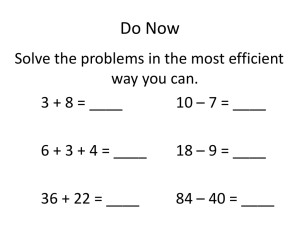exploring_eas - Newcastle Early Career Teachers
advertisement

NSW Curriculum and Learning Innovation Centre Exploring Early Arithmetical Strategies (EAS) Building capacity with the new syllabuses Early Arithmetical Strategies (EAS) Early Arithmetical Strategies (EAS) refers to the range of counting strategies that are used to solve addition and subtraction problems. Arithmetical learning develops through two complementary processes, counting and grouping. The transition from count-by-one strategies to grouping strategies underpins the structure of the Early Arithmetical Strategies (EAS) framework. NSW Curriculum and Learning Innovation Centre The Early Arithmetical Strategies (EAS) Stages EAS Stages describing count-byone strategies Emergent Perceptual EAS Stage describing grouping strategies Facile (Flexible) Figurative Countingon-andback NSW Curriculum and Learning Innovation Centre Emergent counting Stage description The student cannot count visible items. The student either does not know the number words or cannot correctly coordinate number words with items when counting. Videos These videos show students attempting a counting task. Click on an image to view the video Syllabus outcomes Key ideas in the syllabus Working towards: MAe-4NA Counts to 30, and orders, reads and represents numbers in the range 0 to 20 Working towards: Count forwards to 30 and backwards from a number in the range 0 to 20 Working towards: MAe-5NA Combines, separates and compares collections of objects, describes using everyday language, and records using informal methods Compare, order, read and represent numbers to 10, then 20 Combine two groups of objects to model addition Take part of a group away to model subtraction Sample related content Connect number names, numerals and quantities to 10 Recognise numbers in a variety of contexts Compare order and make collections to 10 then to 20 Recognise dice and domino patterns NSW Curriculum and Learning Innovation Centre Perceptual counting Stage description The student is able to count visible items. The student builds numbers by using materials or fingers to represent each number when solving addition and subtraction questions. The materials must always be present during the counting. Videos Syllabus outcomes These videos show students using a perceptual counting strategy. MAe-5NA Combines, separates and compares collections of objects, describes using everyday language, and records using informal methods Click on an image to view the video Key ideas in the syllabus Combine two or more groups to model addition Take part of a group away to model subtraction Compare two groups to determine ‘how many more’ Record addition and subtraction informally Sample related content Use concrete materials or fingers to model and solve simple addition and subtraction problems Use visual representations of numbers, e.g. ten frames, to solve addition and subtraction problems Create and recognise combinations of numbers to at least 10 NSW Curriculum and Learning Innovation Centre Figurative counting Stage description Videos The student is able to count concealed items by visualising the items but always starts counting from “one”. These videos show students mentally solving an addition question using a figurative counting strategy. The student may sub-vocalise when counting. Click on an image to view the video Syllabus outcomes Key ideas in the syllabus MA1-5NA Uses a range of strategies and informal recording methods for addition and subtraction involving oneand two-digit numbers Use and record a range of mental strategies for addition and subtraction of one- and twodigit numbers Solve word problems involving addition and subtraction Sample related content Create, record and recognise combinations for numbers from 11 up to and including 20 Model and record number patterns for individual numbers Use the terms add, plus, equals, is equal to, take away, minus and the difference between NSW Curriculum and Learning Innovation Centre Counting-on-and-back Stage description The student counts-on or counts-back from one of the numbers rather than counting from “one” to solve addition and subtraction problems . The student understands that one of the numbers takes the place of a completed count. Videos This video shows a student counting on to solve addition questions. Click on the image to view the video Syllabus outcomes MA1-5NA Uses a range of strategies and informal recording methods for addition and subtraction involving oneand two-digit numbers Key ideas in the syllabus Use and record a range of mental strategies for addition and subtraction of one- and twodigit numbers Solve word problems involving addition and subtraction Make connections between addition and subtraction Sample related content Use a range of mental strategies to solve addition and subtraction problems involving oneand two-digit numbers including: - counting-on from the larger number to find the total of two numbers - counting-back from a number to find the number remaining - counting-on or counting-back to find the difference between two numbers. NSW Curriculum and Learning Innovation Centre Facile (flexible) number knowledge Stage description Videos Syllabus outcomes Key ideas in the syllabus Sample related content The student uses known facts, number structure and other grouping strategies to solve addition and subtraction problems. This video shows a student using a facile counting strategy. MA1-5NA Uses a range of strategies and informal recording methods for addition and subtraction involving one- and two-digit numbers Recognise and recall number combinations that add to numbers up to 20. Model and apply the commutative property and associative property for addition. Use the inverse operation to check addition and subtraction calculations. Use and record a range of mental strategies for addition and subtraction of one-, two-, three- and fourdigit numbers. Use a range of mental strategies to solve addition and subtraction problems including: - using doubles or near doubles - combining numbers that add to 10 - bridging to 10 - partitioning numbers to at least 20. Click on the image to view the video MA2-5NA Uses mental and written strategies for addition and subtraction involving two-, three- and fourdigit numbers NSW Curriculum and Learning Innovation Centre Where to next? Consider Look Plan Consider assessing each student to determine where he or she is on the Early Arithmetical Strategies aspect. Look at the associated syllabus outcomes as indicated on the numeracy continuum. The syllabus content associated with each outcome will help you to plan a teaching program aimed at progressing each student to the next level along the continuum. NSW Curriculum and Learning Innovation Centre