WJ III Cognitive PP
advertisement

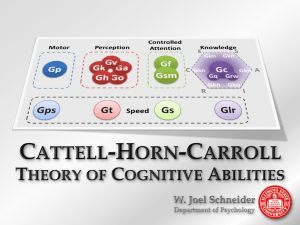
WJ III Training Use and Interpretation of the Tests of Cognitive Abilities Carroll’s Three-Stratum Theory (1993) Multiple factor view of intelligence Narrow Broad General General, Broad, and Narrow Abilities g General Intelligence Gf Fluid Intelligence Gc Gsm Crystallized Intelligence General Memory & Learning Gv Broad Visual Perception Ga Broad Auditory Perception Glr Broad Retrieval Ability Narrow Abilities (70 currently identified) Gs Broad Cognitive Speediness Broad (II) Gf-Gc Abilities Subsume Narrow (I) Abilities: Gf Example Gf Fluid Intelligence General Sequential Reasoning (RG) Induction (I) Quantitative Reasoning (RQ) Speed of Reasoning (RE) Piagetian Reasoning (RP) Cognitive Performance Model BE CAREFUL USING THIS MODEL Stores of Acquired Knowledge (Gc, Gq, Grw) Thinking Abilities (Glr, Gv, Ga, Gf) Cognitive Efficiency (Gsm, Gs) Facilitator-Inhibitors (Internal, External) COGNITIVE PERFORMANCE Comprehension-Knowledge (Gc) • The breadth and depth of knowledge of a culture • The ability to communicate one’s knowledge (especially verbally) • The ability to reason using previously learned knowledge or procedures • Originally described as “crystallized intelligence” Tests comprising this cluster: Verbal Comprehension General Information Gc Comprehension Knowledge Language Development (LD) Verbal Comprehension Picture Vocabulary Lexical Knowledge (VL) General Information Listening Ability General Information Oral Comprehension (K0) (LS) Academic Knowledge © 2002 The Riverside Publishing Company. COG 1 Verbal Comprehension • Requires naming pictured objects, providing synonyms or antonyms, and solving analogies • 4 subtests: Picture Vocabulary, Synonyms, Antonyms, and Verbal Analogies (no derived scores) • Basal/Ceiling Rules apply to each subtest: 3 lowest correct / 3 highest incorrect • Use Suggested Starting Points Clusters Broad Ability GIA, BIA Comprehension-Knowledge (Gc) Verbal Ability Narrow Abilities Comprehension-Knowledge Language Development (LD) Lexical Knowledge (VL) Predicted Achievement COG 11 General Information • Requires answering questions presented orally • 2 subtests: Where and What (no derived scores) • Basal/Ceiling Rules apply to each subtest: 4 lowest correct / 4 highest incorrect • Know correct pronunciation of all items Clusters GIA Verbal Ability Comprehension-Knowledge Knowledge Broad Ability Comprehension-Knowledge (Gc) Narrow Ability General (verbal) Information (KO) Long-Term Retrieval (Glr) • Ability to store information and fluently retrieve it later through association • Associative storage & retrieval • Length of intervening time is not critical feature • Not to be confused with acquired stores of knowledge (Gc and Gq) Tests comprising this cluster: Visual-Auditory Learning Retrieval Fluency Glr Long-Term Retrieval Associative Memory (MA) Visual Auditory Learning & Delayed Recall Meaningful Memory (MM) Story RecallDelayed Ideational Fluency (FI) Retrieval Fluency Naming Facility (NA) Rapid Picture Naming Memory for Names & DR © 2002 The Riverside Publishing Company. COG 2 Visual-Auditory Learning • Controlled learning task, corrective feedback • Requires recalling verbal labels for visual symbols presented in various combinations • Begin with Introduction 1 for all subjects • Discontinue testing when cutoff is met • Score based on number of errors Clusters Broad Ability GIA Thinking Ability Long-Term Retrieval Predicted Achievement Long-Term Retrieval (Glr) Narrow Ability Associative Memory (MA) COG 10 Visual Auditory Learning - Delayed • Changed to relearning task with corrective feedback • Administer 30 minutes to 8 days after Test 2 VAL • Score based on number of errors • Begin with Line 1 for all subjects • Administer all lines (items) to all subjects • Synonyms & no response are errors Broad