It has nothing to do with the Earth`s distance from the Sun
advertisement

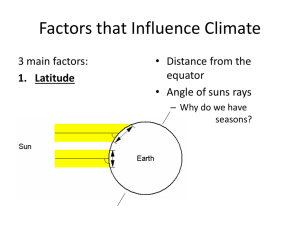
What causes the seasons to occur? What causes the seasons to occur? It has nothing to do with the Earth’s distance from the Sun What causes the seasons to occur? Remember, it’s all about the angle of light that changes as the tilted Earth revolves around the Sun. Light becomes more or less direct from season to season. What causes the seasons to occur? Look carefully at the Northern Hemisphere above and the seasons that occur as it tilts toward (left), away (right) and neither toward nor away (top and bottom) from the Sun. During the year the Sun’s angle changes cyclically. How does this affect the length of daylight in a hemisphere? During the year the Sun’s angle changes cyclically. How does this affect the length of daylight in a hemisphere? On June 21st the summer solstice, the length of day is at its maximum. On the winter solstice in December, the day is at its smallest length. On the equinoxes in March and September the length of daylight equals that of night time 12 hours. Notice as the angle increases so does the length of daylight. Use heat transfer to describe the formation of global and local winds. Sun Earth Use heat transfer to describe the formation of global and local winds. Sun RADIATION The Sun RADIATES energy to the earth where it is absorbed. Earth Use heat transfer to describe the formation of global and local winds. Sun Radiation Conduction Earth Air molecules get the heat energy CONDUCTED to them as the touch the warmed earth. Use heat transfer to describe the formation of global and local winds. Sun Convection Radiation Conduction Earth Warmed air CONVECTS its heat upward. Use heat transfer to describe the formation of global and local winds. Spreads Cools and Falls Sun Convection Cycle Convection Air is leaving Radiation Returns Conduction Earth A CONVECTION CYCLE forms as the risen air spreads sideways, cools, falls and returns. Use heat transfer to describe the formation of global and local winds. Sun Radiation High Pressure Low Pressure Earth WIND forms as air flows from areas of high pressure to low pressure. Use heat transfer to describe the formation of global and local winds. Sun Radiation High Pressure WIND Low Pressure Earth WIND forms as air flows from areas of high pressure to low pressure. Use heat transfer to describe the formation of global and local winds. How does heat transfer’s making of wind relate to land and sea breezes? Use heat transfer to describe the formation of global and local winds. How does heat transfer’s making of wind relate the formation of global winds? Explain the difference between weather and climate. Explain the difference between weather and climate. Weather the state of the atmosphere at a place and time as regards heat, dryness, sunshine, wind, rain, etc Climate Atmospheric conditions the weather conditions prevailing in an area in general or over a long period. "our cold, wet climate" Which of these diagrams refers to weather and which to climate? Diagram A Explain the difference between weather and climate. Why is this so? Diagram B Sleet, Hail, Warm, Rain, Tornadoes, Hurricanes, Cold, Hot, Snow I recognize how the following factors affect climate: earth’s tilt, latitude, proximity to water, global wind patterns, and altitude, and ocean currents. Let’s see what you can remember and make sense of here. The Earth is titled at a _____ degree angle. I recognize how the following factors affect climate: earth’s tilt, latitude, proximity to water, global wind patterns, and altitude, and ocean currents. The Earth is titled at a 23 degree angle. I recognize how the following factors affect climate: earth’s tilt, latitude, proximity to water, global wind patterns, and altitude, and ocean currents. Parts of the Earth tilted toward the Sun receive __________ direct light and so the climate is generally __________ there. I recognize how the following factors affect climate: earth’s tilt, latitude, proximity to water, global wind patterns, and altitude, and ocean currents. Parts of the Earth tilted toward the Sun receive more direct light and so the climate is generally warmer there. I recognize how the following factors affect climate: earth’s tilt, latitude, proximity to water, global wind patterns, and altitude, and ocean currents. Latitude effect climate. At the equator, the rays from the Sun strike ____ directly. As one moves away from the equator, the directness of light _____ and so the climate is ______. I recognize how the following factors affect climate: earth’s tilt, latitude, proximity to water, global wind patterns, and altitude, and ocean currents. Latitude effect climate. At the equator, the rays from the Sun strike more directly. As one moves away from the equator, the directness of light decreases and so the climate is cooler. I recognize how the following factors affect climate: earth’s tilt, latitude, proximity to water, global wind patterns, and altitude, and ocean currents. Bodies of water effect climate. Areas close to shorelines generally have less _______ in temperature than areas away from the ocean or other large bodies of water. These areas are also more __________. I recognize how the following factors affect climate: earth’s tilt, latitude, proximity to water, global wind patterns, and altitude, and ocean currents. Bodies of water effect climate. Areas close to shorelines generally have less extremes in temperature than areas away from the ocean or other large bodies of water. These areas are also more humid. I recognize how the following factors affect climate: earth’s tilt, latitude, proximity to water, global wind patterns, and altitude, and ocean currents. Global winds push around air masses (bodies of air with characteristic qualities) bringing air that can be combinations of _____, _____, _____ or ______to various regions. I recognize how the following factors affect climate: earth’s tilt, latitude, proximity to water, global wind patterns, and altitude, and ocean currents. Global winds push around air masses (bodies of air with characteristic qualities) bringing air that can be combinations of dry, humid, warm or cool to various regions. I recognize how the following factors affect climate: earth’s tilt, latitude, proximity to water, global wind patterns, and altitude, and ocean currents. Altitude is the height above sea level. Areas higher in the atmosphere have _______ climates. I recognize how the following factors affect climate: earth’s tilt, latitude, proximity to water, global wind patterns, and altitude, and ocean currents. Altitude is the height above sea level. Areas higher in the atmosphere have cooler climates. I recognize how the following factors affect climate: earth’s tilt, latitude, proximity to water, global wind patterns, and altitude, and ocean currents. Ocean currents carry _______ or _______waters to various areas. This can warm up or cool down areas and also effect the humidity as well. How do you think it effects the humidity? I recognize how the following factors affect climate: earth’s tilt, latitude, proximity to water, global wind patterns, and altitude, and ocean currents. Ocean currents carry cool or warm waters to various areas. This can warm up or cool down areas and also effect the humidity as well. How do you think it effects the humidity? Greenhouse Gases are a small percentage of the atmosphere but have a big impact on global temperatures. Consider this: Greenhouse Gases are a small percentage of the atmosphere but have a big impact on global temperatures. And this: Greenhouse Gases are a small percentage of the atmosphere but have a big impact on global temperatures. What happens to the temperature as the C02 rises and falls? Explain the positive and negative impact that the greenhouse effect has on life on Earth. Remember the greenhouse effect? Here’s a diagram to jog your memory. Explain the positive and negative impact that the greenhouse effect has on life on Earth. So the positive impact is that it provides enough warmth so that life can exist . . . Right? Explain the positive and negative impact that the greenhouse effect has on life on Earth. What’ could possibly be the negative impact? Explain the positive and negative impact that the greenhouse effect has on life on Earth. You got it! When there’s too much of the greenhouse gases, global warming begins and climate change can occur. What are human and natural causes for the accelerated rise of global temperatures? If you remember the CO2 and Temperature graph, the fluctuations go way back before human influence. What do you suppose caused those peaks in greenhouse gases and the associated temperature? This weather portion of the MCAS review ends with an article on this topic. Click here to read about natural causes and here to read about human causes. What are human and natural causes for the accelerated rise of global temperatures? Can you answer this now? Talk about it with your classmates. Human Causes Natural Causes