Explicit Instruction
advertisement

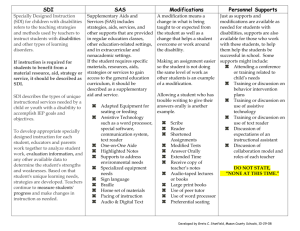
WHAT’S SPECIAL ABOUT SPECIAL EDUCATION Janel Payette Coordinator RSE TASC OUR LEARNING TARGETS TODAY: • • • • Identify the difference between Universal Design for Learning (UDL), Differentiated Instruction (DI), and Specially Designed Instruction (SDI) Identify elements of SDI that increase access to instructional content and materials Identify the elements of EI for students with disabilities that increase academic success Make connections to effective teacher practice The Common Core is the DESTINATION, not the journey. Stated another way: It’s the WHAT, not the HOW. Specially Designed Instruction Explicit Instruction Scaffolding Differentiated Instruction Universal Design for Learning CHECK FOR UNDERSTANDING UDL, DI, SDI, SCAFFOLDING • • • • Several students have parts of their pre-writing graphic organizer completed for them as an extended model. Sam has a voice to text program that he learns to edit after dictation. Students use one of three topics of varying difficulty as a basis for their writing. Every student may use the word processor and is responsible for editing. SPECIALLY DESIGNED INSTRUCTION 200.6(A)(1) Students with disabilities shall be provided special education in the least restrictive environment, as defined in section 200.1(cc) of this Part. To enable students with disabilities to be educated with nondisabled students to the maximum extent appropriate, specially designed instruction and supplementary services may be provided in the regular class, including, as appropriate, providing related services, resource room programs and special class programs within the general education classroom. SPECIALLY DESIGNED INSTRUCTION PART 200.1(VV) Adapting, as appropriate to the needs of an eligible student, the content, methodology, or delivery of instruction to address the unique needs that result from the student’s disability; and to ensure access of the student to the general curriculum, so that he or she can meet the education standards that apply to all students. OPERATIONALIZED DEFINITIONS • • • • Adapting: making changes matched to student need or condition Content: knowledge and skills that comprise curriculum to be mastered Methodology: actions by the teacher intended to produce or facilitate learning which includes the art and science of instruction Delivery of Instruction: teaching that results in access to, participation in, and progress in the curriculum for students with disabilities Developed Valerie Cole Southern Tier RSE TASC 2013 Assistive Technology Adaptive Equipment Accommodations Strategy Instruction Explicit Instruction Scaffolding Specially Designed Instruction Differentiated Instruction Universal Design for Learning Modifications WE PROVIDE SPECIALLY DESIGNED INSTRUCTION THROUGH EXPLICIT INSTRUCTION Explicit Instruction is: Structured, systematic Effective researched-based methodology for teaching classroom routines, behavior expectations, academic content and skills and cognitive learning strategies. In particular, for students with disabilities and novice learners Includes instructional design and delivery procedures (I do, we do, you do) Characterized by a series of scaffolds, explanations, demonstrations, and supported practice with embedded feedback. ELEMENTS OF EXPLICIT INSTRUCTION ARCHER & HUGHES (2011) EXPLICIT INSTRUCTION: EFFECTIVE & EFFICIENT TEACHING 1. Focus instruction on critical content 2. Sequence skills logically 3. Break down complex skills & strategies into smaller units 4. Design organized & focused lessons 5. Begin lessons with a clear statement of the lesson’s goals & your expectations 6. Review prior skills & knowledge before beginning the lesson 7. Provide step-by-step demonstrations 8. Use clear & concise language Green Handout EXPLICIT INSTRUCTION (CONT’D) 9. Provide an adequate range of examples and non-examples 10. Provide guided and supported feedback 11. Require frequent response 12. Monitor student performance closely 13. Provide immediate affirmative & corrective feedback 14. Deliver the lesson at a brisk pace 15. Help students organize knowledge 16. Provide distributed & cumulative practice INSTRUCTIONAL SCENARIOS • • • • • Turn to an elbow partner “I” time to read the scenarios Utilize the 16 elements of explicit instruction hand out to see how many elements you can identify Utilize the five provisions of SDI handout, identify to identify instances that the teacher provided SDI Group share White Handout Scenario #2 INDICATORS THAT A LESSON IS PURPOSEFULLY DESIGNED AND THAT INSTRUCTION IS DELIVERED TO MEET THE NEEDS OF STUDENTS WITH DISABILITIES RSE TASC Walkthrough Tool Supportive Accessible Classroom Environment Explicit Instruction Management Positive Classroom Climate Physical Organization Explicit Instruction Teaching Functions Explicit Instruction Elements Specially Designed Instruction Specially Designed Instruction: Direct Instruction of Targeted Skills, Accommodations, Re-Teaching Yellow Handout CONTINUUM OF SERVICES • • Provision of SDI through EI in all settings Hallmarks PARAPROFESSIONALSWHAT IS THE ROLE OF THE PARAPROFESSIONAL? Purple Handout REVIEW LEARNING TARGETS • • • • Identify the difference between Explicit Instruction (EI), Universal Design for Learning (UDL), Differentiated Instruction (DI), and Specially Designed Instruction (SDI) Identify elements of SDI that increase access to instructional content and materials Identify the elements of EI for students with disabilities that increase academic success Make connections to effective teacher practice TICKET OUT THE DOOR Please write on index cards • 1 Aha • 1 thought you are mulling over • 1 question you still have