Biology 161 Lab 4 - Blood
Vessels, Lymphatics, Pressure
Points, Surface Anatomy
Scott.lehbauer@lethbridgecollege.ab.ca
The Arteries
Circle of Willis - also called
the cerebral arterial circle this
structure surrounds the
pituitary gland and optic
chiasma. It connects the
anterior and posterior blood
supply to the brain. It also
equalizes blood pressure in
the two brain regions and
provides alternate routes for
blood to reach the brain
tissue in case of blockage to
the carotid or vertebral
arteries.
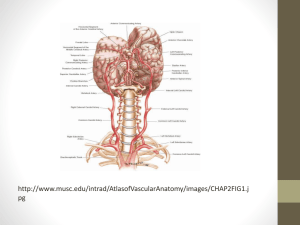
The Circle of Willis
The Circle of Willis
Basilar Artery
Vertebral Arteries
Internal Carotid
Artery
Arteries of the Neck and Face
Superficial Temporal
Artery
Internal Carotid
Artery
Common
Carotid
Artery
External Carotid
Artery
Vertebral
Artery
Arteries coming off the Heart
Right Common
Carotid
Right
Subclavian
Right
Brachiocephalic
Aorta
Left Common
Carotid
Left Subclavian
Arteries of the Arm
Axillary Artery
Circumflex Scapular Artery
Arteries of the Arm Cont.
Brachial Artery
Radial Artery
Median Artery
Superficial Palmer
Arch
Ulnar Artery
Coronary Arteries (Left Side)
Aortic Arch
Left Coronary
Artery
Anterior
Descending
Artery
Circumflex
Artery
Right Coronary Artery and Cardiac
Vein
Great Cardiac
Vein
Right Coronary
Artery
Arteries of the Torso
Gastric Artery
Arteries of the Torso (Superior
Mesenteric)
Superior
Mesenteric
Artery
Superior Mesenteric
Artery
Arteries of the Torso (Inferior
Mesenteric)
Inferior Mesenteric
Artery
Inferior Mesenteric
Artery
Arteries of the Torso
Hepatic Artery
Arteries of the Torso (Celiac Trunk)
Celiac Trunk
Splenic Artery
Arteries of the Torso (Kidneys)
Renal Artery
Renal Vein
Arteries of the Torso (Iliac Arteries)
Common Iliac Artery
External Iliac Artery
Internal Iliac Artery
Arteries of the Leg
Femoral Artery
Arteries of the Leg
Anterior Tibial Artery
Popliteal Artery
Pressure Points
- Are arteries that when
compressed can stop
blood flow into distal
tissues during
hemorrhage.
Facial a.
Subclavian a.
Superficial
Temporal a.
Carotid a.
Brachial a.
Radial a.
Femoral a.
Popliteal a.
Dorsal Pedal a.
Lymphatic System
Lymph – Protein containing fluid transported
by lymphatic vessels.
Lymphatics – an elaborate system of drainage
vessels that collect the excess protein-containing
interstitial fluid and return it to the bloodstream.
Lymph Node – a small lyphoid organ that
filters lymph; they contain macrophages and
lymphocytes.
Lymphatic System
Cervical
Thoracic
Cubital
Axillary
Abdominal
Inguinal
Pelvic
Popliteal
Lymphatic System
Inguinal Lymph
Nodes
Axillary Lymph
Nodes
Spirometry
Tidal Volume – The amount of air that moves into then
out of the lungs during normal quiet breathing.
Vital Capacity – The total amount of exchangeable air in
the lungs. Or the total amount of air blown out during
one forced exhalation.
There are 3 factors which influence vital capacity:
1.) Age
2.) Sex
3.) height