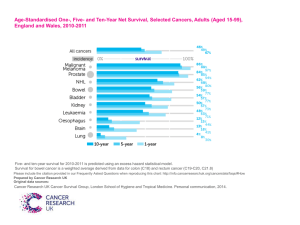
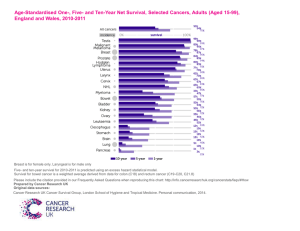
View/Open
advertisement

Effect of Temperature on Osmotic Tolerance Limits for Adherent Endothelial Cells HHMI Summer 2011 Department of Chemical, Biological, & Environmental Engineering By Kenneth Huang Mentor: Dr. Adam Higgins Cryopreservation Preservation of cells or tissues under a low temperature condition 1. Conventional Freezing 2. Vitrification Source: <Fertility Institute of Hawaii> source: <The Infertility Center of Saint Louis> source: <Nature.com> Cryoprotective Agents (CPAs) Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO) Glycerol Protect freezing damage Prevent ice crystal formation Additional Damages due to CPAs • Chemical Toxicity damage while the cells sit under the CPAs. • Damage of volume change due to osmotic transport of water during the addition/ removal procedure Damages in Volume Change Hypertonic Goal Isotonic Hypotonic Determine the osmotic tolerance limits of cell volume under different temperature control. Hypothesis Temperature does affect the osmotic tolerance limits of cell volume. 1.2 1.2 1 1 Cell Survival Cell Survival Exposing Sodium Chloride Solution at Room Temperature 0.8 0.6 Logistic Fit 0.4 PrestoBlue Hypotonic 0.2 0.8 0.6 0.4 PrestoBlue Hypertonic 0.2 Logistic Fit 0 0 0 100 200 Treatment (mmol/kg) 300 300 1300 2300 3300 4300 Treatment (mmol/kg) This data was obtained by experiment conducted by Allyson Fry Variables and Timeline Effect of Different Temp. 6 degree Celsius Room temp. (21 C) 37 degree Celsius 3. 37C 1 room temp. 2. 6C Approaches Bovine Pulmonary Artery Endothelial Cell (BPAEC) is used BPAEC Seeding on 96 well plates ◦ Seeding Density: 5000 cells/ well Approaches continue. Expose to NaCl solution with different concentration for 15 minutes Positive control Concentration 1 Concentration 2 Concentration 3 Concentration 4 Concentration 5 Concentration 6 Negative control Approaches continue. PrestoBlue Viability Assay ◦ Higher the fluorescence units indicates greater cell survival Source: <Life Technology-Invitrogen> Analysis Cell Survival Treatm ent_ Interest Seeding_ Density Isotonic_ Treatm ent Cell Volume • Conservation of moles inside the Cell Volume Concentrat ion mole Vw,Iso (miso ) Vinterest (minterest ) Relative Cell Volume Vinterest mIso 300 4.29 Vw, Iso minterest 70 Results: Verifying NaCl Experiment at room temperature 1.2 1 1 Cell Survival 1.2 Cell Survival 0.8 0.6 Logistic Fit 0.4 PrestoBlue Hypotonic 0.2 0.8 0.6 0.4 PrestoBlue Hypertonic 0.2 Logistic Fit 0 0 0 100 200 300 300 1.2 0.8 0.6 Hypotonic Data Logistic Fit 0 Cell Survival 1 0.2 3300 4300 Hypertonic Data 1.4 0.4 2300 Treatment (mmol/kg) Treatment (mmol/kg) Cell Survival 1300 1.2 Logistic Fit 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 0 100 200 300 Treatment (mmol/Kg) 300 2300 4300 Treatment (mmol/Kg) Results (Cont’d): NaCl Experiment at temperature of 6 degree Celsius 1.200 1.200 1.000 Cell Survival 0.800 0.600 0.400 Hypotonic Data 0.200 Logistic Fit 0 100 0.800 0.600 0.400 Hypertonic Data 0.200 0.000 200 300 Logistic Fit 0.000 300 Treatment (mmol/Kg) 1300 2300 3300 4300 Treatment (mmol/Kg) NaCl Experiment at temperature of 37 degree Celsius 1.6 1.8 1.4 1.6 1.2 1.4 Cell survival Cell survival Cell Survival 1.000 1 0.8 0.6 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.4 0.2 0.2 0 0 0 100 200 treatment (mmol) 300 400 0 1000 2000 3000 treatment (mmol) 4000 5000 Results (Cont’d): high temperature data resulted in high variability Potential source of variability ◦ Cell loss during the wash of PBS++ solution ◦ Contamination of PBS++ solution Investigation of potential source of variability Viability/ Seeding Density Cell loss- wash steps. 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 Neither were the source of variability • 0 1 2 3 # of washes 4 5 Contamination exp. 1.2 Cell survival 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 0hr old PBS 0hr new PBS 24hr old PBS 24hr new PBS • May due to lack of practice in cell culture procedure The experiments were repeated at the extreme conditions • Highly hypotonic • Highly hypertonic Results (Cont’d): Extreme Condition NaCl Experiment at temperature of 6 degree Celsius 1.4 1.2 Cell survival 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 control 5 25 50 300 4000 Concentration (mOsm) 4500 EtOH NaCl Experiment at temperature of 37 degree Celsius 1.6 1.4 Cell survival 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 Control 5 25 50 300 4000 Concentration (mOsm) 4500 EtOH Experimental Conclusion ◦ Temperature does effect the osmotic tolerance limit ◦ Initial high temperature data resulted in high variability ◦ Neither wash steps or suspected contamination were the source of variability ◦ Both low and high temperature controlled data showed differences in cell survival in extreme condition experiment Low temperature data: relatively high cell survival High temperature data: relatively low cell survival ◦ However, the accurate tolerance limits were not determined for specific temperature controlled experiment Future Work: Perform with a different viability assay To investigate the actual relative cell volume tolerance limits for a wide range of temperature conditions Optimization of addition or removal of CPAs for cryopreservation along with toxicity data and permeability data. Acknowledgements Howard Hughes Medical Institute Dr. Adam Higgins Dr. Kevin Ahern Allyson Fry Ratih Lusianti Cameron Glasscock Corey Lerch