Glaciers: Part 1
advertisement

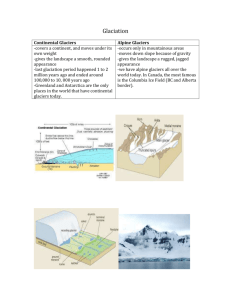
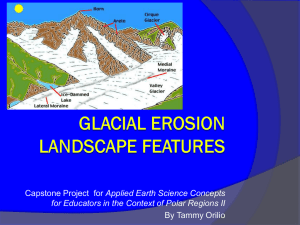
Mysterious rock formations……. What could have caused these formations? GLACIERS!!!!! Evidence for Glaciers Erratics Unsorted material Striations Polished Bedrock Erratic Erratic Boulder-sized rock dumped by a glacier Rock is different type than surrounding rocks Unsorted Materialsall sizes mixed together. Striations Chatter marks (Maine) Striations/ Chatter marks Grooves carved into bedrock Formed by abrasive action of cobbles and pebbles carried at bottom of glacier Direction of scratches shows direction glacier moved Glacial polish Smooth rock surfaces Created as glaciers flow over bedrock Glacial Pavement…. What does a glacier look like? What conditions are necessary for glacial formation? Cold Summers!! Located above the snow line, or in polar regions. Presently occupy 10 % of world’s total land area (32% during ICE AGES) Form on all continents BUT Australia Process of Glacier Formation Snow does NOT melt in summer Recrystallization of snow to form LARGE crystals of ice (rough and granular) –called FIRN: liked packed snowballs Lower layers turn to SOLID ICE under the weight of overlying firn and snow. Snow becomes Firn Glaciers: Types VALLEY GLACIERS: long, slow-moving, wedge-shaped streams of ice Bordered by mountains Size varies* small= 1-2 km long, 100’s m wide, 100’s m deep* largest = Over 100km’s long X 100’s m deep CONTINENTAL GLACIER (ICE SHEETS): very old (1000’s of years) and thick (1000’s of meters) Not confined by mountains Examples: GREENLAND: 1.7 million square miles, 2 miles thick ANTARCTICA: 12.5 million square miles, 3 miles thick Features associated with valley (alpine) glaciers Original valley (V-shaped) Glaciers come and alter landforms Glaciers retreat and new features appear Landscape FeaturesValley Glaciers CIRQUES: semi-circular shaped bedrock feature created as a glacier scours back toward the mountain ARÊTES: steep-sided, sharp-edged bedrock ridge formed by two glaciers eroding away on opposite sides of a ridge TARNS: glacial lakes produced by glacial scouring often found in cirques CIRQUE TARN HORNS: 3 or more cirques adjacent to one another Hanging Valley ARÊTE U-SHAPED VALLEY CIRQUE HANGING VALLEY U-shaped valley CONTINENTAL GLACIERS FEATURES Lateral moraine MORAINES: material left behind when glacier recedes When glacier retreats (melts) rock and sediments are dropped behind Long Island, Cape Cod and the islands are part of a terminal moraine Kettle Lake Drumlins Esker Till Moraine-dammed lake Terminal Moraine Glacial Stream Drumlin drumlins Kettle Lakes River in glacier carries sediment Glacier melts Drops sediment Esker results Eskers