4. surface circulation
advertisement
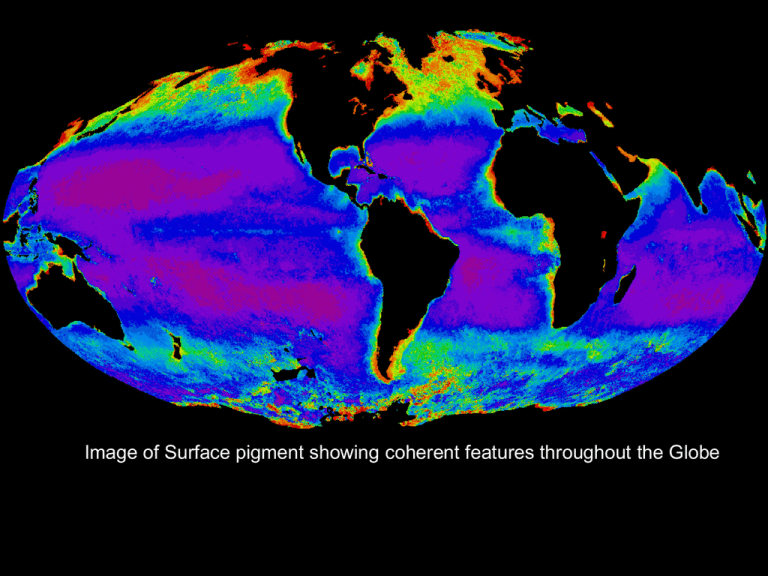
Image of Surface pigment showing coherent features throughout the Globe Due to: LOW Ferrel Cell - Heat flux from equator to polar regions HORSE LATITUDES - Coriolis effects on winds DOLDRUMS LOW HORSE LATITUDES Ferrel Cell LOW From: Pinet, P.: Invitation to Oceanography(2003) From: Pinet, P.: Invitation to Oceanography(2003) Surface Currents Resulting from Wind Drag From: Pinet, P.: Invitation to Oceanography(2003) From Schmitz (1995) 1. Subtropical Convergence (Subtropical Front) Subantarctic Front Polar Front From: Tomczak, Matthias & J Stuart Godfrey: Regional Oceanography: an Introduction 2nd edn (2003) NE MONSOON (Winter) 2. SW MONSOON (Summer) Bay of Bengal East Arabian C. East Indian C. weak seasonal variability From: Tomczak, Matthias & J Stuart Godfrey: Regional Oceanography: an Introduction 2nd edn (2003), 3. From: Tomczak, Matthias & J Stuart Godfrey: Regional Oceanography: an Introduction 2nd edn (2003) 4. From: Tomczak, Matthias & J Stuart Godfrey: Regional Oceanography: an Introduction 2nd edn (2003), (AAIW) 5 From: Tomczak, Matthias & J Stuart Godfrey: Regional Oceanography: an Introduction 2nd edn (2003) 6. ICE AROUND ANTARCTICA February September 7. ARCTIC OCEAN SURFACE CIRCULATION Main surface inflows into Arctic Transpolar drift is the dominant current 8. ICE COVER IN THE ARCTIC AND ANTARCTICA Sea Ice cover website 9. Heating and Cooling Processes 64 emitted by clouds, water vapor and CO2 (long-wave radiation) To Space 100 6 to space 19 30 reflected from clouds, by water and land, and backscattered by air (shortwave radiation) Absorbed by Atmosphere 51 15 23 Evaporation 51 absorbed in ocean 21 long-wave 7 Sensible radiation 10. Annual mean net heat flux From Kallberg et al 2005ERA-40 atlas. ERA-40 Project Report Series No. 19. © 2005 Robert H. Stewart 11. mm/yr 12. 13. El NIÑO-SOUTHERN OSCILLATION - ENSO Weakening of trade winds related to atmospheric pressure difference between western and eastern Pacific How can we predict it? How often does it occur? Periodicity: 2-10 years