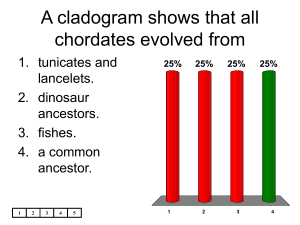
In chordates, the long supporting rod that runs through the body is
advertisement

In chordates, the long supporting rod that runs through the body is called the 1. nerve cord. 2. notochord. 3. pharyngeal pouch. 4. tail. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Which of these chordate characteristics exists as paired structures? 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 tail notochord pharyngeal pouch nerve cord 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 In some chordates, pharyngeal pouches develop into slits that develop into 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 fins. gills. blood vessels. vertebrae. 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 A vertebrate is any chordate that has a 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 backbone. notochord. hollow nerve cord. tail that extends beyond the anus. 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Which of the following statements about a vertebrate’s skeleton is INCORRECT? 1. It supports and protects the body. 2. It is an endoskeleton. 3. It grows as the animal grows. 4. It is made entirely of nonliving material. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Any animal with a spinal cord must be a(an) 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 fish. amphibian. vertebrate. nonvertebrate chordate. 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 The two groups of nonvertebrate chordates are 1. tunicates and lancelets. 2. skates and rays. 3. frogs and toads. 4. lungfishes and coelacanths. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 One difference between lancelets and tunicates is that adult lancelets have 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 a pharynx. a head region. jaws. a backbone. 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 In which of the following ways does a larval tunicate resemble an adult tunicate? 1. overall body shape 2. method of moving from place to place 3. method of feeding 4. structure of notochord 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Most fishes are characterized by each of the following EXCEPT 1. a cartilaginous skeleton. 2. scales. 3. paired fins. 4. gills. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 In most fishes, the structures that are most important for obtaining oxygen from water are the 25% 25% 25% 25% 1. scales. 2. gills. 3. lungs. 4. vertebrae. 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 Vertebrate X has gills. To determine whether vertebrate X is a fish, it would be useful to know if it also has 25% 25% 25% 25% 1. a notochord. 2. pharyngeal pouches. 3. a spinal cord. 4. paired fins. 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 The first vertebrates to evolve were 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 amphibians. lancelets. tunicates. fishes. 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Fishes that lived during the late Cambrian Period 1. lacked paired fins. 2. had powerful jaws. 3. had limbs. 4. had soft bodies with little or no armor. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Which statement correctly describes the likely evolution of fishes? 1. 25% Fishes evolved directly from tunicates and lancelets. Both fishes and lancelets evolved directly from tunicates. Fishes, lancelets, and tunicates probably evolved from common invertebrate ancestors. Fishes probably evolved from vertebrate ancestors, whereas lancelets and tunicates evolved from invertebrate ancestors. 2. 25% 3. 25% 4. 25% 1 2 3 4 5 In fishes with gills, oxygen-rich water enters through the 1. mouth and leaves through the openings in the pharynx. mouth and leaves through the bladder. openings in the pharynx and leaves through the mouth. openings in the pharynx and leaves through the anus. 2. 3. 4. 25% 1 1 2 3 4 5 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Blood flows through the body of a fish in a 1. single-loop open circulatory system. 2. single-loop closed circulatory system. 3. double-loop open circulatory system. 4. double-loop closed circulatory system. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 After passing through the gills of a fish, blood circulates through the rest of the body and then collects in the 25% 25% 25% 25% 1. atrium. 2. ventricle. 3. bulbus arteriosus. 4. sinus venosus. 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 Most fishes get rid of nitrogenous wastes by 1. taking in ammonia through the gills and eliminating it from the kidneys. taking in water through the kidneys and eliminating ammonia from the gills. eliminating ammonia from the gills and from the kidneys. eliminating urine from the gills and ammonia from the kidneys. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 25% 25% 25% 1 2 3 4 If a fish’s olfactory bulbs were damaged, the fish probably would be unable to 1. coordinate its body movements. recognize substances by their smell. discriminate between light and dark objects. detect vibrations in the water. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 The organ that adjusts the buoyancy of many bony fishes is the 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 swim bladder. cerebellum. ventricle. kidney. 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Suppose a fish is swimming upstream in total darkness. Which of the following would be most likely to help the fish sense aquatic predators that approach it from behind? 1. its well-developed eyes 2. its chemoreceptors 3. its lateral line system 4. its bulbus arteriosus 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 If a species of fish reproduces through external fertilization, that species must be 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 oviparous. viviparous. ovoviviparous. either viviparous or ovoviviparous. 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Modern jawless fishes include 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 skates. sharks. lampreys. lungfishes. 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 All fishes in the class Chondrichthyes are alike in the 1. foods that they eat. 2. size and form of their teeth. 3. shape of their bodies. 4. composition of their skeletons. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 The harder a body part is, the greater the chance that it will be well preserved as a fossil. On that basis, which of the following groups of fishes would leave the best-preserved fossils of their skeletons? 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 hagfishes lungfishes sharks lampreys 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of most amphibians? 1. They live on land as adults. They breathe with lungs as adults. They have moist skin that contains mucus glands. They have scales and claws. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Which feature distinguishes most fishes from most amphibians? 