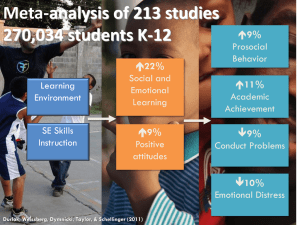
the presentation
advertisement
Meta-analysis, Education Research & the Sutton Trust-EEF Teaching and Learning Toolkit Professor Steve Higgins School of Education, Durham University s.e.higgins@durham.ac.uk @stig_01 Carol Fitz-Gibbon’s vision for education research “that we might eventually have a clearer idea of the conditions under which research findings can be generalised” Meta-analysis provides the means to judge: "the substantive as opposed to statistical significance” of the findings from educational research (Fitzgibbon, 1985, p 45) http://bit.ly/HigCEM30 Development of meta-analysis 1904 – Karl Pearson aggregates typhoid inoculation studies 1940 – Pratt & Rhine – 145 ESP experiments 1976 – Gene Glass – does psychotherapy work? 1984/5 – Carol Fitzgibbon – advocates Glass’ “metaanalysis” in the British Educational Research Journal 1999 – first QUOROM guidelines 2009 – first PRISMA statement http://bit.ly/HigCEM30 Rapid growth of meta-analysis in medicine and psychology Schulze, R. (2007) The state and the art of meta-analysis Zeitschrift fur Psychologie/ Journal of Psychology, 215 pp 87-89. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3049418/ Evidence – what do we need? Evidence from trials and their synthesis (cumulative, comparative aggregation) is necessary, but not sufficient What worked, for whom, in what circumstances? What was the causal mechanism? How consistent is the effect (replication)? How great is the variation? How do we best use findings (re-create the cause)? What is the probability of impact? http://bit.ly/HigCEM30 Cumulative comparative meta-analysis meta-meta-analysis (Kazrin, Durac & Agteros, 1979) mega-analysis (Smith 1982) super-analysis (Dillon, 1982) super-synthesis or meta-synthesis (Sipe & Curlette, 1997) http://bit.ly/HigCEM30 Influential ‘super-syntheses’ 1984 Bloom The 2 sigma problem: The search for methods of group instruction as effective as one-to-one tutoring 1992 Hattie Measuring the effects of schooling 1996 Hattie, Biggs & Purdie Effects of learning skills interventions on student learning 1997 Sipe & Curlette A Meta-Synthesis Of Factors Related To Educational Achievement 1998 Marzano A Theory-Based Meta-Analysis of Research on Instruction 2009 Hattie Visible Learning http://bit.ly/HigCEM30 Current limitations Quality of underlying studies and data Scale of studies Aggregation loses variation Assumes even bias in distribution of studies Limited long term follow up – relies on post-test Provides a large-scale map – hard to see the detail http://bit.ly/HigCEM30 The Education Endowment Foundation Building evidence for what’s worked in schools by identifying and rigorously evaluating innovative and promising approaches Sharing evidence with schools by providing independent and accessible information through the ST-EEF Teaching and Learning Toolkit Promoting the use of evidence-based practice through projects, events and resources (e.g. DIY Evaluation Guide) http://bit.ly/HigCEM30 Sutton Trust-EEF Teaching and Learning Toolkit 2011 2014 Comparative meta-analysis Provides a large-scale ‘map’ of intervention research Uses effect size to identify cost/benefit - – best bets http://educationendowmentfoundation.org.uk/toolkit Average Effects 0.8 0.6 Effect size 0.4 0.2 0 -0.2 -0.4 Approaches http://bit.ly/HigCEM30 The EEF approach http://bit.ly/HigCEM30 The EEF after 3 years (of 15) 34 4,500 topics in the Toolkit schools participating in projects 15 independent evaluation teams £220 m estimated spend over lifetime of the EEF 500,000 11 pupils involved in EEF projects funding rounds to date 4,000 87 heads presented to since launch projects funded to date http://bit.ly/HigCEM30 Initial results Toolkit theme ES (d) EEF Project One to one tuition1 0.44 (overall) 0.22 (TAs) Catch Up Numeracy (using Teaching Assistants) Impact (d) 0.21 0.27 Notes Security findings Catch up group (v controls) Time equivalent group (v. controls) One to one tuition (using TAs) 0.44 (overall) 0.22 (TAs) Switch-On Reading (using TAs) Summer school 0.19 Future Foundations Summer 0.17 School 0.00 English Maths Summer school 0.19 Discover Summer School 0.21 0.24 Very insecure Reading; Writing Grammar2 for Writing 0.10 0.21 Overall impact Small group v control Response to intervention 