Ability Clusters Long-Term Retrieval (Glr) Delayed Recall Narrow Ability Associative Memory (MA) COG 12 Retrieval Fluency • Requires naming as many items in a category as possible in one minute (60 is maximum per item) • 3 items: things to eat or drink, first names, animals • Administer all items to all subjects • 1-minute time limit for each item • Do not count duplicate responses • Do not ask subject to repeat Clusters Broad Ability GIA Long-Term Retrieval (Glr) Thinking Ability Narrow Ability Long-Term Retrieval Ideational Fluency (FI) Cognitive Fluency COG 18 Rapid Picture Naming • Requires quickly naming pictured objects in a row of 5 • Begin with samples and then Item 1 for all subjects • 2-minute time limit • Accept synonyms as correct (e.g., kitty for kitten) • Do not accept responses that are similar but not synonyms (e.g., glass for cup) Broad Ability Clusters Cognitive Fluency Processing Speed (Gs) Narrow Abilities Naming Facility (NA) Visual-Spatial Thinking (Gv) • Ability to perceive, analyze, synthesize and think with visual patterns • Ability to store and recall visual representations • Fluent thinking with stimuli that are visual in the “mind’s eye” Tests comprising this cluster: Spatial Relations Picture Recognition Gv Visual-Spatial Thinking Spatial Relations (SR) Visualization (Vz) Spatial Relations Visual Memory (MV) Picture Recognition Spatial Scanning (SS) Planning Closure Speed (CS) Visual Closure Block Rotation © 2002 The Riverside Publishing Company. COG 3 Spatial Relations • Requires selecting the component shapes to construct a whole • Multiple points possible per item (0, 1, 2, 3) • Begin with Introduction for all subjects • Discontinue testing when cutoff is met Clusters Broad Ability GIA Thinking Ability Visual-Spatial Thinking Predicted Achievement Visual-Spatial Thinking (Gv) Narrow Abilities Visualization (Vz) Spatial Relations (SR) COG 13 Picture Recognition • Requires identifying 1-4 previously seen items • Begin with samples and Item 1 for all subjects • Discontinue testing when cutoff is met • Stimulus is shown for only 5 seconds • Score 1 point for each picture recalled in any order Clusters GIA Thinking Ability Visual-Spatial Thinking Broad Ability Visual-Spatial Thinking (Gv) Narrow Ability Visual Memory (MV) Auditory Processing (Ga) • Ability to analyze, synthesize, & discriminate auditory stimuli • Ability to perceive and discriminate speech sounds that may be presented under distorted conditions • Does not require comprehension of language Tests comprising this cluster: Sound Blending Auditory Attention Ga Auditory Processing Phonetic Coding: Analysis (PC:A) Incomplete Words Word Attack Phonetic Coding: Synthesis Speech Sound Discrimination (PC:S) (US) Sound Blending Spelling of Sounds Resistance to Auditory Stimulus Distortion (UR) Auditory Attention Sound Patterns © 2002 The Riverside Publishing Company. COG 4 Sound Blending • Requires identifying & pronouncing words that are presented as a stream of individual sounds • Begin with samples and then Item 1 for all subjects • Ceiling: 6 consecutive highest items incorrect • Words must be pronounced smoothly • Do not repeat any items during test Clusters GIA Thinking Ability Auditory Processing Phonemic Awareness Predicted Achievement Broad Ability Auditory Processing (Ga) Narrow Ability Phonetic Coding (PC) COG 14 Auditory Attention • Requires detecting differences in sounds as background noises increase in volume • Begin with training items (1-57) presented orally • Administer samples and then Item 1 to all subjects • Ceiling: 6 consecutive highest items incorrect • Use recording for all test items Clusters Broad Ability GIA Auditory Processing (Ga) Thinking Ability Narrow Abilities Auditory Processing Speech Sound Discrimination (US) Resistance to Auditory Stimulus Distortion (UR) Broad Attention COG 8 Incomplete