Factors that Influence Climate
advertisement

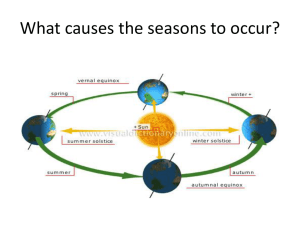
Factors that Influence Climate 3 main factors: 1. Latitude • Distance from the equator • Angle of suns rays – Why do we have seasons? Latitude • • Latitude is at work here; what other factors? • Patterns? • Temperature Animation Factors that Influence Climate 3 main factors: 1. Latitude 2. Altitude Temperatures fall by 6 °C with every 1000 m gained in elevation Altitude • Often said that: ``altitude mimics latitude’’ What does that mean? Swiss Alps http://traumwerk.stanford.edu/archaeolog/2005/12/some_effects_of_altitude_and_c.html Factors that Influence Climate 3 main factors 1. Latitude 2. Altitude 3. Oceanic Circulation • currents Ocean circulation • Global conveyor – Including surface currents such as Gulf stream that influence climate El niño View animations Factors that Influence Climate 3 main factors 1. Latitude 2. Altitude 3. Oceanic Circulation Other important factors • Atmospheric Circulation • Winds • Cold air sinks – Compresses and warms • Warm air rises – Expands and cools Atmospheric circulation • Arrows show direction of winds near ground • Winds are angled because of Earth’s rotation (coriolis effect) • Air at 60 deg N and S rises, most going toward the poles, where it gets cold and sinks. So, poles are cold and dry. Factors that Influence Climate 3 main factors 1. Latitude 2. Altitude 3. Oceanic Circulation Other important factors • Atmospheric Circulation • Solar activity Radiation Animation • Solar maximum – 11 year cycle Factors that Influence Climate 3 main factors 1. Latitude 2. Altitude 3. Oceanic Circulation Other important factors • Atmospheric Circulation • Solar activity • Volcanic activity • Lots of ash and CO2 • O2 and water create atmospheric haze volcanoes • sulfur dioxide can remain in atmosphere for 3 years, forming haze that reflects sunlight, cooling the planet • Mt. Pinatubo in 1991 had that affect • 1815: Mt. Tambora erupts • 1816: Year without a summer Factors that Influence Climate 3 main factors 1. Latitude 2. Altitude 3. Oceanic Circulation Other important factors • Atmospheric Circulation • Solar activity • Volcanic activity • Topography • Shape of the land • Rain shadow How does the Earth gain heat? • The Sun What accounts for the Earth’s temperature? • Energy balance – Electromagnetic energy (light, UV, IR) from the Sun enters the Earth’s atmosphere – Electromagnetic energy is radiated back to space 3 ways for transfer of heat energy • Radiation: electromagnetic waves (such as light from the sun) travel through space • Convection: warm gases or liquids rise, cool, and fall • Conduction: warm body transfers heat directly to a colder body Earth’s Greenhouse Effect The greenhouse effect • One of the main reasons Earth has a livable climate • Not in doubt • Greenhouse gases: ``Trap’’ heat that is radiated from the earth’s surface and re-radiate it. – – – – Water vapor – main greenhouse gas Carbon dioxide Methane -- 26 times CO2’s heat-trapping ability Nitrous oxide – 216 times CO2’s heat-trapping ability Why the interest in CO2? • Increasing rapidly in the atmosphere • Plays a big role high in the atmosphere, where it is quite dry—i.e., little water vapor. Greenhouse gases • Carbon dioxide: released when biomass (wood) or fossil fuels are burned • Methane: released when organic waste decomposes in landfills; by livestock; during processing of fossil fuels • Water vapor: evaporation from ocean. The Carbon Cycle Some of the Sun’s energy is reflected back to space • Albedo = how much light an object or surface reflects 1. 2. Light ice reflects Dark land absorbs