Mr. Short and Mr. Tall
advertisement

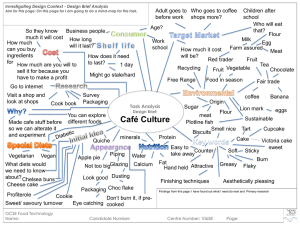
00 11 0 010 1 01 0 110 1 00 01 01 00 1 011 1 2 Relative and Absolute Thinking 4 The Chocolatey Cake Debate I love chocolate, so I’m going to get a slice of the 6-layer cake! 00 11 0 010 1 01 0 110 1 00 01 01 00 1 011 I want the one that has more chocolate flavor, so I’m getting the 3-layer cake! 1 2 4 If you wanted to buy a slice of the cake that had the most chocolate flavor, which slice of cake would you buy? Chocolatey Cake? 00 11 0 010 1 01 0 110 1 00 01 01 00 1 011 • Work on your own to decide which cake is more chocolatey • Put your paper aside when you are done so that we know that you have finished • Then work with your group members to decide on an answer • Are you tempted to change your answer that you wrote down? 1 2 4 Mr. Short and Mr. Tall 00 11 0 010 1 01 0 110 1 00 01 01 00 1 011 1 2 When Mr. Short is measured in paper clips, he is 6 paper clips tall. When he is measured in buttons, he is 4 buttons tall. 4 Mr. Short has a friend named Mr. Tall. When Mr. Tall is measured in buttons, he is 6 buttons tall. How many paper clips tall is Mr. Tall? How many paper clips? 00 11 0 010 1 01 0 110 1 00 01 01 00 1 011 • Work on your own to decide the height of Mr. Tall in paper clips • Put your paper aside when you are done so that we know that you have finished • Then work with your group members to decide on an answer • Are you tempted to change your answer that you wrote down? 1 2 4 Student Work 00 11 0 010 1 01 0 110 1 00 01 01 00 1 011 1 2 4 Proportional Reasoning 00 11 0 010 1 01 0 110 1 00 01 01 00 1 011 • Proportional Thinkers understand that (Van de Walle): – There is a clear difference between proportional relationships and nonproportional relationships, especially in the real world – There are a variety of strategies for solving proportions or comparing ratios (that are not prescribed algorithms) – There are relationships where 2 quantities vary together (covariation) 1 2 4 Proportional Reasoning 00 11 0 010 1 01 0 110 1 00 01 01 00 1 011 • It is important to develop proportional reasoning both in ourselves and our students • Develop slowly over middle school years, not just a couple weeks in 6th grade • Common Core addresses this 1 2 4 California Common Core 00 11 0 010 1 01 0 110 1 00 01 01 00 1 011 1 2 4 6.RP3 00 11 0 010 1 01 0 110 1 00 01 01 00 1 011 • Use ratio and rate reasoning to solve real-world and mathematical problems, e.g., by reasoning about tables of equivalent ratios, tape diagrams, double number line diagrams, or equations. 1 2 4 California Common Core 00 11 0 010 1 01 0 110 1 00 01 01 00 1 011 1 2 4 7.RP2 and 7.RP3 00 11 0 010 1 01 0 110 1 00 01 01 00 1 011 • Recognize and represent proportional relationships between quantities. – Decide whether two quantities are in a proportional relationship, e.g., by testing for equivalent ratios in a table or graphing on a coordinate plane and observing whether the graph is a straight line through the origin. 1 2 4 • Use proportional relationships to solve multistep ratio and percent problems. California Common Core 00 11 0 010 1 01 0 110 1 00 01 01 00 1 011 1 2 4 8.EE5 00 11 0 010 1 01 0 110 1 00 01 01 00 1 011 • Graph proportional relationships, interpreting the unit rate as the slope of the graph. Compare two different proportional relationships represented in different ways. 1 2 4 Proportional Reasoning 00 11 0 010 1 01 0 110 1 00 01 01 00 1 011 • Activities for developing proportional reasoning (Van de Walle): – Identifying multiplicative situations – Equivalent-Ratio – Comparing Ratios – Scaling with Ratio Tables – Construction and Measurement 1 2 4 • What type of activities are “Chocolatey Cake” and “Mr. Short and Mr. Tall”? Relative and Absolute Thinking 00 11 0 010 1 01 0 110 1 00 01 01 00 1 011 1 2 4 00 11 0 010 1 01 0 110 1 00 01 01 00 1 011 1 2 4 00 11 0 010 1 01 0 110 1 00 01 01 00 1 011 1 2 4 00 11 0 010 1 01 0 110 1 00 01 01 00 1 011 1 2 4 Relative and Absolute Thinking 00 11 0 010 1 01 0 110 1 00 01 01 00 1 011 • What are you doing or can you do to distinguish the difference? 1 2 4 00 11 0 010 1 01 0 110 1 00 01 01 00 1 011 1 2 4 00 11 0 010 1 01 0 110 1 00 01 01 00 1 011 1 2 4 00 11 0 010 1 01 0 110 1 00 01 01 00 1 011 1 2 4 00 11 0 010 1 01 0 110 1 00 01 01 00 1 011 1 2 4