1. a vertebral column 2. scales 3. breathing with gills during at least part of the life cycle 4. living in water during at least part of the life cycle 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Most amphibians exist as 1. 25% aquatic larvae that breathe with gills and as terrestria adults that breathe using lungs and skin. aquatic larvae that breathe using lungs and skin and as terrestrial adults that breathe with gills. terrestrial larvae that breathe with gills and as aquati adults that breathe using lungs and skin. terrestrial larvae that breathe with gills and lungs and as aquatic adults that breathe using skin. 2. 25% 3. 25% 4. 25% 1 2 3 4 5 The first amphibians probably resembled 1. jawless fishes, like the lamprey. 2. cartilaginous fishes, like the skate. 3. lobe-finned fishes, like the coelacanth. 4. ray-finned fishes, like the salmon. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 The dominance of amphibians during the Carboniferous Period ended because 1. many of their habitats disappeared due to climate changes. swampy fern forests became more widespread. amphibians were never very numerous during that period. amphibians did not evolve from the first forms that climbed onto land. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 25% 25% 25% 1 2 3 4 At the end of the Permian Period, 1. a great adaptive radiation of amphibians occurred. amphibian species reached their greatest number. most amphibian species became extinct. amphibians first appeared. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Adaptations that helped early amphibians live on land included all of the following EXCEPT 1. strong limb bones. 25% 25% 25% 25% 2. dry, scaly skin. 3. lungs and breathing tubes. 4. sterum, or breastbone. 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 Which of the following is NOT an amphibian adaptation that provides support against the pull of gravity? 1. strong bones in the limbs 2. strong bones in the limb girdle 3. a bony cage around the internal organs 4. lungs for breathing air 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Some species of amphibians have skin color and markings that enable them to blend in with their surroundings. This would be most effective against predators that hunt by sensing the 25% 25% 25% 25% 1. smell of their prey. 2. color of their prey. 3. sounds made by their prey. 4. heat released by their prey. 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 In a frog, the cavity through which digestive wastes, urine, and eggs or sperm leave the body is the 25% 25% 25% 25% 1. cloaca. 2. colon. 3. gallbladder. 4. pancreas. 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 Which of the following structures are missing from many salamanders that live on land? 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 lungs kidneys legs eyes 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 In the circulatory system of an adult amphibian, one loop carries 1. oxygen-poor blood from the body directly to the lungs. oxygen-rich blood from the lungs directly to the body. oxygen-poor blood from the lungs back to the heart. oxygen-rich blood from the lungs back to the heart. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Which chamber of an amphibian’s heart contains blood with the highest oxygen concentration? 25% 25% 25% 25% 1. ventricle 2. right atrium 3. left atrium 4. conus arteriosus 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 The eggs of amphibians can dry out easily because they 1. are never encased in jelly. 2. do not have shells. 3. are usually laid on land. 4. are always fertilized externally. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 A frog’s tympanic membranes would be most useful for 1. enabling the frog to jump long distances. filtering wastes from the frog’s blood. listening to the mating calls of other frogs. keeping the frog’s eyes from drying out on land. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Similarities between most amphibian larvae and fishes include all of the following EXCEPT 1. the presence of a lateral line system. the organization of their circulatory systems. their method of propelling themselves through the water. the basic structure of their brains. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 The amphibian in Figure 30–1 is a 25% 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 25% 25% 25% caecilian. frog. salamander. toad. 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 Amphibians like the one in Figure 30–1 are 25% 25% 25% 25% 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 2 3 herbivores as larvae and carnivores as adults. carnivores as larvae and herbivores as adults. herbivores as larvae and adults. carnivores as larvae and adults. 4 5 In which amphibian would you expect the pelvic girdle to be least well developed? 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 a caecilian a salamander a toad a frog 2 3 4 5 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 In chordates, the nerve cord runs along the dorsal part of the body. _________________________ 1. True 50% 50% 2. False 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 An animal cannot be a chordate if it lacks a backbone. _________________________ 1. True 2. False 1 2 3 4 50% 5 1 50% 2 The nonvertebrate chordate that has all four chordate characteristics as an adult is the tunicate. _________________________ 1. True 50% 50% 2. False 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 The fins of fishes are used for protection. _________________________ 1. True 2. False 1 2 3 4 50% 5 1 50% 2 The first fishes to evolve could not control their movements with great accuracy because they lacked jaws. _________________________ 1. True 2. False 1 2 3 4 50% 5 1 50% 2 The cerebrum is the part of a fish’s brain that coordinates body movements. _________________________ 1. True 50% 50% 2. False 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 If a species of fish is viviparous, its young are born alive and obtain nourishment from the mother’s body. _________________________ 1. True 2. False 1 2 3 4 50% 5 1 50% 2 When a fish that spends most of its life in the ocean enters a river and migrates upstream to breed, its kidneys adjust by producing dilute urine. _________________________ 1. True 2. False 1 2 3 4 50% 5 1 50% 2 If a fish lacks true teeth, has no vertebrae, and has a skeleton that contains cartilage, it belongs to the group known as cartilaginous fishes. _________________________ 1. True 2. False 1 2 3 4 50% 5 1 50% 2 Most amphibians live in water as adults. _________________________ 1. True 2. False 1 2 3 4 50% 5 1 50% 2 A scientist who studies vertebrate fossils would find the earliest amphibian fossils in rocks dating from the late Devonian Period. _________________________ 1. True 2. False 1 2 3 4 50% 5 1 50% 2 The pelvic and pectoral girdles are generally weaker in fishes than in amphibians. _________________________ 1. True 50% 50% 2. False 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 The intestine of a frog becomes shorter when the frog develops from a tadpole into an adult. _________________________ 1. True 50% 50% 2. False 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 Among amphibians with legs, adult salamanders have body movements that most closely resemble those of fishes. _________________________ 1. True 2. False 1 2 3 4 50% 5 1 50% 2 If an amphibian larva loses its tail when it becomes an adult, it is a salamander or newt. ______________________________ 1. True 50% 50% 2. False 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 Participant Scores 0 0 Participant 1 Participant 2 0 0 0 Participant 3 Participant 4 Participant 5 In fishes and amphibians, gills develop from slits that form in the _________________________. