Employability skills - Student Experience & Academic Standards
advertisement

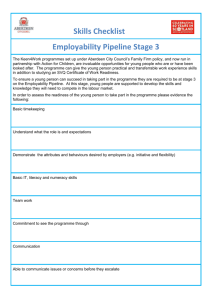
Employability Skills: some modules do have them! PCUTL Group Project Diane Harris (PGMDE) Sherran Milton (SOHCS) Fiona Morgan (INSRV) Lisa Wallace (MEDIC) The Project Team • Diane Harris – Dental Nurse Tutor. Registered and practiced as a dental nurse for over 25 years • Sherran Milton – Operating Department Practitioner. Worked as Senior Clinical Staff & Education Officer in national post • Fiona Morgan – Worked in industry for >20 years with a number of multinational companies • Lisa Wallace – 18 years of medical research experience at two major U.S. Universities Employability “A set of attributes, skills and knowledge that all labour market participants should possess to ensure they have the capability of being effective in the workplace – to the benefit of themselves, their employer and the wider economy” EMPLOYERS: CBI Education and skills survey 2011 70% of employers want to see: • Development of employability skills made a top priority – embedding skills in the curriculum. • University students doing more to prepare themselves to be effective in the workplace. WELSH GOVERNMENT: Higher Education Strategy Employability is a key outcome of the HE experience STUDENTS: Investing for careers Current students (11/12) Fees: £3,400 Student loan: £5,000 3 year debt >£25,000 New students (12/13) Fees: £3,500 (Wales) £9,000 (England) Student loan £5,500 3 year debt: >£27,000 (Wales) >£43,500 (England) CU Graduate Employability and Enterprise Skills Strategy • Employability and Enterprise-related skills provision articulated across all curricula and communicated to students; • New academic programmes designed and existing programmes revised with an employability and/or enterprise dimension incorporated. Teaching staff • Key in communicating strategy – Building skills development into modules and courses • Need clarity: – Unclear on what these skills are – Range of different terms and lack of consistency in University documentation EMPLOYABILITY SKILLS DESCRIPTORS FORMS OF ASSESSMENT (Examples) Preparing a CV Final year projects Self assessment Action plans/setting objectives Portfolio development Personal development plans Negotiate team ground rules Project manage group work Peer review Allocate roles/responsibilities Motivate and support team Evaluation Appraisal docs Job applications Course assignments Clinical logs Testimonies Learning contracts profiles Self Management Time management Flexibility Resilience Self-starting Appropriate assertiveness Team working Respecting others Cooperating Negotiating/persuading Contributing to discussions Awareness of interdependence with others Business and customer awareness Basic understanding of the key drivers for business success including: › the importance of innovation and taking calculated risks › the need to provide customer satisfaction and build customer loyalty • Awareness of professional codes and practice guidelines Case studies and scenarios Quality and risk assessment/ management Audit/survey of practice or satisfaction Analysing facts and solutions Applying creative thinking to develop appropriate solutions Case studies Ethics committees Role play and scenarios Games and puzzles Models Final year projects Guidance materials Clinical audit tools/guidelines Questionnaires Application of literacy Ability to produce clear, structured written work Oral literacy – including listening and questioning Demonstrate telephone skills Present and debate issues Give and accept feedback Gather Information Critically assess material Listening/body language Persuading and negotiating Note taking Critical literature review • Discussion Manipulation of numbers General mathematical awareness and its application in practical contexts (eg measuring, weighing, estimating and applying formulae) Understand concept of a number Handle fractions and decimals Calculate rates and percentages Work with ratios and proportions Interpret data Numerical problem solving Understand basic finance Use spreadsheet software Drug calculation software (safe medicate, authentic world) • Use of Excel/SPSS • Practice tests Basic IT skills including familiarity with word processing, spreadsheets, file management and the use of internet search engines, Complete ECDL or equivalent Present information in a variety of IT formats Systematic searching Problem solving Communication and literacy Application of numeracy Application of information technology Readiness to accept responsibility Readiness to improve own performance based on feedback/reflective learning SKILLS (Examples) Protocol development Induction material for new students Practical observation Audits Peer review Attitude scales Develop : › information leaflets › Procedural documents › Policy position statements › Research proposals/funding applications/ethical approvals Contribute to professional bodies or specialist groups • • • • Poster presentation Oral presentation Debate Present to camera Developing presentations Producing assignments in word and submission via turn it in Negotiating on line library tools i.e. literature search Using Learning Central appropriately Using e learning materials Employability