The Great West African Trading Kingdoms

The Great West African
Trading Kingdoms
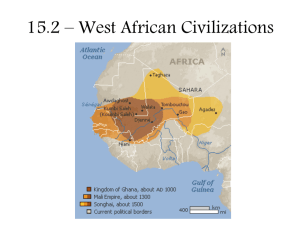
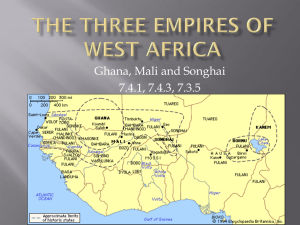
The Kingdom of Ghana
Began 700 A.D. by the Soninke people
This was the first trading empire.
Ghana
Called the “land of gold” because it had so much of it.
The gold trade was largely responsible for the development of
Ghana into a powerful, centralized kingdom.
This gold was traded for salt that came down from the Sahara desert.
Ghana
Today gold is still being mined in West
Africa.
Ghana
The use of iron to make tools and weapons was important because these helped Ghana expand its control over neighboring people.
The use of the horse and camel were also important factors in how rulers were able to incorporate small farmers and herders into the empire.
Ghana
900s-Muslims came south to conquer
Ghana and convert the people to Islam.
Islam brought literacy, learning, a strict code of laws, currency, use of credit, and a common religion.
The kings authority diminished which opened the door for the Kingdom of
Mali to gain power.
The Kingdom of Mali
Mali stretched from the Atlantic Ocean to modern Nigeria, Ghana included.
From 1350 on replaced Ghana as the primary trading kingdom.
Controlled the gold and salt trade.
Profited greatly from the slave trade.
Traded with Egypt and the copper mines to the east.
Mali
The founder and first leader of Mali was Sundiata Keita.
He was the one who took over Ghana and the West
African gold fields.
Mali
Mansa Musa-greatly extended Mali’s territory and power.
In 1324, made pilgrimage
(hajj) to Mecca with 60,000 people and 80 camels carrying 300 lbs of gold each.
Mali
Several centers of Islamic learning were established in Mali.
One was Timbuktu:
Muslim scholars came from all over the world to study religion, math, music, law, & literature.
The Kingdom of Songhai
Established in 1492 by the warrior king
Ali who defeated the rulers of Mali.
It included all of the land that the
Kingdom of Mali once owned.
Songhai was a Muslim kingdom, Islam was a unifying force for the people and an important factor for maintaining state power.
Songhai
Kingdom reached its peak under Askia the Great, stretching from western
Sudan to Mali.
1591- Moroccans raided Taghaza’s salt mine and the Songhai were defeated at the Battle of Tongdibi.
The empire never recovered.
Ashanti
Settled the southern coast of West
Africa.
1600s- Osei Tutu became the king and raised a powerful army which conquered neighboring states.
Ashanti
The Ashanti challenged Britain for control of West African trade.
The British were stronger and defeated the Ashanti in 1901.
Benin
Edo (Bini) tribe founded
Benin between 1000 and 1100 A.D. in the forest region of western
Nigeria.
Became rich by trading cotton for copper, figs, ivory, slaves, and salt.
Benin
Town of Gwato became a slave export center.
Benin is best known for its art in brass, bronze, and ivory.
Benin
Kingdom declined because of revolts among conquered states and warfare with other slave-trading empires.
The British conquered it in 1897.
Islam in the Maghrib
The region of the Maghrib lies in North
Africa in modern day Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia.
This area is very close to the three important West African kingdoms.
Maghrib
Before the 7 th century, the Maghrib’s population consisted of a mix of
Christians, Jews, and traditional African religions.
Arabs gained more and more power in the region, so Islam became the dominant religion in the area.
Maghrib
The people living here were called
Berbers, their descendants still live here and follow the Islamic religion.
Maghrib
The Arabs that brought Islam to the region began being involved in the trans-Saharan gold trade with the Great
Kingdoms of West Africa.
What you should have learned:
Trading empire: a kingdom that rose to prominence because of its ability to trade goods throughout Africa.
These included Ghana, Mali, Songhai, as well as the Ashanti and Benin people.
Gold, salt, and slaves were the major items traded.
Eventually the British took over and the empires declined and fell.