene expression levels – Integrates fragment length distribution, base qualities, pair and strand info – Java implementation available at http://dna.engr.uconn.edu/software/IsoEM/ • Ongoing work – Comparison of RNA-Seq with DGE – Isoform discovery – Reconstruction & frequency estimation for virus quasispecies Acknowledgments NSF awards 0546457 & 0916948 to IM and 0916401 to AZ