Tundra- Polar Grasslands
advertisement

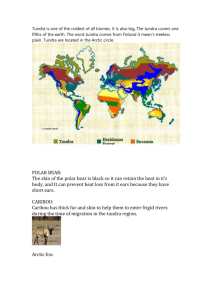
Tundra- Polar Grasslands General Information • Tundra: from Finnish word tunturi which means treeless plain • Also known as polar grasslands • Coldest and driest of all biomes • In northern and southern most latitudes • Areas such as North Europe, Siberia, Northern most part of North America, a few plains in the southern hemisphere (area has more ocean than land) • Simple vegetation structure -Low shrubs, sedges, reindeer mosses, liverworts, grasses -lichen- on rocks, close together -grow close to the ground to protect from cold Climate • Average temperature is less than 5 degrees Celsius • The coldest weather of the tundra occurs in northeastern Siberia. • mild summers with an average temperature of 45 degrees F. • Alaska, Canada, and Siberia have the warmest summers out of the Tundra region. • Precipitation-usually snow-less than 100 mm per year • the Tundra is usually very foggy • the land is wet because of how long it takes the water in the tundra to evaporate and because of poor drainage Biomass and Productivity • Biomass: mass of living biological organisms in a given ecosystem at a given time • Net primary productivity by (kilocalories/ square meter/ year): 600 • Approx. kilocalories per square meter per day: 2 • Rainfall per year in inches: less than 10 • Type of land: barren- ice, sand, tundra desert • % of earths land surface: 33% Threats • Airborne pollutants- such as DDT and PCB’s • Oil and gas development which leads to global warming • Drilling for oil in the Tundra region Animal: The Polar Bear • Apperance: – It has clear fur that appears white when hit by the light – Its shoulder height can be over five feet, and when standing the polar bear can reach heights from eight to eleven feet – Females can weigh anywhere from 660-770 pounds – Males can weigh from 880-990 pounds • Diet: – Mainly seals, but also eats other sea life, and whale and walrus carcasses – In the summer: lemmings, arctic foxes, ducks, and occasionally some plants. Animal: The Polar Bear • Adaptation: – The polar bear is able to handle the cold due to its two layers of fur, which is hollow and creates insulation. Underneath this is black skin that absorbs heat. Also, they have short ears and tails so that little heat is lost. It also has around 4.5 inch thick blubber to help keep warm. – It has a longer neck than other bears to help it keep its head above water. They have strong legs and webbed feet to help them swim. • The polar bear is not currently endangered, but chemicals polluting their food stock and melting ice packs poses a threat to them. • http://dsc.discovery.com/videos/planet-earth-ice-world-polarbears.html Plant- Arctic Moss • Arctic moss (Callieron giganteum) is an aquatic plant that grows underwater at the bottom of lakes, as well as in bogs and fens. • It is a bryophyte, which means that it has no flowers or woody stems and uses spores to reproduce. • It grows very slowly, about 1 cm per year, which helps it to conserve energy, a rare commodity in the tundra. • Arctic moss is very long-lived; shoots live seven to nine years and leaves live four years. • Arctic moss stores nutrients in the winter so that it can generate leaves more quickly in the spring, generating more energy. • It is also protected from the harsh winds and low temperatures of the tundra by growing underwater and remaining close to the ground. • Arctic moss also protects other plants from the cold.