Words • Requires identifying & pronouncing words presented with one or more phonemes missing • Begin with Sample A (Pre) or Sample B (K and up) • Ceiling: 6 consecutive highest items incorrect • Word must be pronounced as a complete word Broad Ability Clusters Phonemic Awareness Auditory Processing (Ga) Narrow Ability Phonetic Coding (PC) Fluid Reasoning (Gf ) • Ability to reason, form concepts, & solve problems (using unfamiliar information or novel procedures) • Basic reasoning processes (minimal effect of learning & acculturation) • Manipulating abstractions, rules, logical relations Tests comprising this cluster: Concept Formation Analysis-Synthesis Gf Fluid Reasoning General Sequential Reasoning (RG) AnalysisSynthesis Induction (I) Quantitative Reasoning (RQ) Applied Problems Concept Formation Speed of Reasoning (RE) Decision Speed? Quantitative Concepts Number Series Number Matrices © 2002 The Riverside Publishing Company. COG 5 Concept Formation • Controlled learning task, corrective feedback • Requires identifying & stating the rule governing a set of colored geometric figures • Begin with Introduction 1 (Pre-Grade 1) or Introduction 2 (Grade 2 and up) • Discontinue testing when cutoff is met Clusters GIA, BIA Thinking Ability Fluid Reasoning Executive Processes Predicted Achievement Broad Ability Fluid Reasoning (Gf) Narrow Ability Induction (I) COG 15 Analysis-Synthesis • Requires analyzing the components of an incomplete logic puzzle and identifying the missing component(s) • Controlled learning task, corrective feedback (1-28) • Begin with Color Pretest and then Introduction • Discontinue testing when cutoff is met • Items 26-35, 1-minute time limit for each Clusters GIA Thinking Ability Fluid Reasoning Broad Ability Fluid Reasoning (Gf) Narrow Ability General Sequential Reasoning (RG) Processing Speed (Gs) • Ability to perform automatic cognitive tasks, particularly when measured under pressure to maintain focused attention • Attentive speediness • Usually measured by tasks that require rapid cognitive processing but little thinking Tests comprising this cluster: Visual Matching Decision Speed Gs Processing Speed Perceptual Speed (P) Rate-of-test Taking (R9) Semantic Processing Speed (R4) Visual Matching Pair Cancellation Decision Speed Cross Out © 2002 The Riverside Publishing Company. COG 6 Visual Matching • Ages 2-4 Version 1 (in Test Book) • Requires pointing to 2 pictures that are the same in row • 2-minute time limit • Ages 5 and up Version 2 (in Test Record) • Requires quickly circling two identical numbers in row of 6 • 3-minute time limit Clusters Broad Ability GIA, BIA Cognitive Efficiency Processing Speed Predicted Achievement Processing Speed (Gs) Narrow Ability Perceptual Speed (P) COG 16 Decision Speed • Requires marking the 2 of 7 objects in a row that go together or are most alike (uses SRB) • Begin with samples and then Item 1 for all subjects • 3-minute time limit • Both pictures must be identified for credit (must be two that are most alike, not just loosely related) • Scoring overlay provided Clusters Broad Ability GIA Cognitive Efficiency Processing Speed Cognitive Fluency Processing Speed (Gs) Narrow Ability Semantic Processing Speed Short-Term Memory (Gsm) • Ability to apprehend and hold information in immediate awareness and then use it within a few seconds • Memory and learning abilities in Carroll’s model Tests comprising this cluster: Numbers Reversed Memory for Words Gsm Short-Term Memory Working Memory Span (MS) Memory for Words Memory (MW) Numbers Reversed Auditory Working Memory Memory for Sentences © 2002 The Riverside Publishing Company. COG 7 Numbers Reversed • Requires repeating series of random numbers backwards • Items 1-10 given orally, rest from audio recording • Basal/Ceiling Rules apply to groups of items: 3 lowest in group correct / 3 highest in group incorrect Clusters GIA Cognitive Efficiency Short-Term Memory Working Memory Broad Attention Predicted Achievement Broad Ability Short-Term Memory (Gsm) Narrow Ability Working Memory (MW) Basal/Ceiling Example 1. Starts with Samples C and D. 2. Continues with Item 11. 