0.19 High attrition Using Self-Regulation Improve Writing Rhythm for Reading to 0.74 Small group 0.34 (Grammar -0.32 instruction) One to one 0.44 Small group 0.34 Meta-cognition 0.62 and self-regulation Arts Participation 0.16 of 0.24 0.03 n.s “self-regulated development” Rhythm based reading findings strategy notation 1 Programmes which used experienced and specifically trained teachers tend to be more effective than those using volunteers or classroom assistants (nearly double the effect): http://educationendowmentfoundation.org.uk/toolkit/one-to-one-tuition/ 2 Grammar instruction d= -0.32 (Graham and Perrin 2007) http://bit.ly/HigCEM30 ‘Data warehouse’ of EEF findings Database of projects and intervention data Designed to be matched with national test results 2014 – first 5 projects as a pilot – exploratory analysis In 3 years, results from up to 100 interventions and over 500,000 pupils By 2027, about 500 interventions, over 1 million pupils, post-test and follow up data? http://bit.ly/HigCEM30 EEF database potential Identify comparative impact Assess variation in impact (on individuals/ sub-groups, etc.) Track impact of interventions over time Estimate number/ extent of interventions needed to ‘close the gap’ Explore methodological issues (e.g. different methods of calculation, ICC, impact of attrition) http://bit.ly/HigCEM30 ‘It may encourage readers who feel grave misgivings about social science qua science to know that Glass, the main proponent of meta-analysis is no thoughtless naïve or dogmatic positivist. … Of metaanalysis, Glass et al. concluded cautiously, “The approach we call meta-analysis seems to be too plainly reasonable to be false in any simple sense. Whether it will be useful is a different matter”.’ (Fitzgibbon, 1985, p 48-9) http://bit.ly/HigCEM30 References Bloom, B. S. (1984). The 2 sigma problem: The search for methods of group instruction as effective as one-to-one tutoring. Educational Researcher, 13(6), 4-16. Dillon, J.T., (1982). Superanalysis. American Journal of Evaluation 3(4) pp 35-43. Fitz‐Gibbon, C. T. (1984). Meta‐analysis: an explication. British Educational Research Journal, 10(2), 135-144. Fitz‐Gibbon, C. T. (1985). The implications of meta‐analysis for educational research. British Educational Research Journal, 11(1), 45-49. Graham, S., & Perin, D. (2007). A meta-analysis of writing instruction for adolescent students. Journal of Educational Psychology, 99(3), 445. Glass, G. V. (1976). Primary, secondary, and meta-analysis of research. Educational Researcher, 5(10), 3-8. Hattie, J.A. (1992). Measuring the effects of schooling. Australian Journal of Education, 36, 5-13. Hattie, J.A. (2008). Visible Learning. London: Routledge. Hattie, J., Biggs, J., & Purdie, N. (1996). Effects of learning skills interventions on student learning: A meta-analysis. Review of Educational Research, 66(2), 99-136. Higgins, S., Katsipataki, M., Kokotsaki, D., Coleman, R., Major, L.E., & Coe, R. (2014). The Sutton Trust-Education Endowment Foundation Teaching and Learning Toolkit. London: Education Endowment Foundation. Available at: http://educationendowmentfoundation.org.uk/toolkit/ Kazrin, A., Durac, J., & Agteros, T. (1979). Meta-meta analysis: A new method for evaluating therapy outcome. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 17(4), 397-399. Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gotzsche PC, Ioannidis JP et al. (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med 6:e1000100 Marzano, R.J. (1998). A Theory-Based Meta-Analysis of Research on Instruction. Aurora, Colorado, Mid-continent Regional Educational Laboratory. Available at: http://www.mcrel.org:80/topics/products/83/ (viewed 31/05/11). Moher D, Cook DJ, Eastwood S, Olkin I, Rennie D, Stroup DF (1999) Improving the quality of reports of meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials: the QUOROM statement. Quality of Reporting of Meta-analyses. Lancet 354:1896–900 Pearson, K. (1904) Report of certain enteric fever inoculation statistics , British Medical Journal, 1, pp. 1243–1246. Sipe, T. & Curlette, W.L. (1997). A Meta-Synthesis Of Factors Related To Educational Achievement: A Methodological Approach To Summarizing And Synthesizing MetaAnalyses. International Journal of Educational Research 25.7. pp 583-698.