West African Kingdoms
advertisement

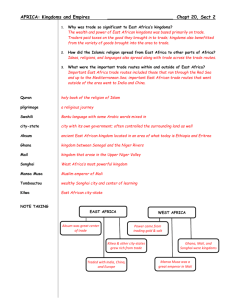
West African Kingdoms Ghana, Mali, & Songhai Early Influences • Bantu people are the root of most kingdoms in Africa (excluding Egypt) – Originally lived in the savanna south of the Sahara (now part of Nigeria) – They were a group of different peoples who shared cultural characteristics – They were farmers, nomadic herders, and were skilled at ironworking Bantu Migration Bantu Migration, cont. • Bantu Migration: 2000+ years ago, small groups of Bantu speakers began moving to the southern and eastern regions of Africa • Migration: a permanent move from one country or region to another • Slash & Burn farming: a farming method in which people clear fields by cutting and burning trees, the ashes of which serve to fertilize the soil Slash and Burn Farming Importance of Bantu Migration Causes of Bantu Migration Effects of Bantu Migration -increased food production -other peoples pushed out -increased population density -territorial wars -lack of sufficient land -ideas and languages exchanged & ethnic groups intermingled • The Bantu Migration strongly influenced the development of African culture! – Migration created many tribes, some of which turned into powerful kingdoms Terms in Traditional African Societies • Extended family: more than the nuclear family (mom, dad, kids)… grandparents or other relatives living in the home • Clan: a group of related extended families who descended from a common ancestor • Tribe: a group of related clans • Lineage: the line of descendents of a particular ancestor; feel strong sense of loyalty to each other • Patrilineal: ancestors are traced through father’s side (inheritance passes from father to son) • Matrilineal: ancestors are traced through mother’s side (inheritance passes from mother’s family to son) West African Kingdoms • The Main Idea: – West Africa contained several rich and powerful kingdoms: Ghana, Mali, and Songhai. For the next 1000 years, these kingdoms dominated West Africa and led to an exchange of ideas, the rise of cities, and increased wealth • Why It Matters Now: – These civilizations demonstrate the richness of African culture before European colonization West African Kingdoms: Overview Time Period: Goods Traded: Key facts: GHANA MALI SONGHAI A.D. 400-1200 A.D. 1250-1450 A.D. 1464-1600 Iron products, animal products, gold, salt Gold and salt Gold and salt Ghana traded gold for salt from the Saharan salt mines Mansa Musa doubled Songhai gained the size of the control of trade in kingdom and created West Africa with the a Muslim center for conquest of Timbuktu learning Importance of Gold & Salt • Gold & salt = two most important trade items! • Gold was luxurious and salt was necessary to live! • Salt was not found in Ghana, but was found to the north in the Sahara desert • Ghana became VERY rich by controlling trade routes and taxing all traders (Gold-Salt Trade) • Trade increased when traders started using camel caravans loaded down with salt Camel Caravan Kingdom of Ghana, 400-1200 • 400: Ghana unites an area between the Niger and Senegal Rivers • Gained control of West Africa’s main trade routes • King taxed all trade passing through the region, especially salt and gold • Tax money financed strong armies and a cavalry • Made iron swords, spears, and lances • 1076: invaded by Muslims from North Africa • Lasted until 1200 Kingdom of Mali, 1240-1400 • 1240: people of Mali conquer the old capital of Ghana and founded a new empire • Rulers took control of the gold and salt mines • Most famous ruler is Mansa Musa, who converts to Islam, makes a hajj to Mecca, and brings many Muslim scholars & architects to back Mali • Timbuktu became a trading & educational center (attracted students from Europe, Asia, and other parts of Africa) • Many West Africans learned to read and write • Arab traveler Ibn Battuta impressed by Mali’s wealth & organization; writes about Mali & makes it famous • Kingdom collapses in the 1400’s Kingdom of Songhai, 1464-1600 • 1464: Sunni Ali, ruler of Songhai people, captured Timbuktu and took control of the Niger River • He expands the kingdom and it becomes the largest trading area of West Africa • Established an elaborate system of taxation and communication to govern the large kingdom • Timbuktu remained a Muslim center for learning • 1591: Morocco’s ruler heard of Songhai’s riches and invaded the kingdom • Moroccans had gunpowder and muskets to defeat the Songhai who only had spears and arrows • Morocco cannot control the large territory and it breaks up into smaller, independent areas