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Individual segments of the backbone are called ____________________. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Unlike an adult tunicate, an adult lancelet has a head region that contains a(an) ____________________. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 One basic characteristic of fishes is the presence of ____________________, which fishes use to obtain oxygen from water. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 The skeletons of some ancient fishes were made of ____________________, which is softer and more flexible than bone. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 The adaptation that greatly expanded the range of food sources available to early fishes was the evolution of ____________________. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Adult salmon can distinguish their home stream from other streams by using their sense of ____________________. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 The part of a fish’s brain that processes olfactory information is the ____________________, which controls voluntary movements in most other vertebrates. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 If a vertebrate is aquatic as a larva and terrestrial as an adult, it is a(an) ____________________. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 The Carboniferous Period is sometimes referred to as the Age of ____________________. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 One adaptation of amphibians for life on land is the presence of mucus glands in the skin, which can help protect amphibians from _________________________. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Figure 30–2 In the frog’s heart shown in Figure 30–2, the structure labeled B is the ____________________. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 In the frog’s heart shown in Figure 30–2, blood from the ____________________ enters the structure labeled A. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 An organ that is part of a frog’s digestive, excretory, and reproductive systems is the ____________________. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 The group of amphibians that can cover relatively large distances on land most rapidly is the _________________________. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 List the four characteristics of chordates. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 In vertebrates, how does the front end of the spinal cord differ from the rear end? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Why are vertebrates classified as chordates even though most adult vertebrates lack a notochord? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 How do lancelets move? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Why is a gradual deterioration of a habitat in a specific place more likely to harm most adult tunicates than adult lancelets? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Identify one feature of early fishes from the Cambrian Period that was probably useful as a defense against predators. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Describe the structure, and list two functions of, the pyloric ceca of fishes. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Distinguish between anadromous and catadromous fishes. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 How does the amount of blood that leaves a fish’s atrium in one minute compare with the amount that leaves the ventricle during the same period of time? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Figure 30–3 To which of the three main groups of fishes do each of the animals in Figure 30–3 belong? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Describe the composition of the skeleton of each fish in Figure 30–3. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Fossil evidence indicates that animal X had a backbone, four limbs, a long tail, and an overall length of about 4.5 meters. Its skin appears to have been smooth, and its toes did not have claws. It resembled a present-day coelacanth. During which geologic period did this animal probably first appear? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 List two adaptations of early amphibians that helped them live on land. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 How can an amphibian see underwater without damaging its eyes? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 What are the three groups of modern amphibians? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Contrast the structure of an adult lancelet and an adult tunicate. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Describe the basic characteristics of fishes, and cite two examples of fishes that do not share all of these characteristics. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Explain how jaws were a useful adaptation for early fishes. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Which group of early fishes is thought to have evolved into the first true land vertebrates? What evidence supports this idea? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Name the five main parts of a fish’s brain, and describe the function of each part. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 How would you go about classifying a previously unidentified species of fish into one of the three major groups of fishes? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Describe the basic characteristics of amphibians, and cite three examples of amphibians that do not share all of these characteristics. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 How are worldwide amphibian populations changing today? What explanations have been proposed to explain the change? 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Describe the circulation of blood through the body of an adult amphibian. Include the chambers of the heart in your description. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5 Describe the changes in structure and behavior that occur as a frog develops from a larva into an adult. 1 2 3 4 5 0 of 5