Transducers_1[1]
advertisement
![Transducers_1[1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005329047_1-b90da3eabfa98717d13e735055577e1f-768x994.png)
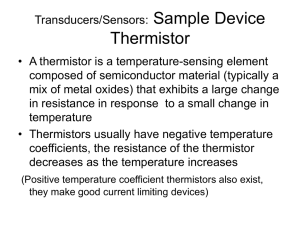
Transducers/Sensors • Transducer/sensor converts a nonelectrical quantity, measurand, into a related electrical output signal • Ideally there is a linear relationship between the measurand and the output • Sensors often need a source of energisation, a power supply Transducers/Sensors • What’s the measurement made for? – Information, to quantify the measurand – Record, to provide a historical profile – Control, use the information to control some process • Sensor measurements are subject to errors – Noise – cross sensitivity, output changes because it’s sensitive to other environmental variables – Characteristic errors, deviation from the predicted response – Dynamic errors, non-ideal frequency or time response Transducers/Sensors • Important Characteristics – Accuracy, usually expressed in %, variation from the stated linear (or other relationship) between measurand and output – Resolution, smallest change in the measurand that can be detected in the output – Range, range of value of the measurand that the sensor can accurately sense Transducers/Sensors • For any form of measurand there are always several sensors that can be used, which one depends on the application • Similarly, many sensors can be used to sense different measurands • E.g: Temperature: thermocouple, resistance thermometer, thermistor, semiconductor sensor, infra-red thermometer…… • E.g: Strain gauge: strain, pressure, height, displacement, velocity, acceleration Transducers/Sensors • Sensors generate analogue outputs such as voltage or frequency • Sensors generate digital outputs such as pulses or digital data Transducers/Sensors: Examples • Linear displacement: – Resistance – Capacitance – Electromagnetism LVDT (linear variable displacement transformer) – Ultrasonic – Optical – ………… Transducers/Sensors: Examples • Temperature: – Thermocouple – Platinum resistance – Thermistor – Semiconductor junction – Semiconductor thermometer Transducers/Sensors: Exercise • Use the rest of the lecture time for a web search on the transducer type given: 1. Range of types available & typical devices (diagrams, photos?) 2. Accuracy, range, resolution 3. Measurand/output law (linear?, shown as a graph?, other?) 4. Cross-sensitivity? Other important electrical characteristics 5. ???