RAD 354 Chapt. 27 Digital Fluoro
advertisement
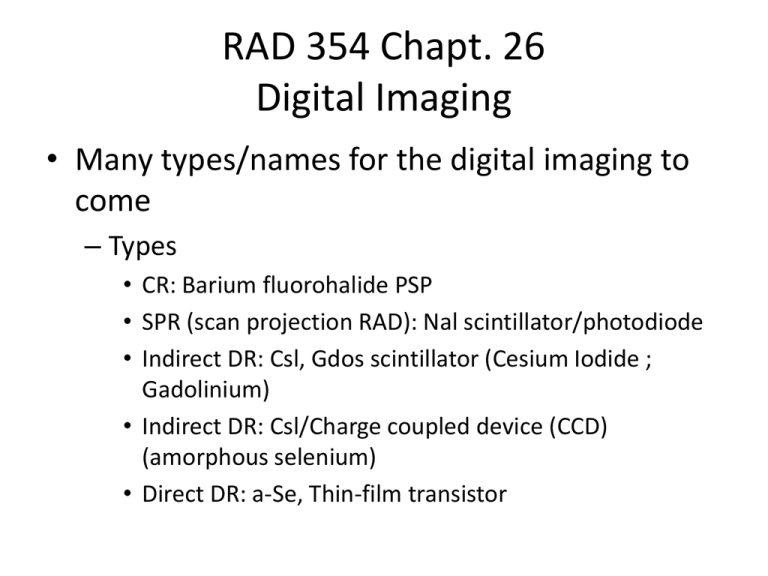
RAD 354 Chapt. 26 Digital Imaging • Many types/names for the digital imaging to come – Types • CR: Barium fluorohalide PSP • SPR (scan projection RAD): Nal scintillator/photodiode • Indirect DR: Csl, Gdos scintillator (Cesium Iodide ; Gadolinium) • Indirect DR: Csl/Charge coupled device (CCD) (amorphous selenium) • Direct DR: a-Se, Thin-film transistor ES’s “Clever approach” (capture element, coupling element, collection element • “Capture element” how the x-rays are captured (PSP’s, Csl,. Gado, etc.) • “Coupling element” transferring the x-ray “signal” to the collection element • “Collection element” devices to either collect light photons or electrons Scan Projection Radiography • As in CT, uses a “fan beam” (collimated by prept collimators), Post pt., remnant beam is collimated to form a “fan” for the detector array – Neither the tube OR detector move! • SPR is NOT too successful, but is hanging around Charge Coupled Devices • CCD’s are SMALL, thus GREAT for digital imaging – Have HIGHJ sensitivity to radiation and WIDE dynamic range (dim to bright light) – STRAIGHT H & D “CURVE” Types of CCD’s • Cesium Iodide/CCD • Cesium Iodide/Amorphus Silicon • Amorphous Selenium RAD 354 Chapt. 27 Digital Fluoro • Terms to remember – DSA – digital subtraction angiography – Registration – Interrogation time – Hybrid subtraction – CCD = charge coupled device – ROI = region of interest – PACS = picture archival and communication system Advantages of DF • Speed of image acquisition • Post processing “tweaking” of the image(s) – Spatial resolution is determined by the matrix size (usually 1024 X 1024) and the size of the image intensifier) • DF operates at “conventional mAs” (hundreds of mA rather than less than 5 mA as conventional fluoro) • BUT – DF operates in “pulsed, progressive” fluoro! “Pulsing” Terms • Interrogation time = time for unit to be switched on and reach the mA and kVp level • Extinction time = time for the tube to be switched off (usually times less than 1 ms) Receptor • The “receptor” is usually a “charge coupled device” (CCD) – CCD’s are VERY sensitive to light and have a much LOWER level of noise than a TV camera • This results in much HIGHER SNR than conventional TV cameras/systems • They also have NO lag time or “blooming” and require NO maintenance • CCD’s may be “docked” directly to the II’s output phosphor Advantages of CCD’s • • • • • • • • High spatial resolution High SNR High Detective Quantum Efficiency (DQE) No warm up required No lag/blooming No spatial distortion/maintenance Unlimited life Unaffected by magnetic fields Lower pt. dose CCD DR Subtraction TWO Primary Types • Temporal subtraction – Single kVp setting – Normal filtration – Good contrast resolution (1% @ 1 mm) – Simple arithmetic image subtraction used – Motion artifacts are a problem (misrepresentation) – Total subtraction is able to be achieved – Subtraction limited by number of images Energy Subtraction • • • • • • • • Rapid voltage switching is used Filter switching is preferred Higher x-ray energy used for + contrast resol. Complex image subtraction is required Motion artifacts (misrepresentation) are reduced Some residual bone is survived (shows) More types of subtraction are possible IF BOTH ARE COMBINED = HYBRID SUBTRACTION DF/D Subtraction RAD Dose • DF & D Subtraction usually result in much higher pt. dose and PULSED imaging is required to lower the dose! • Storage and image distribution are used as already discussed in class Images Lateral Cerebral DSA DSA Hand Latest in hybrid digital fluoro (Sunrise Hospital – 3.9 million $$$ Con’t Con’t