Chapter 1: The Native Americans
advertisement

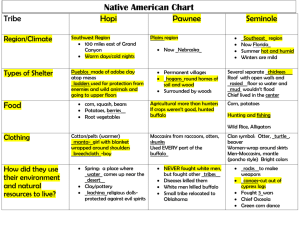
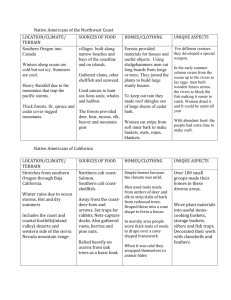
Chapter 1: The Native Americans Vocabulary 1. migrate: to move from on place and establish a home in a new place 2. environment: all of the physical surroundings in a place including land, water, animals, plants, and climate 3. natural resources: useful materials found in nature including water, vegetation, animals, and minerals 4. culture: a people’s way of life including beliefs, custioms, food, dwellings, and clothing 5. cultural region: an area in which a group of people share a similar culture and language Section Notes Section 1.2: Migration Routes of the First Americans 1. Siberia to Alaska to the mainland North America by a landbridge between Siberia and Alaska 2. hunter-gatherers followed the migration patterns of the wildlife 3. as main food source died off learned new skills to survive A. Fishing B. new types of clothing 4. occupied land from Alaska, Canada, throughout South America Section 1.3: Native Americans Adapt to the Environment a. b. c. Adapted to the various environments Lived off of the surrounding natural resources Northern Climates a. b. c. d. used goggles made from bones to avoid snow blindness homes made of driftwood and animal skins igloos in the harsher climates of Alaska Southern/moderate climates a. b. c. gathered plants raised crops such as squash, peppers, beans, and corn agricultural skills eventually lead to more permanent settlements Native American Cultural Regions a. based on and developed around climate and other factors b. 10 cultural regions north of Mexico NW Coast, California, Great Basin, Plateau, SW, Great Plains, E. Woodlands, and SE Section 1. 4: First American’s View of Their Environment viewed themselves as integral part of the community believe in a Great Spirit who unified everything in the universe all parts of nature have a spirit no belief in private property fought to protect what they believed was their homeland adapted nature to suit their lifestyles but rarely if ever harmed the environment very little waste; attempted to make use of everything they used/killed Section 1.5: Native Americans of the NW Coast Southern Oregon to Canada plentiful food supplies depended heavily on the seas for food animal skins/meat from deer, moose, bear, elk, beaver, and mountain goats specialized weapons to catch different types of animals salmon harvest using fencing in the Spring homes made of wood from the forest developed various crafts such as basket making, jewelry from shells Section 1.6: Native Americans of California Southern Oregon to Baja California Western Sierra Nevada Mountains more than 100 different groups lived in this region Food Supply: Salmon and Shellfish deer, rabbits, and ducks roots, berries, and nuts Clothing, houses and Baskets: clothing from animal skins simple houses made from forest wood tools from antlers, bones, rocks excellent weavers Section 1.7: Native Americans of the Great Basin East of California, Sierra Nevada Mountains to the Rocky Mountains extreme weather condition hot to cold nomadic tribes followed the migration patterns of animals for food and water sources Food Supplies Snakes, jackrabbits, and duck eggs various plants berries, roots, seeds, and pine nuts Section 1.8: Native Americans of the Plateau North of the Great Basin, Cascade Mountains to the West, Rocky Mountains to the east dense forest, grassy and sagebrush long harsh winters and mild summers Settlements along major rivers food was enough to support year-round living in some areas many homes built partly underground to combat cold and heat plateau groups were excellent weavers Fall: deer and antelope Camas and Salmon food supply during the Spring wild onions and carrots favored the Camas root: starchy root eaten raw or made into flour Section 1.9: Native Americans of the Southwest Arizona, New Mexico, Utah, Colorado, Texan, Oklahoma, and California canyons, mountains, desert, mesas two major rivers: Colorado, Rio Grande very hot and arid region Mesa People nomadic desert hunters hunter-gatherers/farmers near the rivers adobe brick homes Corn Culture grew corn, beans, and squash corn most important crop planted near flood zones, large streambeds, and at the foot of the Mesas with water runoff ate stew made from corn, rabbit and chili peppers Section 1.10: Native Americans of the Great Plains Grasslands from Rocky Mountains to the Mississippi River Canada to the Gulf of Mexico Buffalo Hunters Eastern Plains: farmers and some buffalo hunting Western Plains: migrated with the buffalo herds Using the Buffalo main food source for Plains people used every part of the buffalo hides: shields, clothing, tents (teepees), containers hair: used for bow strings horns/hooves: spoons, bowls, glue dung used for fire fuels became more efficient when the Spanish brought horses to the region Section 1.11: Native Americans of the Eastern Woodlands Mississippi River to the Atlantic Ocean Canada to North Carolina Iroquois tribes lived in New York area Plentiful Woods Iroquois lifestyle: hunting wood fresh greens, nuts, berries syrup from maple trees fishing log homes with several families living together