Plants
advertisement

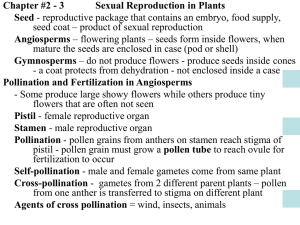
Growing Plants from Seeds All seeds contain an embryo plant with a root and shoot. The seed also contains a starchy food store which the embryo uses as energy to grow. ( germinate ) The seed coat protects the embryo from damage by micro-organisms that live in the soil. Germination • Germination is the growth of a plant embryo into a plant with green leaves. • The embryo uses the food store for energy. • A seed needs three things to grow – Warmth – Water – oxygen Test Tube 1 (warmth ,air, Number of seeds growing 10 2 ( no water) 0 3 ( no air ) 0 4 (no light ) 9 5 ( cold ) 2 water) Photosynthesis Plants make food by a process called photosynthesis. All green parts of the plant make food but most food is made in the leaves. Plants need light to make the food starch. This food is then used by plants for growth. Testing leaves for Starch When leaves are tested for starch, they need to be boiled first to open the cells. Alcohol is used to remove the green colour. Finally, iodine is added. Iodine turns blue/black when starch is present. Testing for Photosynthesis • Glucose manufactured in the process of photosynthesis can be stored as starched. We can test for starch using iodine solution following the steps outlined below. Sowing Seeds When planting seeds, the way they are planted depends on the seed size. Fine seeds should be mixed with silver sand to space the seeds out. This stops them fighting with each other for water, root space and light. Medium size seeds can be scattered over the surface of the compost ( soil ). Large seeds can be sown individually in seed trays or pots. Pelleted seeds • A pelleted seed is coated in layers of material such as clay before it is planted. • This can make irregularly shaped seeds round and smooth to stop them sticking together. • Useful chemicals such as fungicides, pesticides or nutrients can be added to the layers. • Pelleting makes small seeds easier to handle. Dormancy Many seed will not germinate after they are dispersed, Even although they have been given ideal conditions. These seeds are dormant and need a long cold period before they grow. This stops them growing during a warm winter spell. Chitting • Pre-germinating or chitting a seed means making it start to germinate before it has been planted. • This can be done by soaking the seeds in water for a few days. • If the seed coat is very tough and will not allow water to enter, it can be slit open using a sharp knife. • This is best done at the opposite side from the embryo to avoid damage. • If the seed is very big, a nail file can be used instead to file away part of the seed coat. • Very small seeds can be rolled in between sheets of sand paper. Vegetative propagation • Propagation is a way a grower can increase their supply of plants. • Vegetative propagation is a way of growing plants without using seeds. • This involves structures such as bulbs and cuttings and all new plants formed are identical to the original parent plant. • Vegetative propagation produces new plants faster than using seeds. Natural vegetative propagation • Bulbs – A bulb is a natural plant propagation structure. It is made up of several leaf bases (layers) which contain stored food (starch) and has a short, thick stem. – Buds can be found among the leaf bases and grow into new daughter bulbs. – Tulips and daffodils grow from bulbs. • Tubers – A tuber is a large food store found on a root or stem. – A potato is an example of a tuber. – Tubers can grow into whole new plants – In summer, potato plants grow many tubers and each tuber has ‘eyes’ which are really tiny buds. When planted, shoots grow from the bud and turn into new potato plants. • Plantlets • A plantlet is a tiny plant attached to a parent plant. These plantlets eventually separate from the parent and grow on their own. • The Mexican hat plant grows plantlets on the edges of its leaves. • The Piggyback plant grows plantlets at the base of each leaf. Mexican hat plant Piggyback plant • Runners – Some plants grow plantlets at the end of horizontal stems called runners. – Spider plants grow runners. – Strawberries grow plantlets on runners. – If runners are pegged to the ground, the plantlets grow roots and the runner can then be cut. • Offsets – An offset is a plantlet which grows as a side shoot at the base of the parent plant.. – Sometimes lots of offsets grow and form a clump. – Mother-in-law’s tongue is a plant which grows offsets. Plant production Artificial Propagation Artificial propagation is when part of a plant is cut from the parent and used to make a new plant. This is quicker then waiting for the parent plant to make seeds and all the new plants will be identical to the parent. A cutting is a piece of plant stem with leaves which is cut, dipped in rooting hormone ( encourages roots to be made ) and planted . Layering is another method of artificial propagation. A long stem is nicked, dusted with rooting hormone and pegged to a pot of compost. When the roots grow, the new plant can be cut from the parent. This makes bigger new plants and the parent supplies it with water and minerals while they are attached. Using heat during propagation • A propagator is an