External and Internal Anatomy
advertisement

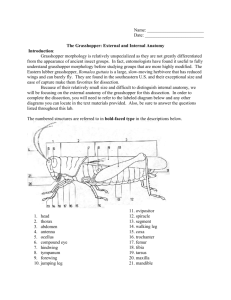
Veterinary Entomology 208 Spring 2010 Today we will be using the grasshopper as a model insect: 1. Work in pairs 2. Read through the handout on external anatomy 3. DO NOT CUT INTO THE GRASSHOPPER antenna compound eye ocelli labrum hypopharynx filler mandible maxilla labium dorsal notum posterior pleuron sternum ventral anterior thorax head thorax divided into • prothorax • mesothorax • Metathorax 1st pair of legs = prothoracic legs abdomen 1st pair of wings = mesothoracic wings 2nd pair of wings = metathoracic wings MALE – CLASPERS (CERCI) FEMALE – OVIPOSITOR 1. Know the underlined structures 2. Pull off the mouthparts to identify them 3. Look at the demonstration material 4. Make sure you are familiar with both male and female external anatomy 1. Read through the handout on internal anatomy 2. We will go through the procedure for dissection and what structures will be visible 3. DON’T CUT THEM YET The first thing you will see is the reproductive system on the dorsal surface of the grasshopper • Male – testes • Female – ovaries Make Look sure you are familiar with both at the demo foregut midgut hindgut anus crop gizzard gastric caecae stomach malpighian tubules ileum colon connective 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Cut off the head Cut off the legs Watch out for the esophagus and cut down both sides of the grasshopper Gently pull the back off Observe the reproductive system lying over the digestive system Observe the digestive system Under the digestive system is the delicate nervous system Clean up Mesothoracic wing antennae - Metathoracic wing