Phases, Phase Changes & Physical Changes
advertisement

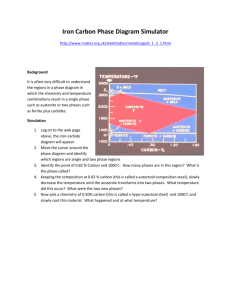
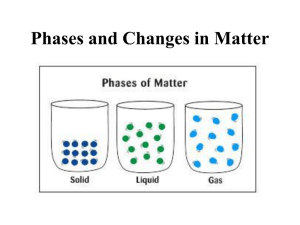
CHEMISTRY- Phases, Phase Changes & Physical Changes BY: BRIANNA SHIELDS DO NOW • Work with your lab partner to list as many observations as possible of the item on the front counter • The group with the most observations will earn a biobuck GOAL • To identify physical properties and physical changes • To discuss the states of matter and the terms relative to changes of state Physical Properties of Matter • Matter • Anything that has mass & takes up space • Physical Property • Characteristic of matter that is observed without changing its identity Describing Physical Properties • Describe the object on the front counter • Use as many descriptions of its physical properties as possible • Group with the greatest number of different properties (qualities) receives a biobuck Physical Properties of Matter • Examples of physical properties • • • • • • • • • • Mass Weight Volume Density Color Shape Hardness Texture Phase Temperature Physical Properties of Matter • Mass • Definition: The amount of matter in an object Physical Properties of Matter • Weight • Definition: Amount of gravitational pull on an object Physical Properties of Matter • Volume • Definition: The amount of space an object takes up Physical Properties of Matter • Density • Definition: The number of particles packed into a space (m/v) Physical Properties of Matter • Color • Definition: The wavelength of light reflected from an object Physical Properties of Matter • Shape • Definition: Describes the outer edges or outline of the object Physical Properties of Matter • Hardness • Definition: The resistance of a material to being scratched Physical Properties of Matter • Texture • Definition: Describes the surface of the object (rough vs. smooth) Physical Properties of Matter • Phase • Definition: Describes whether the matter is in solid, liquid or gaseous form Physical Properties of Matter • Temperature • Definition: The average kinetic energy of the matter’s particles Assessment • Pick two pieces of matter from the front counter • Describe its physical properties by filling in the example boxes on your handout • When you are finished, raise your hand to be checked by Mrs. Shields Physical Changes • Physical Change • Changes the physical appearance of matter without changing what its made of • Is it the same material before and after the change? • Ex: Cutting up a piece of pepper Assessment • Work with your group members to come up with 5 physical changes of matter • List these changes in the proper space on your handout • The class will vote on whether your examples are correct Examples of physical changes • Examples • 1. Carving wood into a baseball bat • 2. Dying your hair a different color Examples of physical changes • Examples • 3. Smashing a rock • 4. Freezing water Examples of physical changes • Examples • 5. Boiling water • 6. Sharpening a pencil Examples of physical changes • Examples • 7. Chopping down a tree • 8. Spilling Milk Examples of physical changes • Examples • 9. Crumpling a paper • 10. Mowing the lawn Examples of physical changes • Examples • 11. Mixing ingredients • 12. Tossing a salad Phase Summary Chart • Work with a partner to fill in the phase summary chart Phases of Matter • Solid • 1. Has a definite shape • 2. Has a definite volume Phases of Matter • Solid • 3. Particles are tightly packed (can’t move or flow well) • 4. Low energy Phases of Matter • Liquid • 1. No definite shape- takes the shape of the container • 2. Has a definite volume Phases of Matter • Solid • 3. Particles are packed loosely and flow slowly • 4. Average energy Phases of Matter • Gas • 1. No definite shape- takes shape of container • 2. No definite volume Phases of Matter • Gas • 3. Particles are spread far apart- fill all spaces • 4. Contantly moving and bumping into eachother • 5. High energy Phases of Matter • Gas • 6. Particles can be squeezed in closer – Bumping into eachother and walls causes pressure Phase Website • Phases of matter at the molecular level Phase Changes • Phase Changes • Matter such as water can from phase to phase by adding or taking away heat energy PHASE CHANGE 1 PHASE CHANGE 2 PHASE CHANGE 3 PHASE CHANGE 4 PHASE CHANGE 5 Phase Changes • Melting • Solid to liquid • Must take in heat energy • M.P of water = 0 C or 32 F Examples of Melting Phase Changes • Freezing • Liquid to solid • Must lose heat energy • F.P of water = 0 C or 32 F Examples of Freezing Phase Changes • Evaporation • Liquid to gas • Must gain heat energy • B.P of water = 100 C or 212 F Examples of Evaporation Phase Changes • Condensation • Gas to liquid • Must lose heat energy Examples of Condensation Phase Changes • Sublimation • Solid skips to gas • Must gain a lot of heat energy • Ex: – Freezer Frost – Dry Ice – Cirrus Clouds Phase Change Website • Click here to view a phase change Phase Change Diagram Assessment • Determine what phase change is the opposite of evaporation. Explain Assessment • What type of phase change is seen in this picture? Explain what occurs during this phase change Assessment • What type of phase change is seen in this picture? Explain what occurs during this phase change Assessment • What phase change is the opposite of freezing? Explain