electric device for providing cuttings and new plants with heat. Propagators are often used inside greenhouses. • Propagators keep the soil at a siutable temperature 24 hors a day. • This encourages roots to grow quickly. • Propagators are mot useful during winter to protect young plants from frost damage. • Gardeners must be careful not to make the temperature too high for young plants as they will lose too much water and wilt. • Some propagators have thermostats which control the temperature. This allows the temperature to be set by the gardener and it will stay constant. Composts For plants to be healthy, the soil ( loam) must be right for the plant. The soil must have : 1. Air 2. Good drainage 3. Minerals 4. Free of most bacteria or fungus There are 2 kinds of compost : loam based and loamless Loam based soils contain mainly loam. Loamless soils contain a 1:1 ratio of peat to sand Loamless soils do not need to be sterilised but can dry out more easily. • Rooting Composts: Sometimes called a cutting compost,this is a mixture of peat and sand in a 1:1 ratio (half and half). Water drains better from this compost because it has more sand and this prevents roots from rotting. Perlite or vermiculite can be used instead of sand. • Potting Composts: This is a mixture of peat and sand in a 3:1 ratio so for example, 6L of peat would be mixed with 2L of sand. Fertiliser is also added to supply the growing plant with enough minerals to keep it healthy. Materials Sand or perlite Peat Fertiliser Loam (soil) Property Fertilisers Plants need minerals for healthy growth. The 3 main minerals : 1. Nitrogen : leaf growth 2. Phosphorous : root growth 3. Potassium : flower and fruit growth Plants also need some other minerals in tiny amounts. These are called trace elements and an example is iron. Fertiliser is used if a soil does not have enough of the right minerals. Different plants need varying amounts of each of the 3 main minerals. For example grass needs nitrogen as the main element of fertiliser whereas, growing tomatoes would need high potassium ( potash). The proportion or ratio of the 3 main minerals is listed on fertiliser containers in the following order Nitrogen (N) : phosphorous (P) : potassum (K) 7 : 7 : 14 Applying Fertilisers Fertilisers come in 2 forms , as liquids or granules ( small pellets) Liquid fertilisers are quick acting but drain away from soil quickly Granules release minerals slowly and are longer lasting. Some liquid fertilisers can be absorbed by the leaves as well as the roots ex Miracle Grow . Man made or natural fertilisers (organic) can be used. An example of an organic fertiliser would be manure but they can be bought from shops also. Watering house plants • Some plants should be watered from above. A watering can can be used to pour water into the plant pot. Water is added until a small amount appears in the drainage saucer underneath. • Some plants should be watered from below. The pot or tray should be placed in shallow water for about 15 mins to allow the roots to absorb as much water as they need. African violets and young seedlings should be watered in this way Watering Systems Automatic watering systems allow plants to be watered without anyone having to do the job. What are the advantages of this ? There are several different types : 1. Trickle irrigation Plastic hose connects a tank of water with several pots. Water “trickles “ continuously between the pots. 2. Capillary Bench Capillary matting is a material that will suck up water and stay moist. If one end of the water is placed in a water trough , it will absorb water along its length , and plant pots can be placed on top. 3. Water Retentive Gels These are chemicals that can absorb and hold a great deal of water. If mixed with soil , they can last many seasons holding water for plants. This is useful for hard to reach plants ex. Hanging baskets Temperature Temperature is measured in degrees Centigrade (ºC ) Different types of plants grow best at different temperatures. For example a spider plant grows well between 10 and 30°C. At temperatures outside this range the plant does not grow well and may die. People who grow plants must find ways of growing them at the correct temperature. Greenhouses are often used or polythene tunnels which are plastic sheets draped over metal poles, almost like a tent for plants! • The temperature inside greenhouses or polythene tunnels can be controlled using an electric heater. • The grower sets the thermostat at a certain temperature and when the greenhouse is warm enough the thermostat switches the heater off. • When the greenhouse begins to cool down the thermostat switches the heater back on. Growers can check the range of temperatures their plants have been exposed to in the previous 24hours using a maximum and minimum thermometer. This is u-shaped. One arm records the maximum temperature that occurred in the previous 24 hours and the other arm records the minimum temperature that occurred in the previous 24hours. As liquid in the thermometer moves up or down it pushes metal markers. These show the max and min temperatures. • Both arms also show the present temperature. The position of the liquid inside the thermometer shows this. Humidity