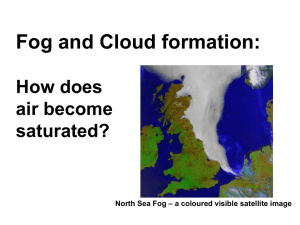
Fog/Foggy Weather
advertisement

Fog/Foggy Weather Overview • Types of fog – – – – – Advection fog Radiation fog Upslope fog Evaporation (mixing) fog Steam fog • Fog formation (1) by cooling…air is cooled below its saturation (2) by evaporation and mixing Condensation: review • Important concept in fog and cloud formation • Evaporation vs. Condensation Radiation fog • Produced by the earth’s radiational cooling • Forms best on clear nights + shallow moist air near the ground + light winds • Common over land in fall and winter • Also called valley fog or Tule fog (e.g., central valley) • Valley fog can persist for weeks unless cold air moves in aloft or strong winds mix it up. http://www.cabrillo.edu/~crsmith/tule.html Reference: wikipedia Advection fog • Forms by condensation of warm, moist air carried by winds over the cold coastal water • common along summertime West Coast – Water near the coast is much colder than offshore water (see upwelling in Ch.8) + onshore winds • Fog disappear as it is pushed inland by onshore winds (due to evaporation) Burn off (of fog) • Refers to dissipation of fog • Sunlight warms the ground → enhances evaporation of fog and mixing of air Summary & additional info • http://www.geog.ucsb.edu/~joel/g110_w08/ lecture_notes/california_fog/california_fog. html