Byzantines, Islam & Crusades (posted 11/8/10)
advertisement

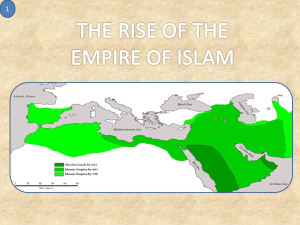
Byzantines, Islam & Crusades I. Byzantines A. Justinian (527-565) II. Islam A. Arab World B. Muhammad (570?-632) C. Religion of Islam D. Expansion III. Two Popes IV. Crusades A. Why? B. What? • • • • • • • Key Terms Code of Justinian Koran Five Pillars of Islam Jerusalem Pope Gregory VII Pope Urban II Indulgences Justinian 1. He reunified most of the old Roman empire 2. Christianity was the official religion; nonChristian worship was outlawed 3. Established Code of Justinian Code Of Justinian Justinian (r. 527-565) 1. Established a single code of laws for all 2. Its influence today: a) Laws should be written b) Punishments for a crime should be the same for all Byzantine Empire & Justinian Code Of Justinian Justinian (r. 527-565) 1. Established a single code of laws for all 2. Its influence today: a) Laws should be written b) Punishments for a crime should be the same for all Code of Justinian = JUSTICE US Supreme Court Building (Stone Sculpture of 18 “Lawgivers) Muhammad Justinian Arabian/Islamic Impact… • Irrigation - increased agricultural production • Mathematics: – Numbering System: Arabic Numerals replaced cumbersome Roman Numerals – “Algebra” comes from Arabic word “Al-jabar” included in a math book from 820 AD Arab World • Arabs flourished in the desert. • Many were nomads & herded sheep and camels; other specialized in trade. • Outsiders tried to conquer Arabs, but were unable. • Mecca was an important city. Muhammad (570?-632) 1. Born about 570 AD and grew up in Mecca. 2. After marriage, he became a social activist. 3. Received revelations from the angel Gabriel eventually included in the Koran. 4. In 622 he moved from Mecca to Medina and became VERY influential, spreading the word of Islam. Five Pillars Of Islam 1. Creed/Faith: The belief there is only one God (Allah); Muhammad is the prophet of Allah. 2. Prayer: Five times per day believers must wash and purify themselves, face Mecca, and pray. 3. Almsgiving: All should contribute money to the poor/needy. 4. Fast: between daylight until nightfall during the month of Ramadan. 5. Pilgrimage: to Mecca during one’s lifetime. Islam, Judaism, Christianity 1. All worship the same God (the God of Abraham) 2. Much of the Old Testament, including prophets Abraham & Moses, are accepted (Muslims & Jews don’t accept Jesus as the Savior) 3. The belief in charity to the poor/weak 4. Jerusalem is an important city: a) Jews: land of Abraham; promised by God b) Christians: land of Jesus’ ministry c) Muslims: where Muhammad ascended to heaven Dome Of The Rock & Western Wall (Jerusalem) Solomon’s Temple, Jerusalem Following Muhammad’s Death • Islamic world grew and covered more territory than the old Roman Empire at its height. Muslim Conquest Up to 750 Crusades • A series of wars fought between Christians and Muslims. • Access to and control of Jerusalem was one key cause. Two Popes • The Christian Church (Roman Catholic) became a powerful unifying institution by 800-900 AD • It was headed by the Pope • Pope Gregory VII (1073-1085): – What was Papal Primacy? • Pope Urban’s call (1095): – If they decide to fight, what will they receive? Crusades (1100-1200) • 1st Crusade: 1097-1099 – Christians regain control of Jerusalem. • 2nd Crusade: 1147-1149 – Muslims recapture Jerusalem. • 3rd Crusade: 1189-1192 – Draw: Muslims retain control of Jerusalem but allow access to the city. Indulgences • Money paid to the Church to help the war effort. • Why pay? – If a person gave the Church money, sins were forgiven and a place in heaven was secured. Byzantines, Islam & Crusades I. Byzantines A. Justinian (527-565) II. Islam A. Arab World B. Muhammad (570?-632) C. Religion of Islam D. Expansion III. Two Popes IV. Crusades A. Why? B. What? • • • • • • • Key Terms Code of Justinian Koran Five Pillars of Islam Jerusalem Pope Gregory VII Pope Urban II Indulgences