This is the amount of water vapour in the air. Plants lose water from their leaf surfaces. This has a cooling effect similar to sweating in humans. If the air is very humid, hardly any water will evapourate from the plant. If the air is very dry, the plant may lose too much water and could die. Different levels of humidity suit different types of plants. Relative humidity is the percentage of water vapour the air is holding. The higher the percentage, the more humid the air. 100% humidity means the air can hold no more water vapour and is saturated • A wet and dry hygrometer is used to measure relative humidity • It is made up of two ordinary thermometers but one bulb is wrapped in wet muslin and will show a lower temp. • Relative humidity is worked out as follows: – Read dry bulb temp – Read wet bulb temp – Subtract wet reading from dry reading. Refer to table of relative humidities and find value Ventilation This is providing fresh air. Stale moist air means mould and mildew will grow and kill plants. Automatic vent openers are cylinders full of wax. The wax expands when the temperature gets too high and this pushes the window open. As the green house cools down the wax contracts and the window closes. Extractor fans can also be used to cool green houses. These are switched on and off by thermostats. Potting On If a plant grows too large for the pot it is in,it will not have enough space for the roots to grow. We say it has become pot-bound. You will recognise such a plant by the following features: ~ slow growth rate ~ compost dries quickly ~ roots growing out holes in bottom of pot Potting on means re-potting the plant in a larger pot. Pricking Out When seeds are planted in a seed tray, they eventually start to fight for light and root space. They are now ready to transplant into pots and this process is called pricking out . This means transferring them to a new location where they will have more room to grow. Seedlings are ready to prick out when their first set of leaves open out. Dead Heading • Normally a plant produces a set of flowers which die after making seeds. If the heads of dead flowers are removed regularly the plant may produce more flowers. • This removal of dead flower heads to encourage the plant to continue flowering is called dead heading. • Dead heading allows the plant to direct energy to dormant flower buds instead of fruit production. Types of Plants House plants can be divided into 4 groups : Flowering Plants : we grow these for their attractive flowers. Some varieties flower year after year (geranium) and some only once. Foliage Plants : we grow these for the shape and colour of their leaves. Succulent Plants : these have fleshy leaves or stems that store water eg. Cacti. Some may have sharp spines and sometimes produce flowers. Native to dry enviroments such as desert or jungle. • Ferns: Non-flowering plants native to damp woodlands that are not brightly lit. Will not survive in dry, hot conditions. Pests and disease • A pest is an animal which causes damage to a plant. An example in an aphid (greenfly). Greenfly suck the plants sugary sap using their sharp, syringe-like mouthparts. • The greenfly usually attack young parts of the plant like the flower buds. The plant cannot grow properly because it is not getting a full supply of energy • Disease is caused by a micro-organism that can damage the plant. An example is grey mould which is a fungus. • This disease causes a fuzzy grey fungal growth on the leaves . Infected leaves quickly rot and die and infection can spread to the rest of the plant. • This disease thrives in damp, poorly ventilated conditions. Control of Aphids • A pesticide is a chemical that kills insects and other pests. An insecticide is a type of pesticide especially for insects. • Plants can be sprayed with insecticide and so any aphid which tries to feed on its sap will die. • Aphids can also be controlled by biological methods. This means introducing one of its natural predators (ladybirds) which will eat them before they can destroy the plants. Control of grey mould • We can prevent this disease by making sure plants are well spaced out and given good ventilation. Any infected plants should be removed and burned immediately to prevent spread of the disease to other plants. • Plants can also be sprayed with a chemical called a fungicide which kills fungi such as grey mould. Protected cultivation • Plants can be damaged by wind, rain, low temperatures and in particular, frost. • We can protect plants from damage by protective cultivation. This also allows farmers to plant seeds earlier and therefore sell their crops early and receive a higher price. Methods of protection • Glass (ex.greenhouse or cloche) – – – – Lets light through Permanent Retains heat Not damaged by wind • Plastic (cloche) – Light and easy so handle – Less easily broken than glass – cheap • Polytunnels – Good for large areas – Made of transparent plastic stretched over wire hoops like a tent. – Can be raised at either end for ventilation • Floating fleece – Sheet of woven man-made fibres – Place over crops and is gradually lifted up by plants as they grow. – Helps keep soil warm and protects against pests – Water and air can still get through