Anatomy of the Cardiovascular System
advertisement
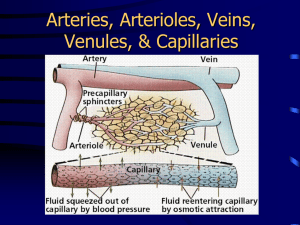
Anatomy of the Cardiovascular System Anatomy & Physiology Heart song http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q0s-1MC1hcE Location of the heart In mediastinum behind the sternum between 2nd & 6th ribs. Shifted to left. Posteriorly between 5th to 8th thoracic vertebrae Apex (lowest point) lies on diaphragm Pericardium Sac covering the heart Fibrous pericardium – tough, inelastic Serous pericardium- 2 layers Parietal layer- lines fibrous pericardium Visceral layer (epicardium)adheres to outside of heart; space between parietal & visceral layer contain small amount of fluid Function of pericardium Provides protection against friction Layers of the heart Epicardium (also the serous pericardium) Myocardium-thick contractile layer of muscle cells Endocardium-cover trabeculae (muscular projections); specialized folds of endocardium make up the major valves of heart Chambers of heart Atria: upper chambers Ventricles: lower chambers Chambers are separated by an extension of heart wall, septum Atria Receive blood from veins Send blood to ventricles Thin myocardial wall Auricle: earlike flap protruding from each atrium Ventricles Receive blood from the atria Pump blood out of heart into arteries Thicker myocardium Myocardium of left ventricle thicker than right ventricle Heart valves Permit flow of blood in one direction Atrioventricular valves Semilunar valves Atrioventricular valves Made of flaps of endocardium Flaps anchored to papillary muscle by chordae tendineae Rt AV valve: tricuspid valve Lt AV valve: mitral (bicuspid) valve Semilunar valves Consists of half moon shaped flaps Pulmonary semilunar valve: at the entrance to the pulmonary artery Aortic semilunar valve: at the entrance to aorta Flow of blood through the heart Heart video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DAXa4eR1s0M Blood supply to heart Blood supplied thru the right & left coronary arteries Coronary arteries are first branches off aorta After blood has passed thru capillary beds, enters cardiac veins then thru common channel, coronary sinus, then into rt atrium Conduction system of heart Sinoatrial node (pacemaker): in rt atrium near opening of superior vena cava Atrioventricular node: in rt atrium along lower part of interatrial septum Atrioventricular bundle: originate in AV node & extend by 2 branches thru the 2 sides of the interventricular septum Purkinje fibers: extension of AV bundle out to the lateral walls of the ventricles & papillary muscles Conduction System Blood vessels Arteries: carry blood away from heart Arterioles: small arteries Veins: Carry blood toward heart Venules: small veins Capillaries: microscopic blood vessels that carry blood from arterioles to venules 3 layers of blood vessels Tunica adventitia: outer layer, fibrous connective tissue Tunica media: layer of smooth muscle & elastic connective tissue Tunica intima: made of smooth endothelium Blood Vessel Structure Type of vessel Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica adventitia artery Smooth lining Thicker than in veins Thinner than tunica media vein Smooth lining with valves Thinner than in arteries Thicker than tunica media capillary Makes up absent entire wall: very thin absent Functions of capillaries Transport materials to and from cells Capillaries so numerous & so small that blood flows at its slowest rate in capillaries Functions of arteries Function as “distributors” Arterioles also function as resistance vessels Smooth muscle cells on arterioles act as precapillary sphincters where a capillary originates Functions of veins Return blood to heart Act as reservoir vessels Ability to stretch by veins called capacitance thus veins are capacitance vessels Circulatory routes Systemic circulation: blood flow from heart to all parts of body (except lungs) Pulmonary circulation: blood flow from heart to lungs Arteries End-arteries: most of the arteries, they diverge into capillaries A few arteries open into branches of other arteries; this communication is an arterial anastomosis Incidence of arterial anastomosis increases as distance from the heart increases Aorta Major artery that serves as trunk of the entire systemic arterial system First few cm conducts blood up away from lt ventricle-ascending aorta Then turns 180 degreesaortic arch Then downward from arch-descending aorta Veins Large veins that return blood to heart in systemic circulation are superior & inferior vena cava