The Potential of Multimodal MRI for Understanding Sports Concussion
advertisement

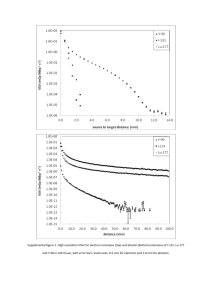
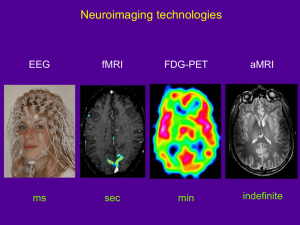
"THE POTENTIAL OF MULTIMODAL MRI FOR UNDERSTANDING SPORTS CONCUSSION" Victoria Morgan, Ph.D., Manus Donahue, Ph.D., Megan Strother, M.D., Allen Sills, M.D., Andrew Gregory, M.D., Gary Solomon, Ph.D., and Hakmook Kang, Ph.D. The Challenge: To identify and quantify brain injury after concussion R • Diagnose acute injury • Monitor recovery • Assess treatment strategies • Evaluate long term effects of single and multiple concussions Diffusion Tensor Imaging – Examining White Matter Tracts • Looks at the direction of diffusion of water along white matter tracts • Measured by Fractional Anisotrophy (FA) • Used to assess diffuse axonal injury Literature: • Many studies reported • Most find decreases related to injury severity or symptoms, but some found increases in some tracts DTI Tractography and Fractional Anisotrophy BOLD effect Blood Oxygen Level Dependence This is what makes it possible for MRI to detect brain function in addition to anatomy (eyes open) (eyes closed) neurons OxyHb de-OxyHb - High deOxyHb concentration - Low deOxyHb concentration Neuronal activity needs oxygen Blood flow increases bring oxygen Not all increase in oxygen is used % OxyHb increases, % deOxyHb decreases MRI SIGNAL INCREASES !! This sounds easy! • The signal change is small - <5% task control R D PREDICTED ACTIVATION IN VISUAL AREA PREDICTED ACTIVATION IN OBJECT AREA fMRI compares each voxel signal time course Slicebased 9, Voxel to a KNOWN expected time course on0, 0 Even where there’s no brain, there’s noise stimulus timing: REST TASK Why do we need stats? principle, analyze data by voxel surfing: move the cu Slice 9, Voxel 9, 27 intere t areas and see if any of the time courses look Activated voxel time course VED RF 0, 0 Expected time course Design of comparison and analyses of differences are the primary challenges of fMRI there’s noise Slice 9, Voxel 1, 0 Here’s a voxel that responds well whenever there’s visual stimulation The high is br still Slice 9,voxel Voxel 22, 7 Not activated time course Slice 9, Voxel 13, 41 Here’s one that responds well whenever Functional MRI – Task Mapping • Uses BOLD effect • Can look at many tasks o language o memory o attention o motor • Depends on performance Literature: • Approx 20 studies • Investigations reported weeks to years after injury • Increases and decreases in activation levels • Changes with treatments, severity of symptoms, performance Language Functional Mapping Word Generation From Categories Healthy control Broca’s and Wernicke’s Area L rCVR – cerebrovascular reactivity R Functional MRI measured with either breath holding or increase CO2 breathing increases vasodilation without increase in metabolic rate of oxygen consumption No studies found in concussion mTBI Resting Functional Connectivity • Uses same BOLD signal • Looks at synchronization of low frequency fluctuations in BOLD signal • Networks are known to fluctuate in synchrony • Seed region analysis Literature: • Approx 8 studies done • Looked at specific network- default mode • Showing decreases in network • One study looked at thalamus – found increased connectivity to cortex Resting Functional Connectivity R Connectivity to seed region in precuneus which is part of the defaultmode network. healthy control Resting Functional Connectivity to Precuneus R mTBI patient healthy control Resting Functional Connectivity to Left Motor Cortex R mTBI patient healthy control Long term affects of concussion in retired NFL player Multimodal MRI protocol Table 1. MRI Protocol Sequence Localizer Reference T1-weighted T2-weighted T2-relaxation-under-spin-tagging (TRUST) T1-weighted (matched to fMRI) Resting fMRI Hypercarbia fMRI Arterial spin labeling (ASL) T1-weighted (matched to ASL) Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) Measurement Time (min) 3 parallel imaging calibration 2 anatomy, segmentation 8 anatomy 6 oxygen extraction fraction (OEF) 5 spatial normalization 6 functional connectivity (FC) 7 regional vascular reactivity (rCVR) 15 regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) 4 spatial normalization 3 structural connectivity (SC) 15 Total scan time: 74 min Project Ideas 1. To recruit Vanderbilt and Belmont athletes immediately after concussion and scan longitudinally and compare to ImPACT scores during recovery 2. To recruit retired professional athletes to compare MRI measures to neuropsychological exam Multiple novel measurements at multiple time points Investigators: • Victoria Morgan, Ph.D. (VUIIS) • Manus Donahue, Ph.D. (VUIIS) • Gary Solomon, Ph.D. (VSCC) • Megan Strother, M.D. (Radiology) • Andrew Gregory, M.D. (VSCC) • Allen Sills, M.D. (VSCC) • Hakmook Kang, Ph.D. (Biostats)