India and South Asia
advertisement

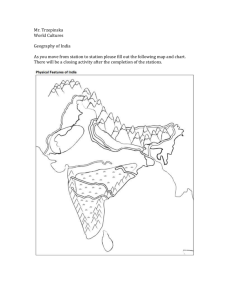
India and South Asia A little Geography and a few questions you will see on test Landforms South Asia’s landforms affect where people live and influence seasonal rain patterns. • Northern landforms: – Himalaya Mountains – Hindu Kush range – Khyber Pass The Himalayan separate the Indian subcontinent from the rest of Asia. Random but relevant Hindus believe that after death, a. a person’s spirit ceases to exist. b. each person will be offered the chance to enter nirvana. c. people join many gods and goddesses. d. most people are reborn as another living being. The theory of continental drift, is generally the idea that scientist explain how the Himalaya’s were formed Sri Lanka teardropshaped island that broke away from the original Indian landmass Located in the Himalaya, Mount ____________________ is the world’s tallest peak The eastern and western Ghats block rainfall to the What? Deccan Plateau Question India opened its economy to foreign investment in the a. 1940s. c. 1980s. b. 1960s. d. 1990s. Question Which of the following is located between the Eastern and Western Ghats? a. Chota Nagpur Plateau b. Deccan Plateau c. Sri Lanka d.Khyber Pass Water Systems South Asia’s major river systems bring fertile soil to the floodplains, serve as transportation routes, and provide hydroelectricity. • Three major river systems: – Ganges—most important river in South Asia – Indus Water Systems Himalaya source for the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Indus Rivers. Water Systems Indus River flows mainly through Pakistan. Remember until independence Pakistan was part of India! Question Where is the source for the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Indus Rivers? a. Hindu Kush c. Himalaya b. the Arabian Sea d. the Indian Ocean Natural Resources South Asia has a variety of natural resources upon which large populations are dependent for their livelihoods. – Drinking water – Hydroelectric power – Alluvial soil – Fish – Transportation – Mineral resources Random but relevant How much of the world’s population lives in India? a. about 5 percent b. about 10 percent c. more than 15 percent d. more than 20 percent Cultural Hearths--- started on river systems with a wealth of natural resources Seasonal Weather Patterns Seasonal weather patterns bring muchneeded rainfall to South Asia, but monsoon winds, as well as other natural disasters, can also bring devastating hardships. Question Cyclones are the same as ____________________ in the Atlantic Ocean. a. tsunamis c. earthquakes b. hurricanes d. tornadoes Seasonal Weather Patterns (cont.) • These seasons depend on seasonal winds called monsoons. • Temperature and rainfall impact agriculture in the region. • Factors: – Extreme heat – Monsoon winds Random but relevant Which of the following actions helped to grow the Indian economy in the 1990s? a. deregulation and private ownership of businesses b. closing off foreign investment c. implementing a command economy d. high tariffs on foreign goods Seasonal Weather Patterns (cont.) • Natural disasters: – Flooding from monsoon rains – Cyclones – Earthquakes – Tsunamis Seasonal Weather Patterns (cont.) Random but relevant The British employed a policy of ______________—an economic system of using colonies for supplying materials and markets to the colonizing country—in India. a. mercantilism b. imperialism c. market economy d. mixed economy Review Economics terms gross domestic product (GDP) gross national product (GNP) • dollar amount of all final goods and services produced within a country's borders in a year • the dollar value of all final goods, services, and structures produced in one year with labor and property owned by a country’s residents READING CHARTS Per Capita GDP Luxembourg $80,800 Qatar $75,900 Norway $55,600 Singapore $48,900 United States $46,000 Random but relevant Portuguese, Dutch, and British colonial powers fought for control over __________ because of its strategic trade route location. a. Sri Lanka b. Maldives c. Bangladesh d. Pakistan The End