skills: a set of attributes, skills and knowledge… • • • • • • • Self-management Team working Business and customer awareness Problem solving Communication and literacy Application of numeracy Application of information technology All underpinned by a positive attitude Stage 1 Employability skills Stage 2 Descriptors GRADUATE EMPLOYABILITY AND ENTERPRISE SKILLS STRATEGY 2010 - 2015 EMPLOYABILITY SKILLS DESCRIPTORS SKILLS (Examples) Self Management Time management Flexibility Resilience Self-starting Appropriate assertiveness Team working Respecting others Cooperating Negotiating/persuading Contributing to discussions Awareness of interdependence with others Business and customer awareness Basic understanding of the key drivers for business success including: › the importance of innovation and taking calculated risks › the need to provide customer satisfaction and build customer loyalty Problem solving Analysing facts and solutions Applying creative thinking to develop appropriate solutions Communication and literacy Application of literacy Ability to produce clear, structured written work Oral literacy – including listening and questioning Application of numeracy Manipulation of numbers General mathematical awareness and its application in practical contexts (eg measuring, weighing, estimating and applying formulae) Application of information technology Readiness to accept responsibility Readiness to improve own performance based on feedback/reflective learning Basic IT skills including familiarity with word processing, spreadsheets, file management and the use of internet search engines, FORMS OF ASSESSMENT (Examples) Questions to the group • Was your partner from a similar discipline? • If not, were you able to reach a consensus in your response? • Is it already in your module/course? So what’s in it for you? EMPLOYABILITY SKILLS DESCRIPTORS FORMS OF ASSESSMENT (Examples) Preparing a CV Final year projects Self assessment Action plans/setting objectives Portfolio development Personal development plans Negotiate team ground rules Project manage group work Peer review Allocate roles/responsibilities Motivate and support team Evaluation Appraisal docs Job applications Course assignments Clinical logs Testimonies Learning contracts profiles Self Management Time management Flexibility Resilience Self-starting Appropriate assertiveness Team working Respecting others Cooperating Negotiating/persuading Contributing to discussions Awareness of interdependence with others Business and customer awareness Basic understanding of the key drivers for business success including: › the importance of innovation and taking calculated risks › the need to provide customer satisfaction and build customer loyalty • Awareness of professional codes and practice guidelines Case studies and scenarios Quality and risk assessment/ management Audit/survey of practice or satisfaction Analysing facts and solutions Applying creative thinking to develop appropriate solutions Case studies Ethics committees Role play and scenarios Games and puzzles Models Final year projects Guidance materials Clinical audit tools/guidelines Questionnaires Communication and literacy Application of literacy Ability to produce clear, structured written work Oral literacy – including listening and questioning Demonstrate telephone skills Present and debate issues Give and accept feedback Gather Information Critically assess material Listening/body language Persuading and negotiating Note taking Critical literature review • Discussion Application of numeracy Manipulation of numbers General mathematical awareness and its application in practical contexts (eg measuring, weighing, estimating and applying formulae) Handle fractions and decimals Calculate rates and percentages Work with ratios and proportions Interpret data Numerical problem solving Understand basic finance Use spreadsheet software Drug calculation software (safe medicate, authentic world) • Use of Excel/SPSS • Practice tests Basic IT skills including familiarity with word processing, spreadsheets, file management and the use of internet search engines, Complete ECDL or equivalent Present information in a variety of IT formats Systematic searching Problem solving Application of information technology Readiness to accept responsibility Readiness to improve own performance based on feedback/reflective learning SKILLS (Examples) Protocol development Induction material for new students Practical observation Audits Peer review Attitude scales Develop : › information leaflets › Procedural documents › Policy position statements › Research proposals/funding applications/ethical approvals Contribute to professional bodies or specialist groups • • • • Poster presentation Oral presentation Debate Present to camera Developing presentations Producing assignments in word and submission via turn it in Negotiating on line library tools i.e. literature search Using Learning Central appropriately Using e learning materials Conclusion Defined and clarified employability skills. Made clear their importance to: • Students • Employers • Cardiff University. Produced a practical output: • A simple tool to help staff who are developing and revising modules. Work on the grid will continue as a Module 2 project.