SMARTER UK – RESOURCES FOR SCHOOLS
Please feel free to use this PowerPoint presentation in the classroom. It is intended to support the KS3 & KS4 curriculum and the
Scottish S3-S4 curriculum.
KEY LEARNING:
The different effects of drugs, from stimulants through to depressants, and how they act upon the central nervous system.
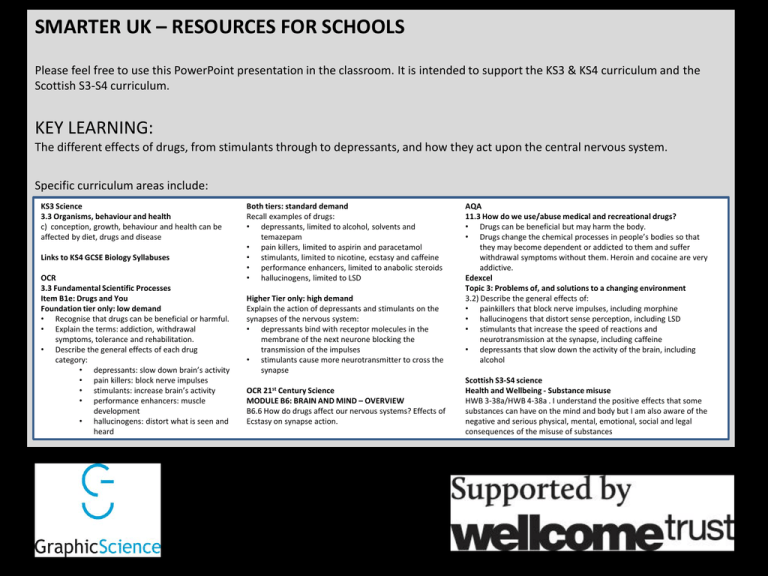
Specific curriculum areas include:
KS3 Science
3.3 Organisms, behaviour and health
c) conception, growth, behaviour and health can be
affected by diet, drugs and disease
Links to KS4 GCSE Biology Syllabuses
OCR
3.3 Fundamental Scientific Processes
Item B1e: Drugs and You
Foundation tier only: low demand
• Recognise that drugs can be beneficial or harmful.
• Explain the terms: addiction, withdrawal
symptoms, tolerance and rehabilitation.
• Describe the general effects of each drug
category:
• depressants: slow down brain’s activity
• pain killers: block nerve impulses
• stimulants: increase brain’s activity
• performance enhancers: muscle
development
• hallucinogens: distort what is seen and
heard
Both tiers: standard demand
Recall examples of drugs:
• depressants, limited to alcohol, solvents and
temazepam
• pain killers, limited to aspirin and paracetamol
• stimulants, limited to nicotine, ecstasy and caffeine
• performance enhancers, limited to anabolic steroids
• hallucinogens, limited to LSD
Higher Tier only: high demand
Explain the action of depressants and stimulants on the
synapses of the nervous system:
• depressants bind with receptor molecules in the
membrane of the next neurone blocking the
transmission of the impulses
• stimulants cause more neurotransmitter to cross the
synapse
OCR 21st Century Science
MODULE B6: BRAIN AND MIND – OVERVIEW
B6.6 How do drugs affect our nervous systems? Effects of
Ecstasy on synapse action.
AQA
11.3 How do we use/abuse medical and recreational drugs?
• Drugs can be beneficial but may harm the body.
• Drugs change the chemical processes in people’s bodies so that
they may become dependent or addicted to them and suffer
withdrawal symptoms without them. Heroin and cocaine are very
addictive.
Edexcel
Topic 3: Problems of, and solutions to a changing environment
3.2) Describe the general effects of:
• painkillers that block nerve impulses, including morphine
• hallucinogens that distort sense perception, including LSD
• stimulants that increase the speed of reactions and
neurotransmission at the synapse, including caffeine
• depressants that slow down the activity of the brain, including
alcohol
Scottish S3-S4 science
Health and Wellbeing - Substance misuse
HWB 3-38a/HWB 4-38a . I understand the positive effects that some
substances can have on the mind and body but I am also aware of the
negative and serious physical, mental, emotional, social and legal
consequences of the misuse of substances
Drugs and the human body
How do drugs affect the brain?
in the brain most
drugs work by altering activity at the synapse
synapse
dendrites
nerve endings
vesicle
myelin sheath
synaptic cleft
nucleus
cell body
receptor
neurotransmitter
the signal
is transmitted to
another neurone across a
junction called a synapse by
axon
chemicals called
neurotransmitters.
Smarter UK
different
drugs do different things to the brain
Some drugs affect the whole brain
(e.g. alcohol)
Others mainly affect specific
areas (e.g. cocaine)
Some drugs mimic the effects of
neurotransmitters (e.g. heroin)
Credit: Wellcome Library, London
Smarter UK
Many drugs change the rate that
neurotransmitters are released into and
removed from the synaptic cleft (e.g. ecstasy)
different
drugs give a different experience to the drug-user
Some drugs, such as alcohol and
solvents, slow down the brain’s
activity by making the synapse
less active. These are known as…
Some drugs, such as
morphine, block nerve
impulses that cause pain.
These are known as…
pain killers
depressants
And some, such as nicotine,
ecstasy and caffeine, make
the synapse more active.
These are known as…
Credit: Wellcome Library, London
stimulants
Some drugs, such as LSD distort
what the user sees and hears,
by effecting the receptors for a
particular type of
neurotransmitter: serotonin.
These are known as…
hallucinogens
drugs cause addiction because they over-activate
the parts of the brain responsible for feeling pleasure
addictive drugs cause an increase in levels of a
neurotransmitter called dopamine
this makes you feel good
feeling good makes you want to keep on feeling good
your brain tries to get things back to normal by becoming less sensitive to
dopamine. (You become
tolerant to the drug)
you need more and more of the drug to make you feel good
you need some of the drug just to feel
normal
without the drug, there isn’t enough dopamine in your brain
and you feel terrible. This is called
withdrawal
messing with the delicate balance of your
brain can have very serious consequences!
Smarter UK












