transpiration - s3.amazonaws.com
advertisement

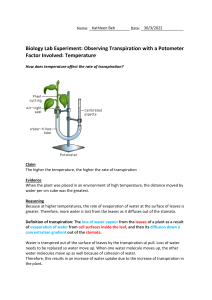
transpiration Why do plants need transport Some small or primitive plants, such as mosses, absorb all the nutrients they need directly from their environment.systems? Larger plants do not have a large enough surface area to take in what they need. Like most multicellular animals, they have developed specialized tissues for transporting water and nutrients to all their cells. Plants that have specialized transport systems are known as vascular plants. Transporting water and nutrients Plant transport tissues Plant anatomy What is transpiration? Transpiration is the loss of water from the leaves of a plant. Most of this occurs from the underside of a leaf, where there are many stomata in the epidermis. Most plants control their water intake by opening and closing their stomata. This happens when water levels change in the guard cells around each stoma. This occurs either passively by osmosis, or by active transport of solutes. Transpiration rates also vary naturally in response to environmental factors such as temperature and humidity. What is water potential? Water tends to move from areas of high water concentration to areas of low water concentration. This is osmosis. Water also tends to move from areas of high hydrostatic pressure to areas of low hydrostatic pressure. It is also affected by gravity and electrostatic forces, such as those that cause surface tension. The collective term for the tendency of water to move due to any of these effects is water potential. Cohesion–tension theory Water is a polar molecule, meaning that its positive and negative charges are not evenly distributed. The oxygen atom has a slight negative charge, while the two hydrogen atoms are slightly positive. This means that, in the xylem, water molecules spontaneously arrange so that positive and negatively charged poles lie next to each other. This causes the molecules to cohere, or stick together, so that as some leave a plant by transpiration, others are pulled up behind them.