3. Items 11-13 are correct so basal is established. (3 lowest in group correct) 4. Items 16-18 are incorrect so ceiling is established. (3 highest in group incorrect) 1 2 What is Number Correct? 3 4 COG 17 Memory for Words • Requires repeating lists of unrelated words in order (ranges from one word to a series of 7 words) • Basal/Ceiling Rules: 3 in group of 3 /3 in group of 3 • Words must be repeated in exact order presented • Accept very similar sounding or rhyming responses (e.g., son for some, bat for that) Clusters GIA Cognitive Efficiency Short-Term Memory Broad Ability Short-Term Memory (Gsm) Narrow Ability Memory Span (MS) COG 9 Auditory Working Memory • Requires listening to a series of words and digits intermingled, then repeating words in sequence first followed by digits in sequence • Score items 2, 1, 0 (1 for words, 1 for digits) Very similar sounding or rhyming responses are scored as correct. • Basal/Ceiling Rules apply to groups of items: all 3 in lowest group scored 2 / all 3 in highest group scored 0 Broad Ability Clusters Short-Term Memory (Gsm) Working Memory Broad Attention Narrow Ability Working Memory (MW) PHONEMIC AWARENESS CLINICAL CLUSTER Gf Fluid Reasoning Gc Verbal Ability Gv VisualSpatial Thinking Glr Long-term Retrieval Ga Auditory Processing Gsm Short-term Memory Gs Processing Speed Sound Blending Ability to analyze, synthesize, and manipulate sounds. Measures aspects of phonological awareness Incomplete Words Was the WJ-R Ga cluster Can be combined with Sound Awareness (ACH) for Phonemic Awareness 3 cluster WORKING MEMORY CLINICAL CLUSTER Gf Fluid Reasoning Gc Verbal Ability Gv VisualSpatial Thinking Glr Long-term Retrieval • Ability to temporarily store and perform a cognitive operation on information • Requires divided attention and the management of the limited capacity of short-term memory Ga Auditory Processing Gsm Short-term Memory Numbers Reversed Aud Working Memory Gs Processing Speed AUDITORY MEMORY SPAN CLINICAL CLUSTER Gf Fluid Reasoning Gc Verbal Ability Gv VisualSpatial Thinking Glr Long-term Retrieval • Measurement of short-term memory span/capacity. Ga Auditory Processing Gsm Short-term Memory Memory for Words Memory for Sentences (DS) Gs Processing Speed ASSOCIATIVE MEMORY CLINICAL CLUSTER Gf Fluid Reasoning Gc Verbal Ability Gv VisualSpatial Thinking Glr Long-term Retrieval VisualAuditory Learning Memory for Names (DS) Measurement of learning & recall for new associations. Ga Auditory Processing Gsm Short-term Memory Gs Processing Speed COGNITIVE FLUENCY CLINICAL CLUSTER Gf Fluid Reasoning Gc Verbal Ability Fluency/speed of retrieval from stored knowledge Gv VisualSpatial Thinking Glr Long-term Retrieval Ga Auditory Processing Gsm Short-term Memory Retrieval Fluency Fluency/speed of forming simple concepts. Fluency/speed of lexical (vocabulary) access/recall Gs Processing Speed Decision Speed Rapid Pic Naming Ability to quickly and fluently perform simple to complex cognitive tasks Corresponding achievement cluster: Academic Fluency VISUALIZATION CLINICAL CLUSTER Gf Fluid Reasoning Gc Verbal Ability Gv VisualSpatial Thinking Glr Long-term Retrieval Ga Auditory Processing Gsm Short-term Memory Gs Processing Speed Spatial Relations Ability to envision patterns or objects and perceive how they may appear if altered. Block Rotation (DS) NUMERICAL REASONING CLINICAL CLUSTER Gf Fluid Reasoning Number Series (DS) Number Matrices (DS) Gc Verbal Ability Gv VisualSpatial Thinking Glr Long-term Retrieval Ga Auditory Processing Ability to reason with mathematical concepts. Gsm Short-term Memory Gs Processing Speed